SAR of Penicillins
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antibiotics
6-Acyl side chain: The substitution of R on the primary amine with an electron withdrawing group decreases the electron density on the side chain and protects from acid degradation.
SAR of Penicillins
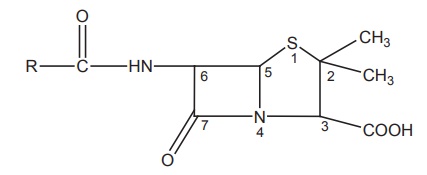
6-Acyl
side chain: The substitution of
R on the primary amine with an electron withdrawing group decreases the
electron density on the side chain and protects from acid degradation.
Substituents on the α-carbon of the side chain, such as amino (ampicillin),
chloro, and guanidine exerts good resistance to inactivation by acids. Benzyl
penicillin undergoes acid and alkali degradation and is susceptible to all
known β-lactamase. The increased latitude in varying the acyl amino side chain
through acylation of 6APA results with superior biological activity.
Substitution of α-aryl of the alkyl group in the side chain gives increased
stability and oral absorption.
1.
Substitution
of bulky groups on α-carbon of the side chain confers β-lactamase resistance.
Examples: methicillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, etc. In all these penicillins, an
aromatic ring is attached directly to the side chain amide carbonyl, and there
is substitution at both positions ortho to the point of attachment. The size of
the ring systems play an important role in determining the ability of the ortho
substitutent to confer penicillinase resistance.
2.
The isomeric
forms of penicillins differs in their activity. Example: D-isomer is
2–8 times more active than L-isomer of amoxicillin. The introduction
of polar group or ionized molecule into the α-position of the side chain in the
benzyl carbon atom of penicillin-G confers against the gram-negative bacilli.
Amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl, and sulphonyl increases gram-negative activity.
Example: ampicillin and carbenicillin.
3.
Replacement
of acyl side chain with hydroxymethyl groups shows improved gram-negative
activity and introduction of C-6 α-methoxy group produces greater stability
against β-lactamase. N-acylated ampicillins (ureidopenicillins) have increased
activity against Pseudomonas.
4.
Many esters
of the carboxyl group attached to C-3 have been prepared as prodrugs to
increase lipophilicity and acid stability. Example: Acetoxymethyl ester
derivatives are used for preparing prodrugs.
5.
The sulphur
of the thiazolidine ring with O, CH , and CH-β-CH3 gives
broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. The geminal dimethyl group at C-2
position is a characteristic of the penicillin. In general, derivatization of
the C-3 carboxylic acid functionality is not tolerated unless the free
penicillin carboxylic acid can be generated in vivo. Doubly activated
penicillin esters, undergo rapid cleavage in vivo to generate active
penicillin. Example: pivampicillin and becampicillin. The antibacterial
activity is evidented by N-4 atom at ring junction.
6.
In vitro
degradation is retarded by keeping the pH of the solution between 6.0 and 8.0.
More lipophilic side chain increases the plasma protein binding. Example:
Ampicillin: 25% plasma protein bound and phenoxy methyl penicillin: 75% plasma
protein bound.
Related Topics
