Anti-HIV agents
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antiviral Agents
a. RT inhibitors : Zalcitabine (DDC, Hivid), Zidovudine (ZDV) [azido-deoxythymidine (AZT), Retrovir], Lamivudine (Lamda, Rolam, Lamvir) b. HIV protease inhibitors : i. Saquinavir (Saquin) ii. Indinavir (Crixivan) iii. Ritonavir (Empetus, Ritomax, Ritovir) iv. Nelfinavir (Emnel, Nelvir, Retronel)
Antiviral Agents - Synthesis and Drug Profile
Anti-HIV agents
HIV virus is
the cause of AIDS, both HIV-1 and HIV-2 cause AIDS. Anti-HIV agents are
classified according to their mode of actions as follows:
a.
RT inhibitors
Reverse
transcription is RNA dependent DNA polymerase. The drug inhibiting RT
interferes with the replication of HIV and stops the synthesis of further viral
particle. They are classified into nucleoside and nonnucleoside RT inhibitors.
Didanosine (2’,3’-dideoxyinosine (DDI), Videx)
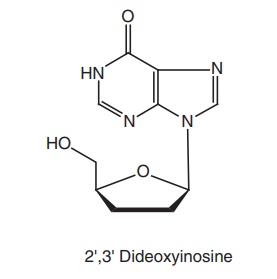
Metabolism: Didanosine is ultimately converted into hypoxanthine, xanthine,
and uric acid through the usual metabolic pathways of purines. The latter is a
nontoxic metabolic product.
Properties and uses: Didanosine is a white crystalline powder,
sparingly soluble in water, soluble in dimethyl sulphoxide, slightly soluble in
methanol and ethanol. It is a nucleoside RT inhibitor recommended for the
treatment of patients with advanced HIV infections.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in glacial acetic acid and titrate with 0.1
M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: The recommended dose for adults as tablets, which may be
chewable and dispersible, for body weight more than 75 kg is 300 mg; for 50–74
kg body weight, 200 mg; for 35–49 kg body weight, 125 mg with antacids.
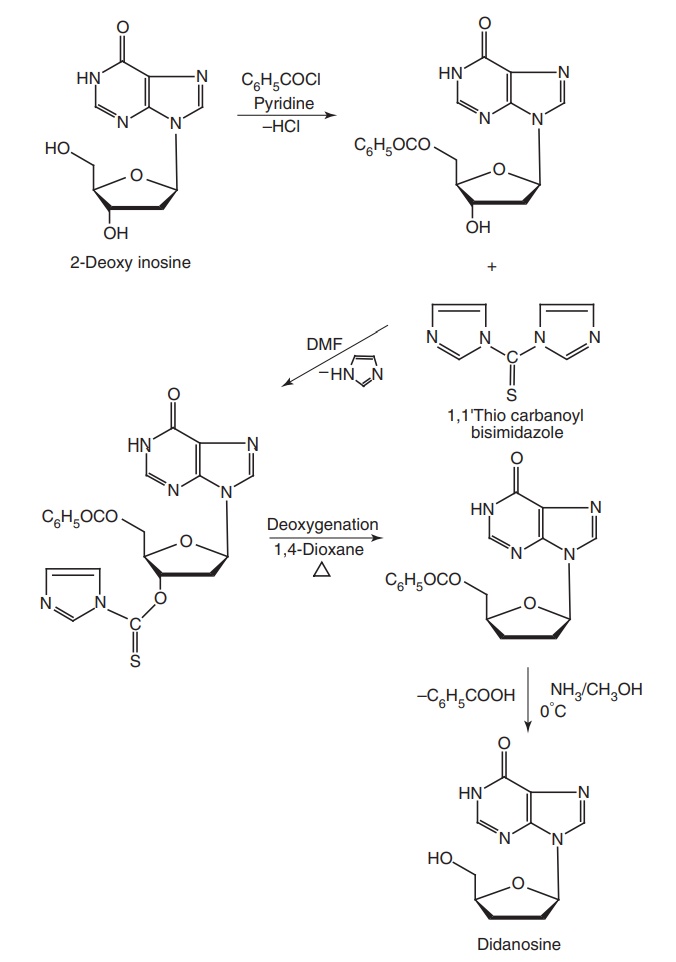
Synthesis
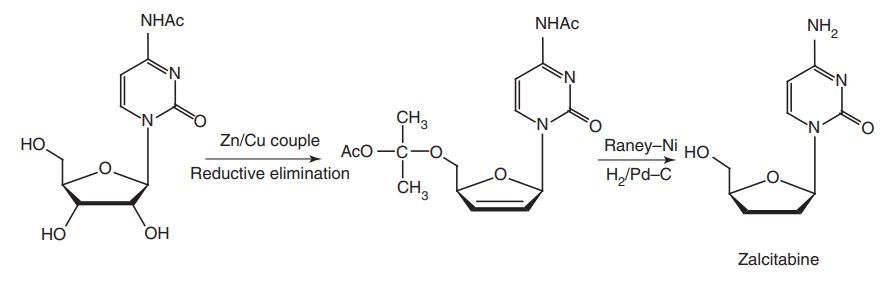
Zalcitabine (DDC, Hivid)
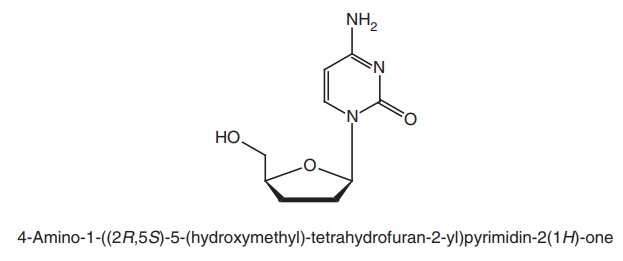
Properties and uses: Zalcitabine exists as white crystals. It is
approved for combination therapy with zidovudine in advanced HIV infection, who
has demonstrated significant clinical or immunological deterioration, showing
intolerance to zidovudine.
Dose: Zalcitabine is administered with zidovudine at the dose level of
2–25 mg of zalcitabine and 600 mg of zidovudine per day.
Synthesis
Route I.
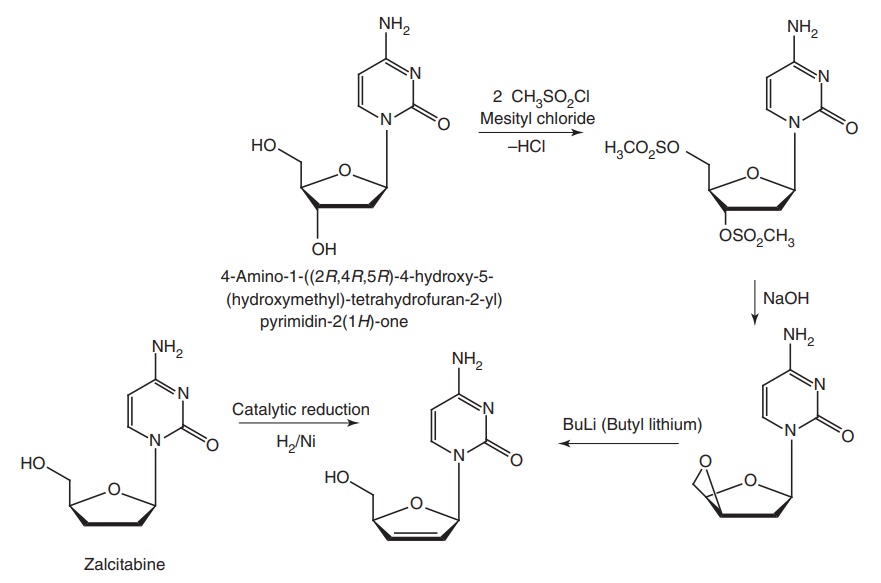
Route II.
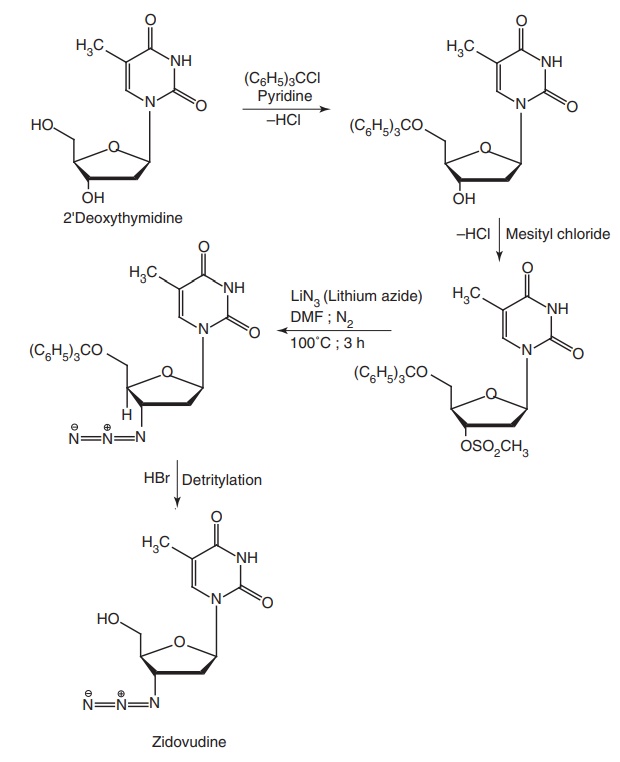
Zidovudine (ZDV) [azido-deoxythymidine (AZT), Retrovir]
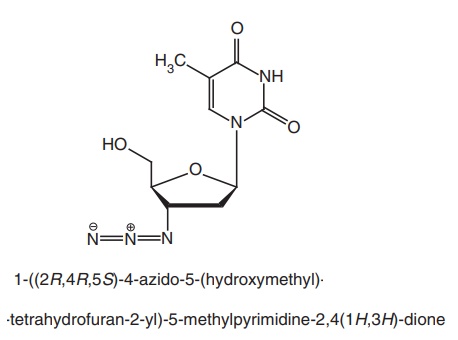
Metabolism: Most of the administered drug is converted to its inactive
glucuronide metabolite and it is excreted unchanged through urine.
Properties and uses: ZDV is a white or brownish powder, sparingly
soluble in water and soluble in anhydrous ethanol. It is a nucleoside RT
inhibitor, having activity against HIV, and hence, it is used for the treatment
of AIDS and AIDS-related complex (ARC). It increases the survival and improves
the quality of life of patients with complications, such as severe weight loss,
fever, and pneumocytosis. As it crosses the blood brain barrier, it has
favourable effect on the neurological symptoms of AIDS.
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique.
Dose: The recommended dose for adults in the case of oral asymptomatic
HIV-infection initially is 100 mg every 4 h, while awake (500 mg a day), after
1 month, the dose may be reduced to 100 mg every 4 h. For intravenous infusion,
the dose is 1–2 mg/kg infused over 1 h for every 4 h around the clock (6 times a day).
Synthesis
Lamivudine (Lamda, Rolam, Lamvir)
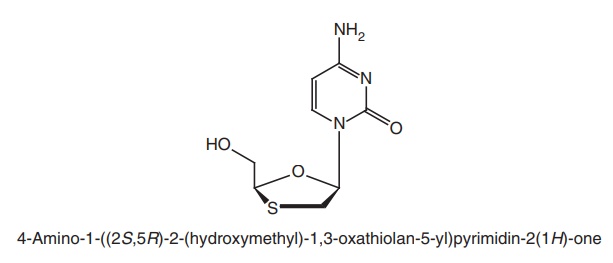
Synthesis
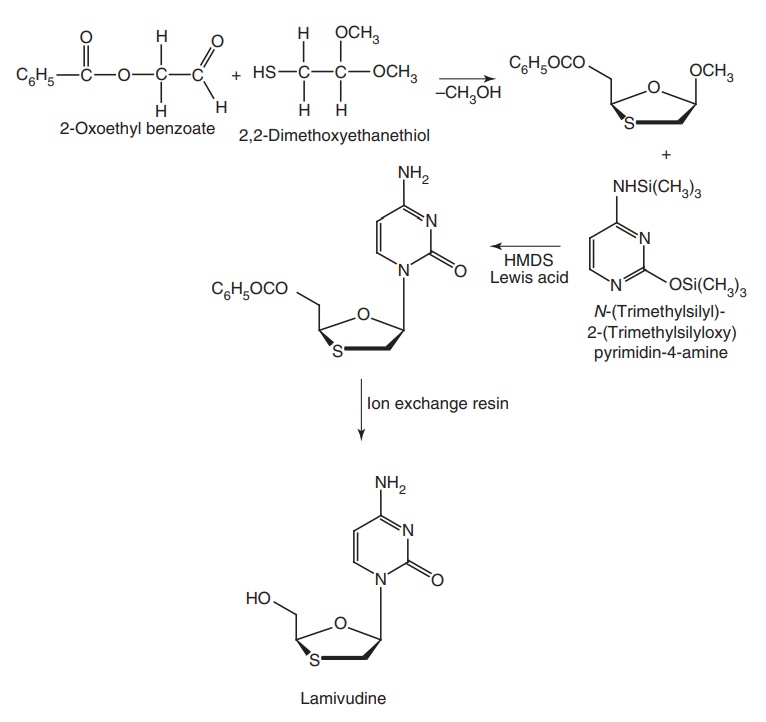
Properties and uses: Lamivudine is a white powder, soluble in water,
sparingly soluble in methanol and slightly soluble in ethanol. It is a
nucleoside RT inhibitor, used in combination with ZDV for the treatment of
diseases caused by HIV infection.
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique.
Dose: The recommended dose for chronic hepatitis B in the case of
adults is 100 mg once daily. For a child more than 2 years, the dose is 3 mg/kg
once daily, maximum is 100 mg per day for HIV infection. The recommended dose
for concomitant HIV and hepatits B infection, in the case of adults is 150 mg
twice a day or 300 mg once daily, in combination with other antiretrovirals. In
the case of a child, 3 months–12 years, the dose is 4 mg/kg twice a day,
maximum dose is 300 mg per day.
b.
HIV protease inhibitors
i. Saquinavir (Saquin)
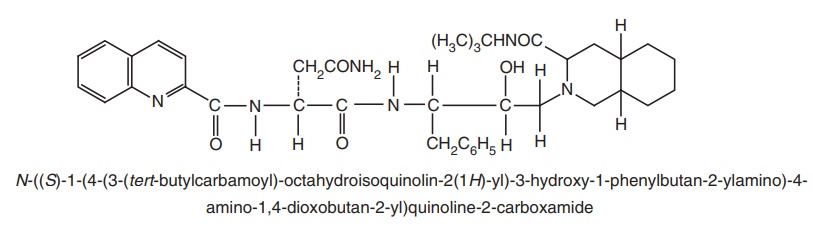
Metabolism: Metabolism of saquinavir is catalyzed by CYP3A4 and
possibly by CYP3A5. The metabolites mono and dihydroxylated
compounds are not active.
Properties and uses: It is a white to off-white fine powder, which is
soluble in water. It is a synthetic peptide analogue and inhibitor of HIV-1 and
HIV-2 proteases. It is used in combination with RT inhibitors, but it has less
cross-resistance with other protease inhibitors.
Dose: The recommended oral dose of saquinavir for HIV infection
combined with other antiretrovirals, in the case of adults more than 16 years
is 1 g twice a day, when taken with ritonavir 100 mg, it is twice a day.
Alternatively, the administered dose of saquinavir could also be 400 mg twice a
day with ritonavir 400 mg twice a day. In the case of postexposure prophylaxis,
during occupational exposure to HIV, the
dose for adults is 1 g of saquinavir twice a day with ritonavir 100 mg twice a
day, combined with other antiretrovirals, and should be started as soon as
possible and continued for 4 weeks, if tolerated.
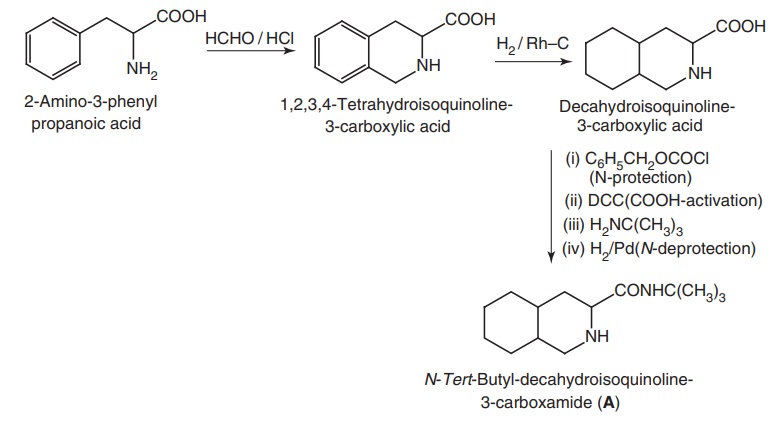
Synthesis
Step I. Synthesis of N-t-butyl-decahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxamide
(A)
Step II. Condensation of (A) and
(B)
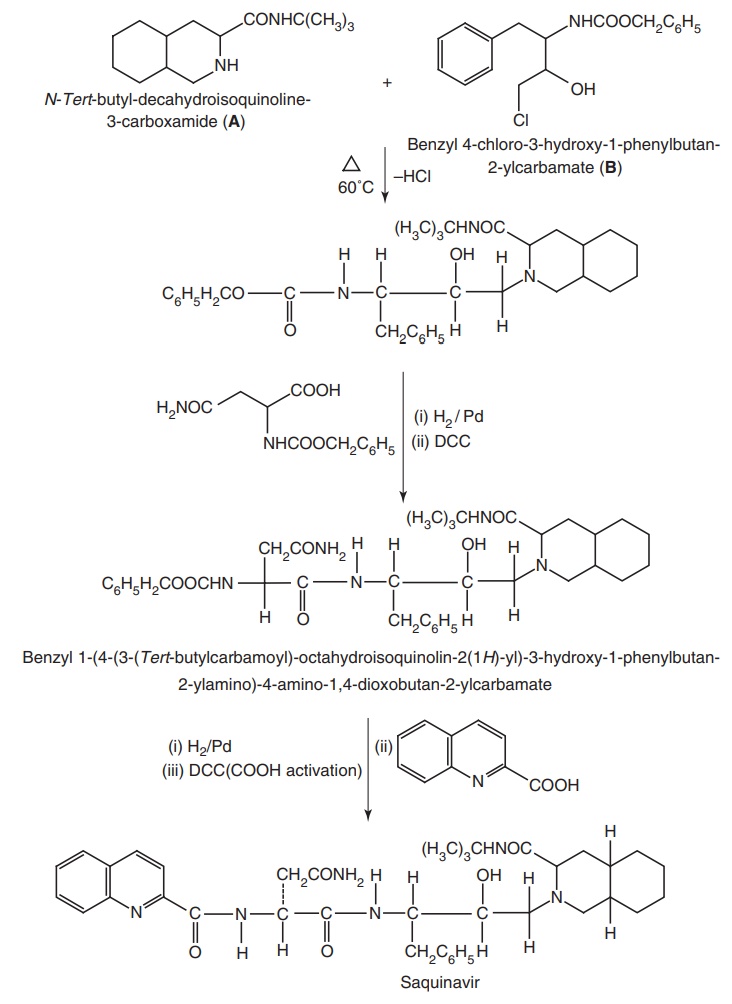
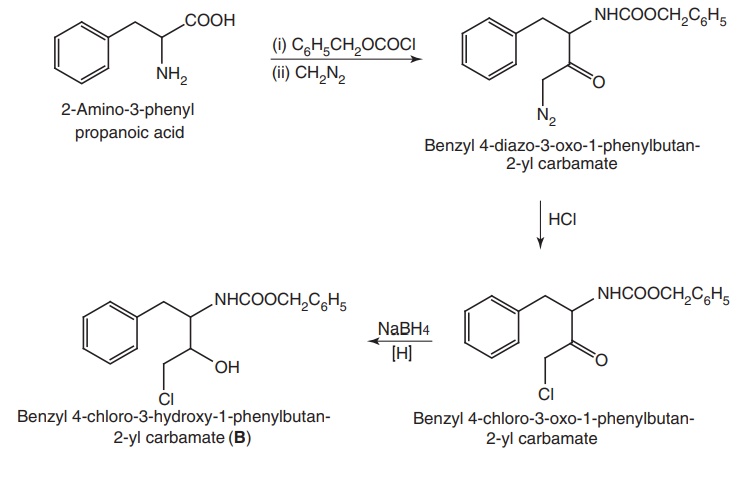
Step III. Synthesis of Benzyl 4-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl
carbamate (B)
ii. Indinavir (Crixivan)
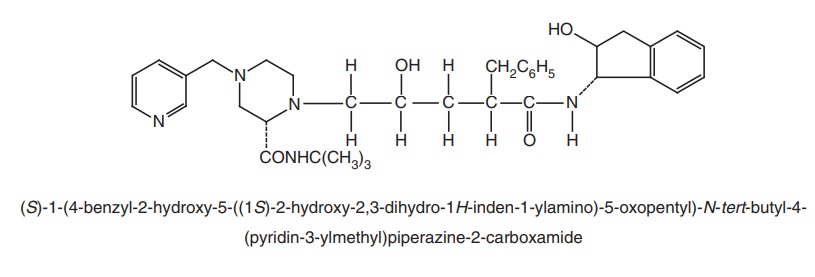
Properties and uses: Indinavir is a white to off-white hygroscopic
powder, soluble in water or in methanol. Used as anti-HIV agent.
Dose: Indinavir is administered in multiple doses of 100–400 mg every 6 h for up to 10 days.
Synthesis
Step I: Synthesis of an intermediate (A)
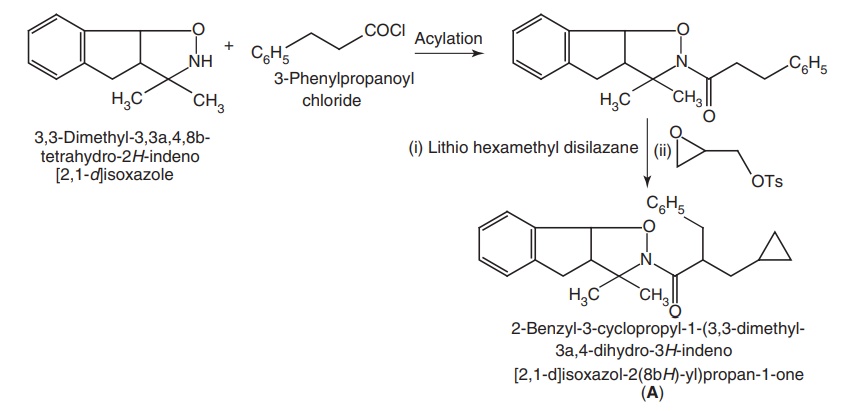
Step II:
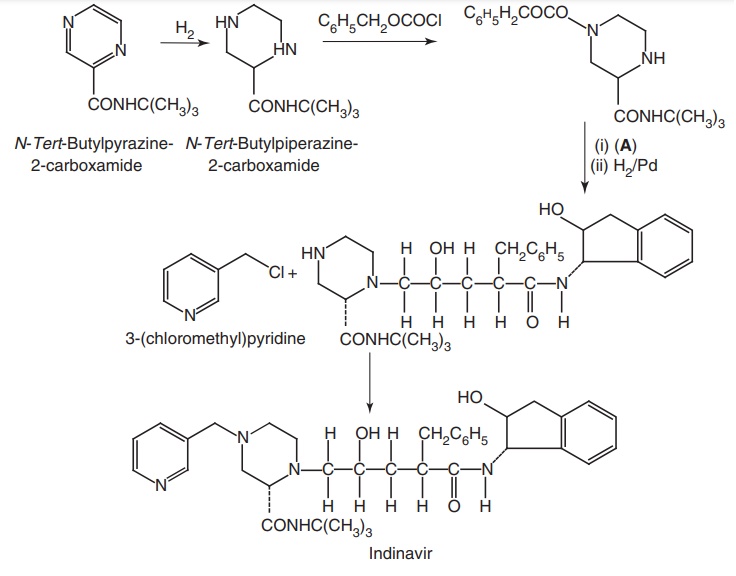
iii. Ritonavir (Empetus, Ritomax, Ritovir)
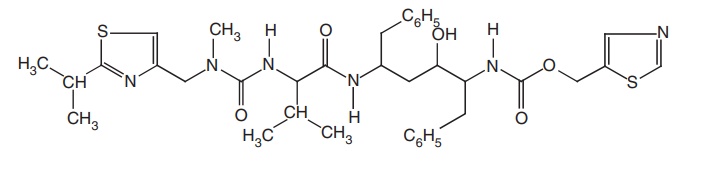
Synthesis
Step-I. Synthesis of Ritonavir
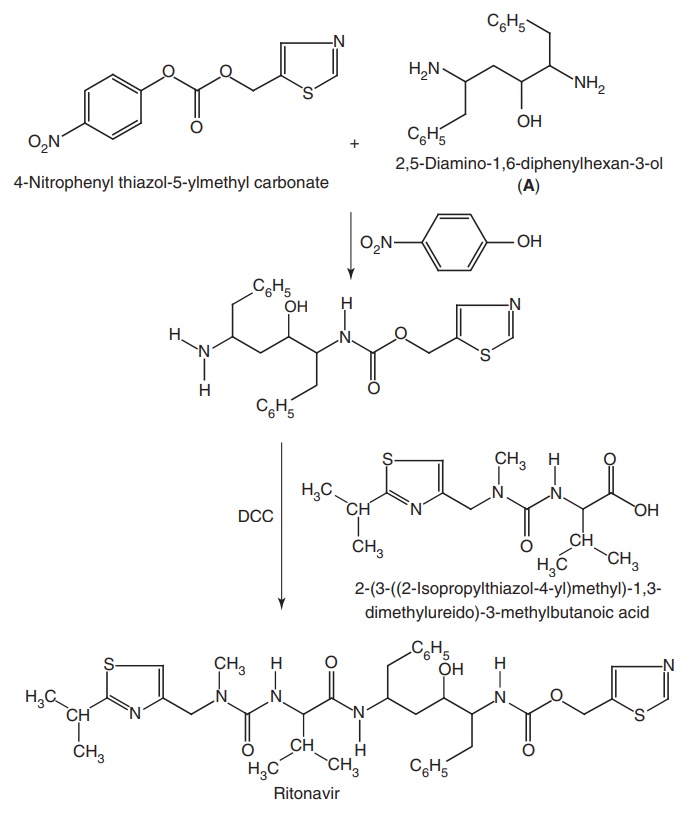
Step-II: Synthesis of (A)
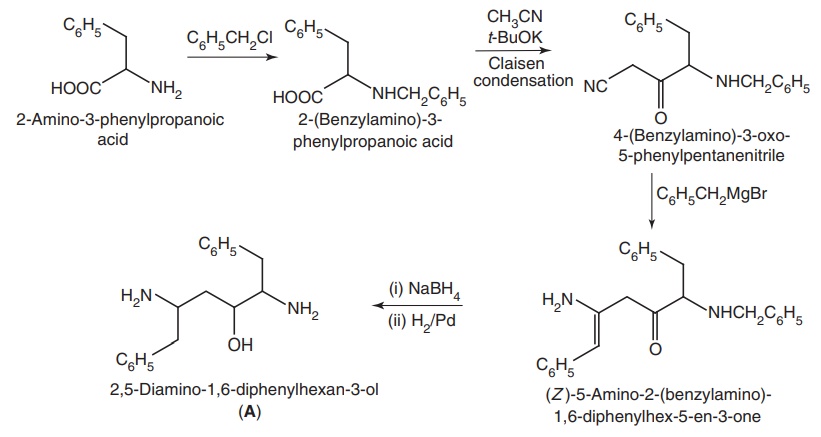
Metabolism: Ritonavir is metabolized by CYP3A4; the metabolites are isolated
from urine. They are isopropylthiazole oxidation products.
Properties and uses: Ritonavir is white to light tan powder with a
bitter metallic taste. It is soluble in methanol and in isopropyl alcohol, but
insoluble in water.
Dose: The recommended oral dose for HIV infection combined with other
antiretroviral, in the case of adults, initially is 300 mg twice a day for the
day one. The dose may be increased gradually by 100 mg twice a day and over a
period of up to 14 days to 600 mg twice a day. In the case of a child more than
2 years, the recommended dose is 250 mg/m2 twice a day. Increase the dose by 50
mg/m2 twice a day, at 2–3 day intervals, up to 400 mg/m2
twice a day. Maximum dose is 600 mg twice a day. As a pharmacokinetic enhancer,in the case of adults, to enhance the
efficacy of other protease inhibitors the dose is 100–200 mg once or twice a
day.
iv. Nelfinavir (Emnel, Nelvir, Retronel)
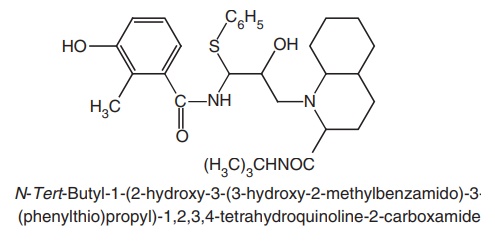
Synthesis
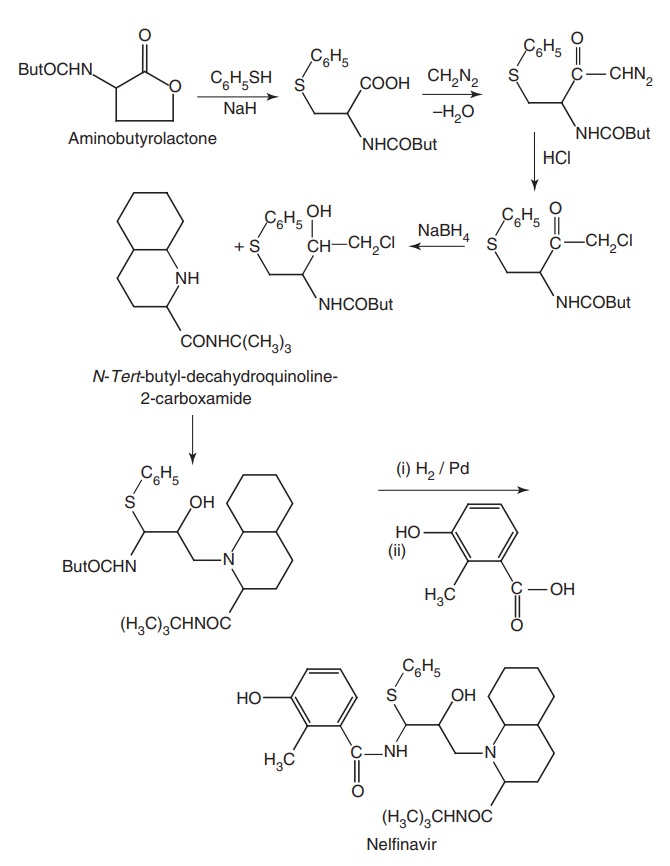
Properties and uses: It is a white to off-white amorphous powder, which
is slightly soluble in water, soluble in methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol,
or propylene glycol. It is used as an anti-HIV agent.
Dose: The recommended dose for HIV infection combined with other
antiretrovirals in the case of adults is 1.25 g twice a day or 0.75 g thrice a
day. In the case of a child: For 2–13 years is 45–55 mg/kg twice a day or 25–35
mg/kg thrice a day. Maximum dose for a child is 0.75 g thrice a day.
