Convulsant stimulants
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : CNS Stimulants
CNS Stimulants - Convulsant stimulants - Synthesis and Drug Profile - a. Pentylene Tetrazole b. Strychinine c. Picrotoxin - Structure, Properties, uses, Synthesis, Assay, Storage, Dosage forms, Dose | Synthesis and Drug Profile
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Convulsant stimulants
a. Pentylene Tetrazole
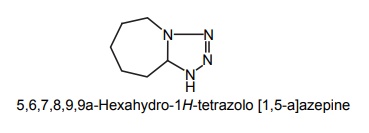
Synthesis
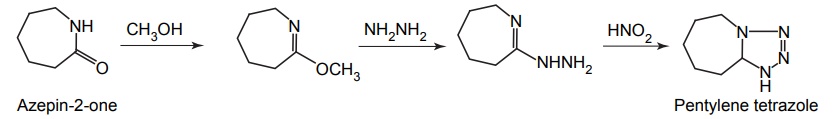
Mode of action: It is a powerful CNS stimulant, believed to be acting by direct depolarization of the central neurons. However, it has also inhibited action on GABA channel openings. Low doses cause excitation, high doses cause convulsion.
Uses: It is used to induce convulsion in animals to locate epileptic foci in conjugation with the electro encephalograph.
b. Strychinine
Mode of action: It stimulates the entire cerebrospinal neuroaxis and produces convulsion. It produces reflex tonic-clonic and symmetrical convulsions. Strychinine acts by blocking postsynaptic inhibition produced by inhibitory transmitter glycine. One of the site is Renshaw cell-motor neurojunction in the spinal cord through which inhibition of antagonistic muscle is achieved. Due to the synaptic inhibition, all the nerve impulses become generalized resulting in apparent excitation and convulsions.
c. Picrotoxin
Mode of action: It is a potent convulsant, produces clonic spontaneous and asymmetrical convulsions. The convulsions are accompanied by vomiting, respiratory and vasomotor stimulation. It acts by blocking presynaptic inhibition mediated by GABA. However, it is not a competitive antagonist, it acts on the distinct site of GABA receptors and prevents the chloride channel opening. Thus, produces depolarization of neurons and excite the central nervous system.
