Newer anticonvulsants
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants - Synthesis and Drug Profile - a. Denzimol b. Denzinamide c. Fosphenytoin (Fosolin, Fosphen) d. Lamotrigine (Lamogine, Lamitor, Lamorig) e. Nafimidone f. Ralitoline g. Topiramate (Epitop, Topamac, Topamate) h. Zonisamide - Structure, Properties, uses, Synthesis, Assay, Storage, Dosage forms, Dose | Synthesis and Drug Profile
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Newer anticonvulsants
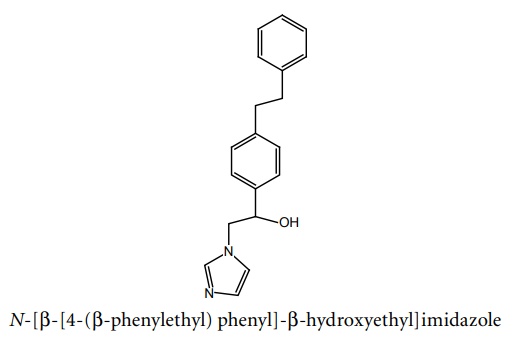
a. Denzimol
Synthesis
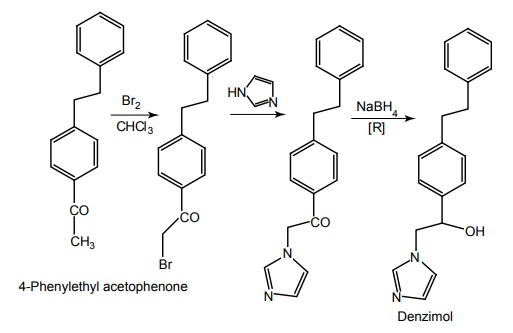
Propeties and uses: It is a racemic mixture, white, odourless, and crystalline powder, soluble in water and alcohol, used in complex partial seizures.
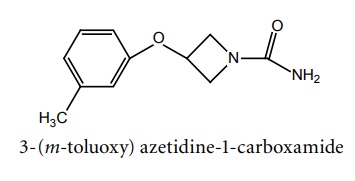
b. Denzinamide
Synthesis
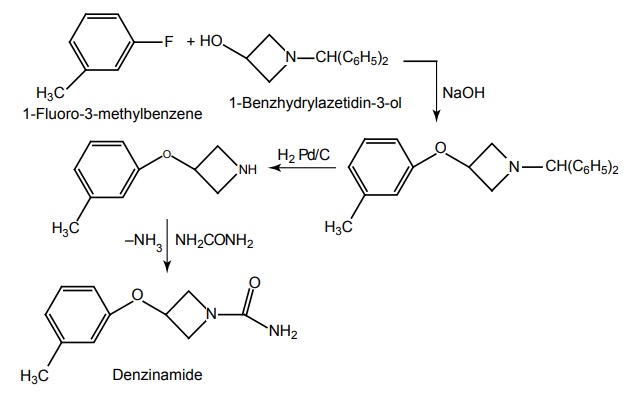
Uses: Used in partial and petitmal seizures.
c. Fosphenytoin (Fosolin, Fosphen)
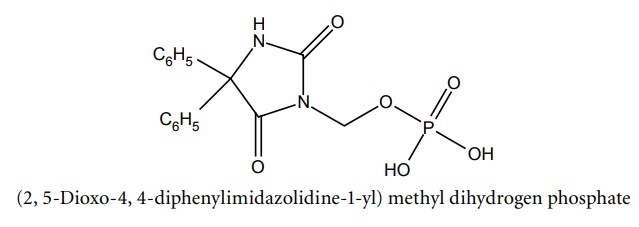
Synthesis
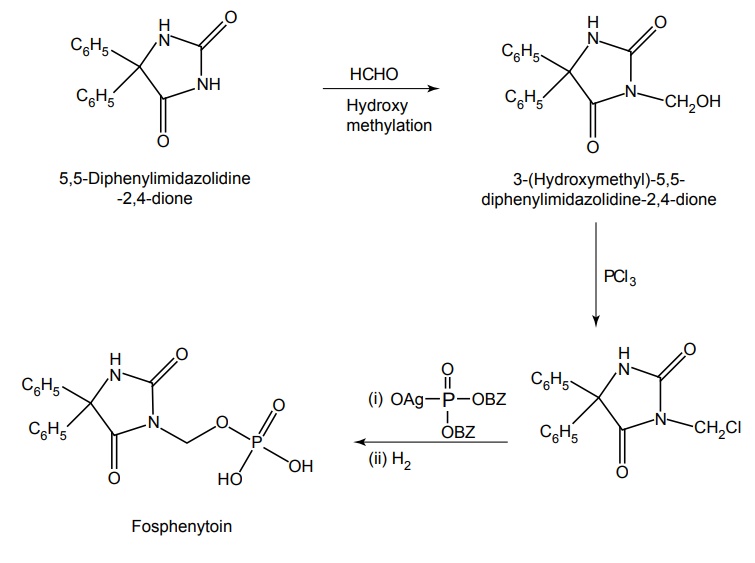
Properties and uses: It is a pro-drug form of phenytoin, and is rapidly cleared by phosphatases in vivo to form phenytoin.
Dose: For tonic-clonic status epilipticus: Adult: As phenytoin Na equivalents (PSE): Loading dose: 15 mg/kg given, via IV infusion at a rate of 100–150 mg/min. Maintenance: Initially, 4–5 mg kg/day by IM injection or IV infusion at a rate of 50–100 mg/min; subsequent doses depend on patient’s response and plasma phenytoin levels.
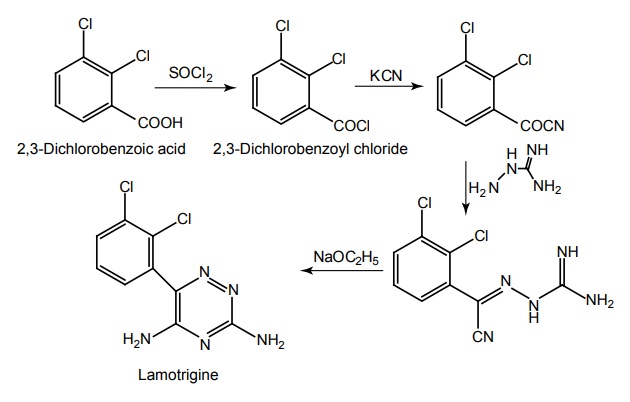
d. Lamotrigine (Lamogine, Lamitor, Lamorig)
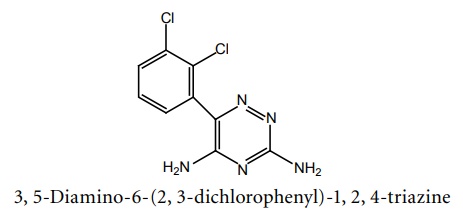
Synthesis
Metabolism: It is metabolized by N-glucuronidation and subsequent urinary elimination of its major metabolite quarternary 2-N-glucuronide and minor 5-amino-N-glucuronide.
Properties and uses: It is one of the most potent and long acting anticonvulsant, with potency similar to or greater than that of phenytoin. It may prove to be of therapeutic value in several CNS-degenerative disorders, such as brain ischaemia, stroke and senile dementia. No toxic side effects have been noted. It is used as an add-on therapy for the treatment of generalized seizures not satisfactorily controlled by other antiepileptics. It acts as sodium channel blocker used for the management of generalized tonic-clonic, petitmal, myoclonic seizures, and myoclonic jerks in children.
Dose: For monotherapy in epilepsy: Adult: Initially, 25 mg once daily for 2 weeks followed by 50 mg once daily for 2 weeks; thereafter, increase the dose by a maximum of 50–100 mg every 1–2 week to usual maintenance dose of 100–200 mg daily, as a single dose or in two divided doses. Some patients may require up to 500 mg daily.
e. Nafimidone
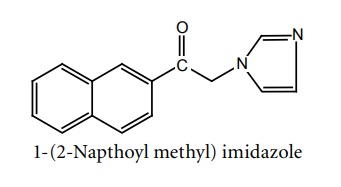
Synthesis
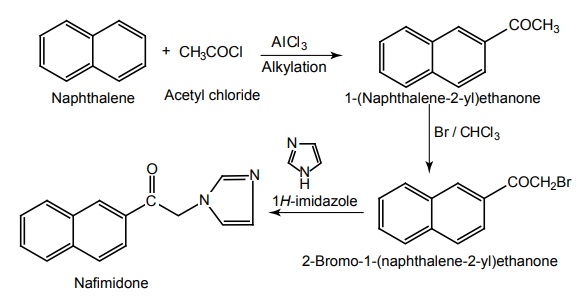
Properties and uses: Its pharmacological effect includes protection against both tonic-clonic and partial seizures in rodents with an ED50 comparable to those of Phenytoin and Phenobarbital. Used in tonic-clonic and partial seizures.
f. Ralitoline
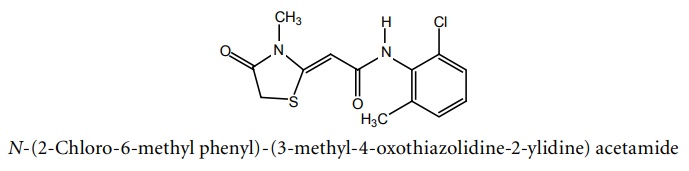
Synthesis
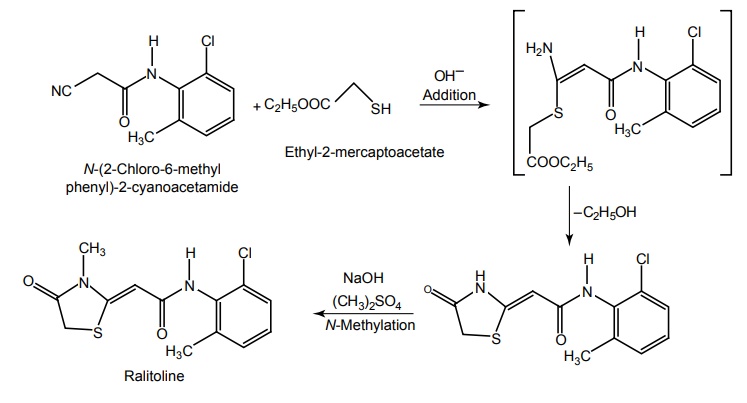
Properties and uses: It is a sodium channel blocker used for the management of generalized seizures.
g. Topiramate (Epitop, Topamac, Topamate)
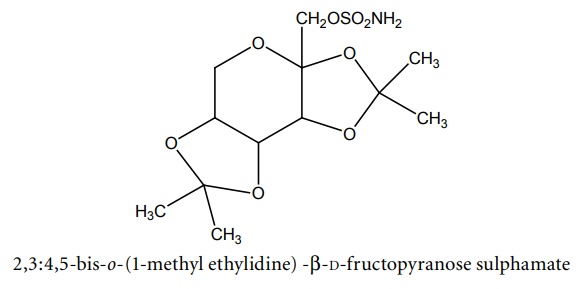
Synthesis
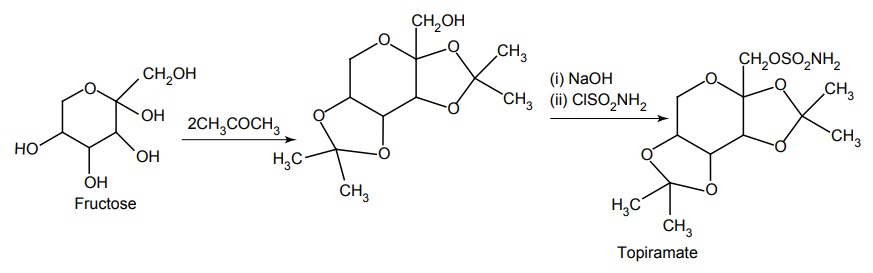
Properties and uses: It exists as white crystalline powder, includes efficacy against generalized seizures, absence, and myoclinic seizures.
Dose: The usual dose 40 mg/day in two divided dose.
h. Zonisamide
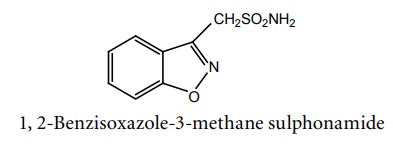
Synthesis
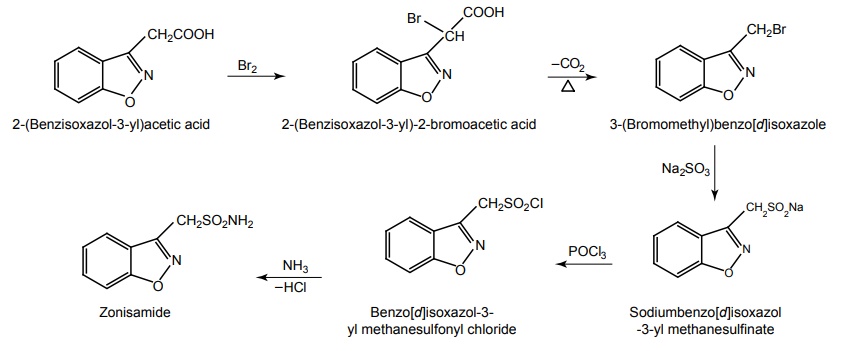
Properties and uses: It exists as white needles, soluble in water, chloroform, hexane, methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate and acetic acid. It also has weak carbonic anhydrase inhibiting activity, but this pharmacologic effect is not thought to be a major contributing factor in the antiseizure activity of zonisamide. Used as sodium channel blocker prevents tonic seizures.
Related Topics
