Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesis
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesis
The catabolism of the amino acids involves the removal of α-amino groups, followed by the degradation of the resulting carbon skeletons.
Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesis
OVERVIEW
The catabolism of the
amino acids involves the removal of α-amino groups, followed by the degradation
of the resulting carbon skeletons. These pathways converge to form seven
intermediate products: oxaloacetate, pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, fumarate,
succinyl coenzyme A (CoA), acetyl CoA, and acetoacetate. These products
directly enter the pathways of intermediary metabolism, resulting either in the
synthesis of glucose or lipid or in the production of energy through their
oxidation to CO2 by the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Figure 20.1
provides an overview of these pathways, with a more detailed summary presented
in Figure 20.14. Nonessential amino acids (Figure 20.2) can be synthesized in
sufficient amounts from the intermediates of metabolism or, as in the case of
cysteine and tyrosine, from essential amino acids. In contrast, the essential
amino acids cannot be synthesized (or produced in sufficient amounts) by the
body and, therefore, must be obtained from the diet in order for normal protein
synthesis to occur. Genetic defects in the pathways of amino acid metabolism
can cause serious disease.
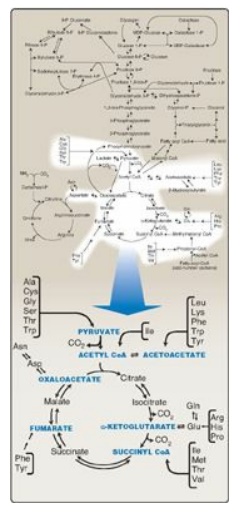
Figure 20.1 Amino acid
metabolism shown as a part of the essential pathways of energy metabolism. (See
Figure 8.2 , for a more detailed view of these processes.) CoA = coenzyme A.
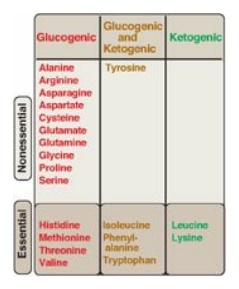
Figure 20.2 Classification of
amino acids. [Note: Some amino acids can become conditionally essential. For
example, supplementation with glutamine and arginine has been shown to improve
outcomes in patients with trauma, postoperative infections, and
immunosuppression.]
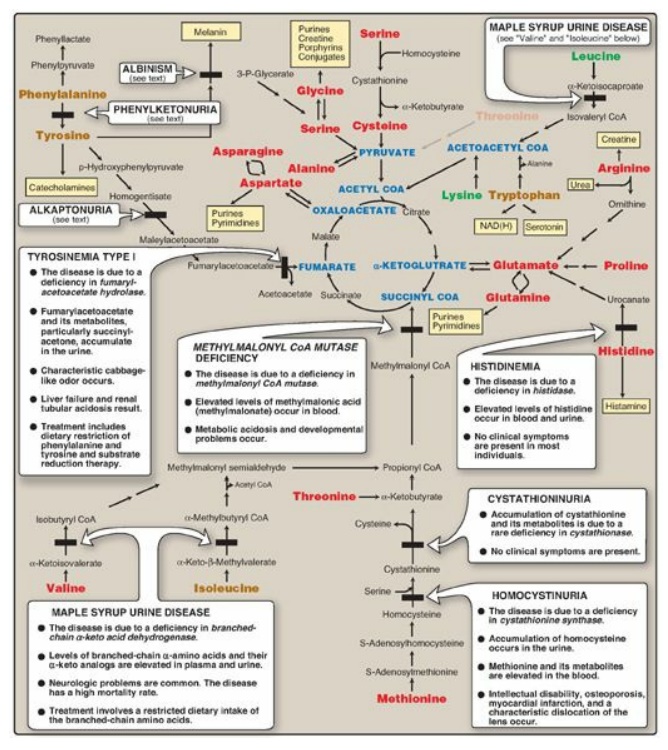
Figure 20.14 Summary of the
metabolism of amino acids in humans. Genetically determined enzyme deficiencies
are summarized in white boxes. Nitrogen-containing compounds derived from amino
acids are shown in small, yellow boxes. Classification of amino acids is color
coded: Red = glucogenic;
brown = glucogenic and ketogenic; green
ketogenic.
Compounds in BLUE ALL CAPS are the seven
metabolites to which all amino acid metabolism converges. CoA = coenzyme A;
NAD(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
Related Topics
