Potassium sparing diuretics - Nonmercurial diuretics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Diuretics
Nonmercurial diuretics : Potassium sparing diuretics (Pteridine derivatives and related compounds) : i. Amiloride ii. Triamterene (Ditide) - Synthesis and Drug Profile
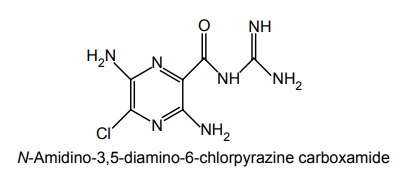
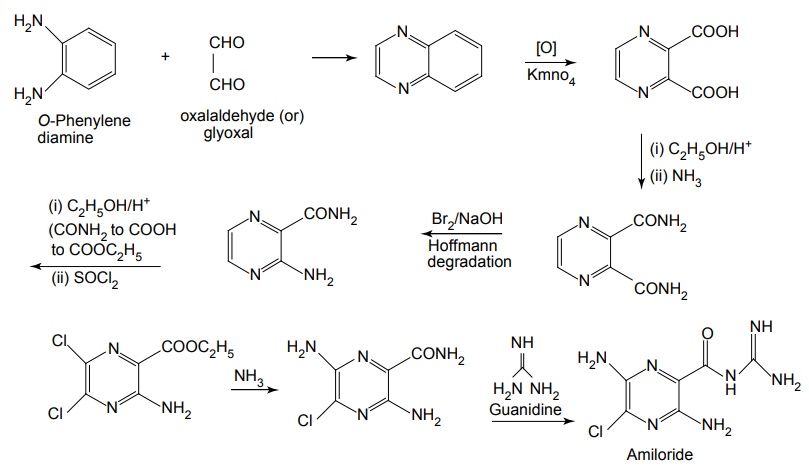
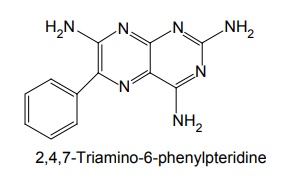
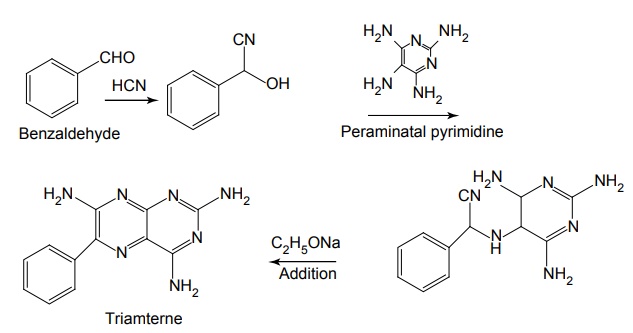
Mode of Action: These drugs act on Na+ channel from the luminal side and block the actions. Thus, it reduces the lumen negative transepithelial potential difference, which governs K+ and H+ secretion. Synthesis Properties and uses: Amiloride hydrochloride is a pale-yellow to greenish-yellow powder, slightly soluble in water and in anhydrous ethanol. It is a potassium-conserving drug with natriuretic diuretic and antihypertensive activity. It is an aminopyrazine, considered an open chain analogue of triamterene. It blocks the reabsorption of sodium ion and the secretion of potassium ion. Amiloride is more potent than triamterene. Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and ethanol and titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Determine the end point potentiometrically. Dosage forms: Amiloride tablets I.P., B.P., Co-amilofruse tablets B.P., Co-amilozide oral solution B.P., Coamilozide tablets B.P. Synthesis Properties and uses: Triamterene is a yellow crystalline powder, very slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is a pteridine with structural resemblance to folic acid. Replacement of phenyl group with small basic heterocyclic nucleus such as thiazole and pyridine produces highly active compounds. 2 and 7 phenyl isomers of triamterene were very potent K+ blockers. Triamterene may be used alone in the treatment of mild oedema associated with congestive heart failure or cirrhosis of the liver with ascites. It is used in the treatment of oedema associated with nephritic syndrome, cirrhosis of liver and congestive heart failure. Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous formic acid, add anhydrous acetic acid and titrate against 0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically. Dose: 100 mg every alternate day to 300 mg per day; usually 100 mg once daily. Dosage forms: Triamterene capsules I.P., B.P., Co-triamterzide tablets B.P.SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Nonmercurial diuretics
Potassium sparing diuretics (Pteridine derivatives and related compounds)
i. Amiloride
ii. Triamterene (Ditide)
Related Topics
