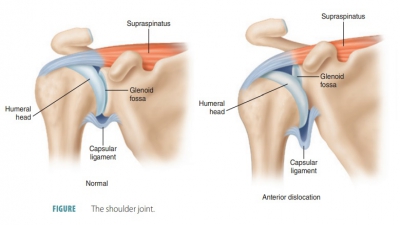
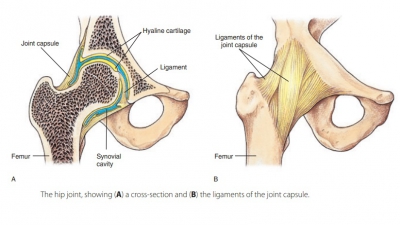
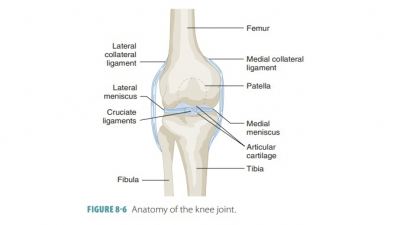
Cartilaginous Joints
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Support and Movement: Articulations
1. Compare synchondroses with symphyses. 2. What term is a synonym for joint?
Cartilaginous
Joints
Connected by hyaline cartilage or
fibrocartilage, cartilaginous
joints include those that separate the
vertebrae. Each intervertebral disc is an example of a cartilaginous joint and
has slight flexibility. Cartilag-inous joints also lack a joint cavity. The two
types of cartilaginous joints are synchondroses and symphyses.
Synchondroses
Synchondroses
are plates or bars of hyaline cartilage uniting
the bones. Nearly all synchondroses are synarthrotic. In children, the best
example of synchondroses is the epiphyseal plates in the long bones. These
plates are temporary joints, eventually becoming synostoses. The immovable
joint between the manubrium of the sternum and the first rib’s cos-tal
cartilage is another example.
Symphyses
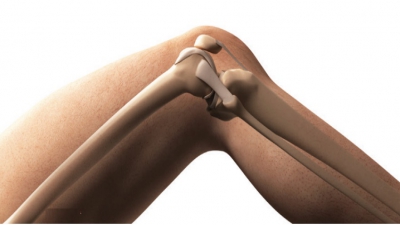
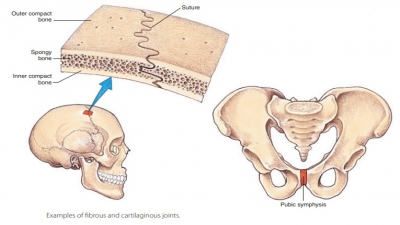
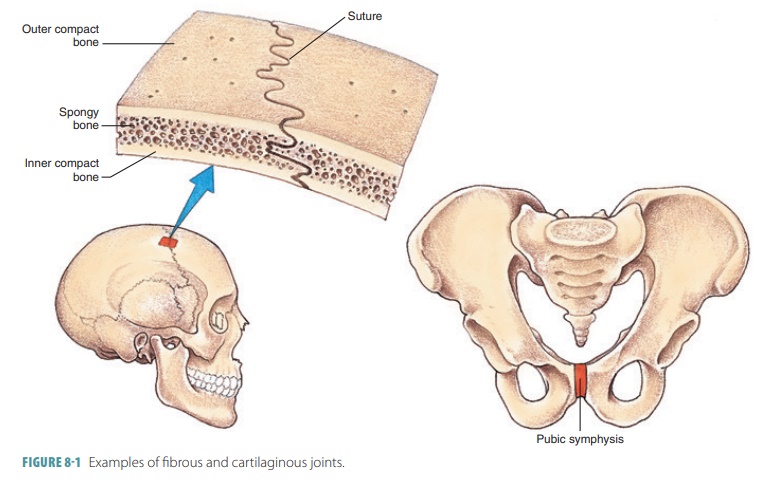
Symphyses are joints where fibrocartilage unites bones (Figure 8-1).
Fibrocartilage acts as a shock absorber because of its ability
to be compressed and then recover its original shape. A limited amount of
movement at the joint is allowed. Hyaline cartilage is also present in
symphyses, as articular cartilage on bony surfaces. Symphyses are
amphiarthrotic joints allowing flexibility but maintaining strength. Exam-ples
include the pubic symphysis of the pelvis and the symphyses of the
intervertebral joints.
1. Compare
synchondroses with symphyses.
2. What
term is a synonym for joint?