Amla
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Tannins
This consists of dried, as well as fresh fruits of the plant Emblica officinalis Gaerth (Phyllanthus emblica Linn.), belonging to family Euphorbiaceae.
AMLA
Synonyms
Emblica, Indian goose berry, amla.
Biological Source
This consists of dried, as well as fresh fruits of the plant Emblica officinalis Gaerth (Phyllanthus emblica Linn.), belonging to family Euphorbiaceae.
Geographical Source
It is a small- or medium-sized tree found in all deciduous forests of India. It is also found in Sri Lanka and Myanmar. The leaves are feathery with small oblong pinnately arranged leaflets. The tree is characteristic greenish-grey and with smooth bark.
Cultivation and Collection
It is grown by seed germination. It can also be propagated by budding or cutting. It does not tolerate the frost or drought. It is normally found up to an altitude of 1500 m. Commercially, it is collected from wild-grown plants.
Nowadays, the newly released varieties are selected for better yield. These are known as Banarasi, Kanchan, Anand-2, Balwant, NA6, NA7 and B5-1. Seeds or seedlings are placed at a distance of 4.5 × 4.5 meters in red loamy or coarse gravely soil. Proper arrangement for irrigation is required, Drip irrigation is most suitable. Fertilizers in the dose range of 750–900 gm of urea, 1 kg superphosphate, and 1 to 1.5 kg of potash per annum depending upon the quality of soil are sufficient. The above dose is divided into two equal parts, one part is applied in September/October, whereas the other in April to May every year. Pruning is done regularly and only four to six branches about 0.75 to 1.0 meter above the ground are retained. Plant bears male and female flowers separately. Male flowers are reported in the axil of the leaf, in bunches, whereas female flowers in the axil of the branches are solitary. The extent of fertilization is 25–30% of flowers. Cultivated plants bear comparatively large fruits. The tree flowers in hot season and the fruits ripen during the winter.
Morphology
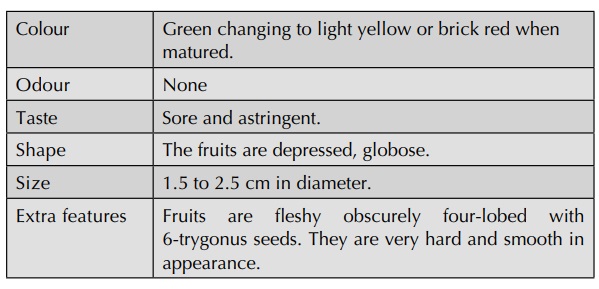
Microscopy
Fruit shows an epicarp consisting of epidermis with a thick cuticle and two to four layers of hypodermis; the cells in hypodermis is tangentially elongated, thick-walled, smaller in dimension than epidermal cells; mesocarp consists of thin-walled isodiametric parenchymatous cells; several collateral fibrovascular bundles scattered throughout mesocarp; xylem composed of tracheal elements, fibre tracheids and xylem fibres; tracheal elements, show reticulate, scalari form, and spiral thickenings; mesocarp also contains large aggregates of numerous irregular silica crystals.
Chemical Constituents
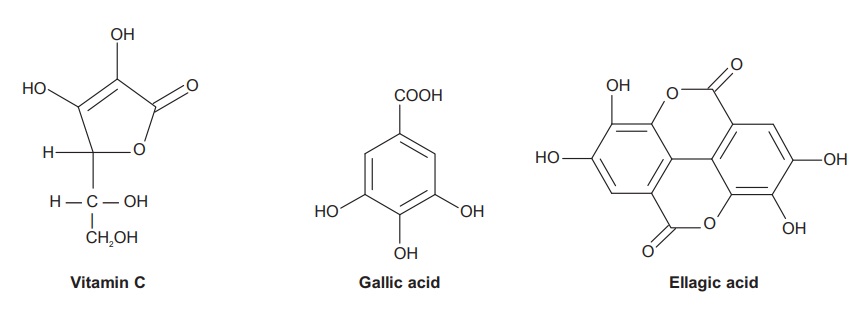
It is highly nutritious and is an important dietary source of vitamin C, minerals, and amino acids. The edible fruit tissue contains protein concentration 3-fold and ascorbic acid concentration 160-fold compared to that of the apple. The fruit also contains considerably higher concentration of most minerals and amino acids than apples. The pulpy portion of fruit, dried and freed from the nuts contains: gallic acid 1.32%, tannin, sugar 36.10%; gum 13.75%; albumin 13.08%; crude cellulose 17.08%; mineral matter 4.12%; and moisture 3.83%. Tannins are the mixture of gallic acid, ellagic acid, and phyllembin. The alkaloidal constituents such as phyllantidine and phyllantine have also been reported in the fruits. An immature fruit contains indolacetic acid and four other auxins—a1, a3, a4, and a5 and two growth inhibitors R1 and R2.
Chemical Tests
1. Alcoholic or aqueous extract of the drug gives blue colour with ferric chloride solution.
2. To aqueous extract add gelatine and sodium chloride milky white colour is produced.
3. To the aqueous extract of amla add lead acetate remove precipitate by filtration. To the filtrate add solution of 2:6 dichlorophenol—indophenol, colour disappears.
Uses
The fruits are diuretic, acrid, cooling, refrigerant, and laxative. Dried fruit is useful in haemorrhage, diarrhoea, diabetes, and dysentery. They are useful in the disorders associated with the digestive system and are also prescribed in the treatment of jaundice and coughs. It has antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, and. antiviral activities. Amla is one of the three ingredients of the famous ayurvedic preparation, triphala, which is given to treat chronic dysentery, bilousness, and other disorders, and it is also an ingredient in chyavanprash.
Marketed Products
It is the chief component of the preparation known as Jeevani malt (Chirayu Pharma), Triphala churna (Zandu), and Chyavanprash (Dabur).
