Pharmaceutical Microbiology
Pharmaceutical Microbiology - Covers all topics with images and clear explanation. Study Pharmaceutical Microbiology Online course, study material, important questions and answers, Notes, textbook.

Part 1 - Biology of microorganisms
Chapter 1: Introduction to pharmaceutical microbiology
=> Introduction to pharmaceutical microbiology
Chapter 2: Fundamental features of microbiology
=> Fundamental features of microbiology
=> Naming of microorganisms
=> Microbial metabolism
=> Microbial cultivation
=> Culture media
=> Cultivation methods - Microbial Cultivation
=> Planktonic and sessile (biofilm) growth
=> Enumeration of microorganisms
=> Microbial genetics
=> Bacteria - Microbial Genetics
=> Eukaryotes - Microbial Genetics
=> Genetic Variation and Gene Expression - Microbial Genetics
=> Pharmaceutical Importance of the Major Categories of Microorganisms
=> Preservation of Microorganisms
Chapter 3: Bacteria
=> Bacteria
=> Bacterial Ultrastructure
=> Cellular Components - Bacterial Ultrastructure
=> Cell Wall
=> Biofilms
=> Bacterial sporulation
=> Bacterial Ultrastructure
=> Bacterial Reproduction and Growth Kinetics
=> Population Growth of Bacteria
=> Bacterial Growth on Different Media
=> Growth and Genetic Exchange of Bacteria
=> Transformation - Bacterial Reproduction
=> Transduction - Bacterial Reproduction
=> Conjugation - Bacterial Reproduction
=> Environmental Factors that Influence Growth and Survival of Bacteria
=> Physicochemical Factors that affect Growth and Survival of Bacteria
=> Nutrition and Growth - Factors Affecting the Growth of Bacteria
=> Detection, Identification and Characterization of Organisms of Pharmaceutical and Medical Significance
=> Culture Techniques - Bacteria
=> Culture Techniques - Types
=> Microscopy of Organisms of Pharmaceutical and Medical Significance
=> Biochemical Testing and Rapid Identification of Organisms of Pharmaceutical and Medical Significance
=> Molecular Approaches to Identification of Bacterial Species
=> Pharmaceutically and Medically Relevant Microorganisms
Chapter 4: Fungi
=> Fungi
=> Structure of the Fungal Cell
=> Medical significance of fungi
=> Antifungal Therapy
=> Medically Important Fungal Pathogens of Humans
=> Emerging Fungal Pathogens
=> Antibiotic Production By Fungi
Chapter 5: Viruses
=> Viruses
=> General Structure of Viruses
=> Virus-Host Cell Interactions
=> HIV - Virus-Host Cell Interactions
=> Tumour Viruses - Virus-Host Cell Interactions
=> Multiplication of Human Viruses
=> Cultivation of Human Viruses
=> Cell Culture - Types of Cultivation of Human Viruses
=> The Chick Embryo - Types of Cultivation of Human Viruses
=> Animal Inoculation - Types of Cultivation of Human Viruses
=> Antiviral chemotherapy- Control of Viruses
=> Vaccination
=> Viricidal Effects of Chemical and Physical Agents on Viruses
=> Control of Viruses in Pharmaceutical Products
=> Viruses and Gene Therapy
=> Bacteriophages - Viruses as Antimicrobials
=> Use of Bacteriophages to Treat Bacterial Infection
=> Epidemiological Uses and Diagnosis - Viruses
=> Prions
Chapter 6: Protozoa
=> Protozoa
=> Physiology of Parasitic Protozoa
=> Blood and Tissue Parasites
=> Malaria
=> Life Cycle of Plasmodia (Malarial causative)
=> Trypanosomatids
=> American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease)
=> African Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping Sickness)
=> Cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis
=> Visceral Leishmaniasis ( Kala Azar)
=> Toxoplasma Gondii
=> Intestinal Parasites
=> Giardia lamblia (syn. intestinalis, duodenalis) - Intestinal Parasites
=> Entamoeba histolytica - Intestinal Parasites
=> Cryptosporidium parvum - Intestinal Parasites
=> Trichomonas and Free living Amoebas
=> Host response to infection
=> Immune Response - Host Response to Infection
=> Immune Pathology - Host Response to Infection
=> Immune Evasion - Host Response to Infection
=> Detection of Parasites
=> Methods of detection of Parasites
=> Antibody Based Technologies - Methods of Detection of Parasites
=> DNA Based Technologies - Methods of Detection of Parasites
=> Alternative Methods - Methods of Detection of Parasites
=> Analysis of Samples
=> Control of Protozoan Parasites
=> Chemotherapy - Control of Protozoan Parasites
=> Other Approaches to Control - Control of Protozoan Parasites
Part 2 - Pathogens and host responses
Chapter 7: Principles Of Microbial Pathogenicity And Epidemiology
=> Principles of Microbial Pathogenicity and Epidemiology
=> The Human Microbiome
=> Skin - Portals of Entry
=> Consolidation
=> Nutrient Acquisition - Consolidation
=> Biofilms - Consolidation
=> Resistance to Host Defences - Consolidation
=> Manifestation of Disease
=> Damage to Tissues
=> Recovery From Infection: Exit of Microorganisms
=> Epidemiology of Infectious Disease
Chapter 8: Microbial Biofilms: Consequences For Health
=> Microbial Biofilms: Consequences For Health
=> Biofilms
=> Biofilms in Nature and the Consequences to Health
=> Biofilms in the Food Industry
=> Biofilms in Hospitals
=> Biofilms and Medical Devices
=> Tolerance of Biofilms to Antimicrobials
=> Mechanisms of Biofilm Tolerance
=> Treatment of Chronic Biofilm Infections
=> A New Biofilm Assay
=> Better Use of Existing Antimicrobials
=> Next-Generation Antimicrobials
=> Conceptual Evaluation of Antibiotics
=> Biofilm Assays
Chapter 9: Immunology
=> Immunology
=> Immunology
=> Definitions and Outline Structure of the Immune System
=> Cells of the Immune System
=> The Innate Immune System
=> The Humoral Adaptive Immune System
=> B-Lymphocyte Antigens - The Humoral Adaptive Immune System
=> Basic Structure of Antibody Molecule
=> Clonal Selection and Expansion
=> Humoral Immune Effector Functions
=> Opsonization of Antigen
=> Mucosal Immunity
=> Antibody-Dependent Cell Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
=> Immediate Hypersensitivity
=> Neonatal Immunity
=> Activation of the Classical Complement Pathway
=> Cell-Mediated Adaptive Immune System
=> T-Lymphocyte Antigen Recognition and MHC Proteins
=> Processing of Proteins to Allow Peptide Presentation by MHC Molecules
=> More on T-Lymphocyte Subpopulations
=> Effector T-Helper Cell Subtypes
=> Transplantation Rejection - Clinical Perspective
=> Hypersensitivity
Chapter 10: Vaccination And Immunization
=> Vaccination and Immunization
=> Spread of Infection
=> Objectives of A Vaccine/Immunization Programme
=> Classes of immunity
=> Passive (Artificially Acquired) Immunity
=> Active (Artificially Acquired) Immunity
=> Types of Vaccine
=> Live Vaccines
=> Killed and Component Vaccines
=> DNA Vaccines
=> Poliomyelitis Vaccination
=> Measles, Mumps And Rubella Vaccination (MMR)
=> Tuberculosis
=> Diphtheria, Tetanus and A Cellular Pertussis (DTaP) Immunization
=> Immunization against Bacteria Associated with Meningitis
=> Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccination
=> The UK Routine Childhood Immunization Programme
=> Immunization of Special Risk Groups
Part 3 - Prescribing therapeutics
Chapter 11: Antibiotics And Synthetic Antimicrobial Agents: Their Properties And Uses
=> Antibiotic Development, Past and Present
=> Antibiotic Usage
=> β -Lactam Antibiotics
=> Penicillins
=> Cephalosporins
=> β-Lactamase inhibitors
=> Carbapenems and aztreonam
=> Hypersensitivity
=> Tetracyclines
=> Macrolides
=> Sulphonamides, Trimethoprim and Related Drugs
=> Quinolones
=> Aminoglycosides
=> Glycopeptides
=> Antitubercular Antibiotics
=> Newer antibiotics for MRSA and other Gram - positive cocci infections
=> Miscellaneous Antibacterial Antibiotics
=> Antifungal Antibiotics
=> Antiviral Drugs
Chapter 12: Mechanisms of action of antibiotics and synthetic anti-infective agents
=> Introduction - Mechanisms of action of antibiotics and synthetic anti-infective agents
=> Peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria and its inhibition
=> β-Lactams-penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems and monobactams
=> β-Lactamase Inhibitors-Clavulanic Acid, Sulbactam and Tazobactam
=> Mycolic Acid and Arabinogalactan Biosynthesis in Mycobacteria
=> Echinocandins-Caspofungin, Anidulafungin and Micafungin
=> Protein synthesis and its selective inhibition
=> Chromosome Function and Replication - Basis for the Selective Inhibition of Chromosome Replication and Function
=> Fluoroquinolones
=> Rifampicin and Rifabutin
=> 5- Fluorocytosine
=> Folate Antagonists
=> The Cytoplasmic Membrane - Mechanisms of action of antibiotics and synthetic anti-infective agents
Chapter 13: Bacterial Resistance To Antibiotics
=> Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics - Introduction
=> Origins of Resistance
=> Mechanisms of Resistance
=> Resistance to β-lactam antibiotics
=> Altered Penicillin-Binding Proteins and Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
=> Resistance to Glycopeptide Antibiotics
=> Resistance to Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
=> Resistance To Other Antibiotics
=> Multiple Drug Resistance
=> Clinical Resistance-Mic Values, Breakpoints, Phenotype and Outcome
Chapter 14: Clinical Uses Of Antimicrobial Drugs
=> Clinical Uses of Antimicrobial Drugs - Introduction
=> Principles of Use of Antimicrobial Drugs
=> Clinical Uses of Antimicrobial Drugs
=> Respiratory Tract Infections
=> Urinary Tract Infections
=> Gastrointestinal Infections
=> Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
=> Central Nervous System Infections
=> Fungal Infections
=> Medical Device Associated Infections
=> Antibiotic Policies
=> The Antimicrobial Stewardship Team
Chapter 15: Antibiotic Prescribing And Antibiotic Stewardship
=> The Need for Antimicrobial Stewardship
=> Components of Antimicrobial Stewardship Programmes
=> The Effectiveness of Stewardship Strategies
=> Monitoring of Antibiotic Resistance
=> The Impact on Resistance of Antibiotic Availability to the Public
Chapter 16: Public Health Microbiology: Infection Prevention And Control
=> Public Health Microbiology: Infection Prevention and Control
=> Healthcare-Associated Infections-Definitions and Range
=> Microorganisms that Cause HCAI
=> Scale of the HCAI Problem-Prevalence and Incidence
=> Responsibility for HCAI Prevention and Control
=> Keys to Infection Prevention and Control
=> Zero Tolerance and the Principles of Infection Management
=> Professional Support for Infection Prevention and Control
Part 4 - Contamination and infection control
Chapter 17: Microbial Spoilage, Infection Risk And Contamination Control
=> Microbial Spoilage, Infection Risk and Contamination Control
=> Spoilage-Chemical and Physicochemical Deterioration of Pharmaceuticals
=> Pharmaceutical Ingredients Susceptible to Microbial Attack
=> Observable Effects of Microbial Attack on Pharmaceutical Products
=> Factors Affecting Microbial Spoilage of Pharmaceutical Products
=> Hazard to Health
=> Sources and Control of Contamination
=> The Extent of Microbial Contamination
=> Factors Determining the outcome of a Medicament-Borne Infection
=> Preservation of Medicines Using Antimicrobial Agents: Basic Principles
=> Effect of Preservative Concentration, Temperature and Size of Inoculum
=> Factors Affecting The ‘Availability’ of Preservatives
=> Quality Assurance and the Control of Microbial Risk in Medicines
=> Quality Assurance in Formulation Design and Development
=> Good Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Practice (GPMP)
=> Quality Control Procedures
=> Postmarket Surveillance
Chapter 18: Laboratory Evaluation Of Antimicrobial Agents
=> Laboratory Evaluation of Antimicrobial Agents
=> Definitions
=> Factors Affecting the Antimicrobial Activity of Disinfectants
=> Evaluation of Liquid Disinfectants
=> Evaluation of Solid Disinfectants
=> Evaluation of Air Disinfectants
=> Evaluation of Preservatives
=> Rapid Evaluation Procedures
=> Evaluation of Potential Chemotherapeutic Antimicrobials
=> Tests for Biofilm Susceptibility
Chapter 19: Chemical Disinfectants, Antiseptics And Preservatives
=> Chemical Disinfectants, Antiseptics and Preservatives
=> European Union Regulation for Chemical Disinfectants, Antiseptics and Preservatives
=> Definitions - Chemical Disinfectants, Antiseptics And Preservatives
=> Economic Aspects - Chemical Disinfectants, Antiseptics and Preservatives
=> Factors Affecting Choice of Antimicrobial Agent
=> Types of Compound
=> Disinfection Policies
Chapter 20: Non-Antibiotic Antimicrobial Agents: Mode Of Action And Resistance
=> Non-Antibiotic Antimicrobial Agents: Mode of Action and Resistance
=> Mechanisms of Action
=> Enhancing Activity of Non-Antibiotic Antimicrobial Agents
=> Mechanisms of Resistance to Biocides
=> Viricidal Activity of Biocides
=> Biocides and Protozoa
=> Biocides and Fungi
=> Inactivation of Prions
Chapter 21: Sterilization Procedures And Sterility Assurance
=> Introduction
=> Sensitivity of Microorganisms
=> Sterilization Methods
=> Heat Sterilization - Sterilization Methods
=> Gaseous Sterilization - Sterilization Methods
=> Radiation Sterilization - Sterilization Methods
=> Filtration Sterilization - Sterilization Methods
=> New Sterilization Technologies
=> Sterilization Control and Sterility
=> Bioburden Determinations
=> Environmental Monitoring
=> Validation and In-Process Monitoring of Sterilization Procedures
=> Sterility Testing
Part 5 - Pharmaceutical production
Chapter 22: Sterile Pharmaceutical Products
=> Introduction
=> Types of Sterile Product
=> Injections
=> Non-Injectable Sterile Fluids
=> Ophthalmic Preparations
=> Dressings
=> Implants
=> Absorbable Haemostats
=> Surgical Ligatures and Sutures
=> Instruments and Equipments
=> Sterilization Considerations
=> Quality Control and Quality Assurance
Chapter 23: Principles Of Good Manufacturing Practice
=> Principles of Good Manufacturing Practice
=> Definitions
=> Control of Microbial Contamination During Manufacture: General Aspects
=> Manufacture of Sterile Products
=> Aseptic Areas
=> Guide to Good Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Practice
Chapter 24: The Manufacture And Quality Control Of Immunological Products
=> The Manufacture and Quality Control of Immunological Products
=> Vaccines, Types of Vaccines
=> The Seed Lot System
=> Production of the Bacteria and the Cellular Components of Bacterial Vaccines
=> Fermentation
=> Production of the Viruses and the Components of Viral Vaccines
=> Blending
=> Filling and Drying
=> Quality Control
=> In Vivo Diagnostics
=> Immune Sera
=> Human Immunoglobulins
=> Monoclonal Antibodies
Chapter 25: Recombinant DNA Technology
=> Biotechnology in Pharmaceutical Sciences
=> Enabling Techniques
=> Cutting and Joining DNA Molecules - Enabling Techniques
=> Cloning Vectors - Enabling Techniques
=> Introduction of Vector Into Hosts
=> Construction of Genomic Libraries
=> Screening of Genomic Libraries
=> Optimizing Expression of Recombinant Genes
=> Amplifying DNA: The Polymerase Chain Reaction
=> Biotechnology in the Pharmaceutical Industry
=> Recombinant Human Insulin
=> Recombinant Somatostatin
=> Recombinant Somatotropin
=> Recombinant Hepatitis B Vaccine
=> Recombinant Influenza Virus Vaccines
=> Production of Recombinant Antibiotics
=> New Diagnostics Using Recombinant DNA Technology
=> Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
=> Diagnosis of Genetic Disorders
Part 6 - Current trends and new directions
Chapter 26: The Wider Contribution Of Microbiology To The Pharmaceutical Sciences
=> The Wider Contribution of Microbiology to the Pharmaceutical Sciences
=> Pharmaceuticals Produced by Microorganisms
=> Iron-Chelating Agents
=> Enzymes
=> Applications of Microorganisms in the Partial Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals
=> Applications of Microorganisms in the Discovery of Pharmaceuticals
=> Use of Microorganisms and their Products in Assays
=> Phenylketonuria Testing
=> Carcinogen and Mutagen Testing
=> Use of Microbial Enzymes in Sterility Testing
=> Immobilized Enzyme Technology
=> Use of Microorganisms as Models of Mammalian Drug Metabolism
=> Microorganisms as Therapy
=> Insecticides
=> Bioterrorism
=> Bioterrorism
Chapter 27: Alternative Strategies For Antimicrobial Therapy
=> Alternative Strategies for Antimicrobial Therapy
=> Essential Oils
=> Honey Therapy
=> Garlic
=> Probiotics
=> Maggot Therapy
=> Photodynamic Therapy (Photoactivated Disinfection)
=> Vaccines and Immunotherapies
=> Silver
=> Bacteriophage Therapy
=> Bacteriophage Lysins
Chapter 1: Introduction and Scope
=> Scope of Pharmaceutical Microbiology
=> Historical Development and Milestones of Microbiology
Chapter 2: Structure and Function of Bacterial Cells
=> Introduction
=> Characteristic Features of bacteria
=> Predominant activities of bacteria
=> Organization of Microbial Cells
=> Types of Microbial Cells
=> Archaeobacteria and Eubacteria
=> Structure and Function of Bacterial Cells
=> Typical Bacterial Cell
=> Capsules and Slimes
=> Flagella and Fimbria
=> Cell Envelope
=> Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
=> Significance of Teichoic Acids
=> The Cell Membrane
=> Bacterial Cytoplasm
=> Ribosomes
=> Cellular Reserve Materials
Chapter 3: Characterization, Classification and Taxonomy of Microbes
=> Introduction
=> Characterization of Microbes
=> Classification of Microbes or Microorganisms
=> Difficulties Encountered in Classification of Microorganisms
=> Objectives of Classification of Microbes
=> Genetic Methods of Classifying Microbes
=> Systematized Classification of Microbes or Microorganisms
=> Taxonomy of Microbes or Microorganisms
=> The Kingdom Prokaryotae
=> Actinomycetes
=> Actinomycetes and Related Organisms
=> Bacteria [Plural of ‘Bacterium’]
=> Rickettsia and Coxiella
=> Spirochaetes
Chapter 4: Identification of Microorganisms
=> Introduction
=> Morphology
=> Selective and Diagnostic Media
=> Cultural Characteristics
=> Biochemical Tests (or Properties)
=> Profile of Microbial Stains
=> Preparation of Bacterial Specimens for Light Microscopy
=> Microscopy : The Different Instruments
=> Concepts of Microscopy
=> Microscope Variants
=> Types of Electron Microscopes
Chapter 5: Nutrition, Cultivation and Isolation of microorganisms : Bacteria-Actinomycetes-Fungi-Viruses
=> Introduction
=> Nutrition, Cultivation and Isolation of Bacteria
=> Nutrition, Cultivation and Isolation of Actinomycetes
=> Nutrition, Cultivation, Reproduction and Isolation of Fungi
=> Industrial Importance of Fungi
=> Nutrition, Cultivation and Isolation of Viruses
Chapter 6: Microbial Genetics and Variations
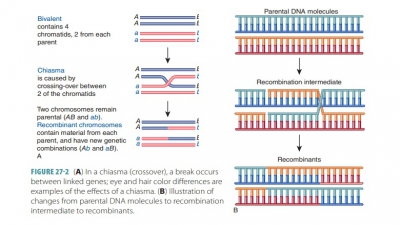
=> Microbial Genetics and Variations
=> Microbial Genetics
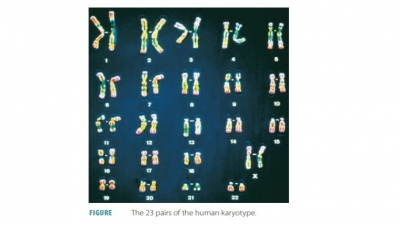
=> Structure and Function of Genetic Material
=> Genotype and Phenotype
=> Adaptation and Mutation
=> DNA and Chromosomes
=> DNA Replication
=> Rate of DNA Replication
=> Flow of Genetic Information
=> Bacterial Transformation
=> Bacterial Transcription
=> Bacterial Translation
=> Bacterial Conjugation
=> Bacterial Transduction
=> Bacterial Transfection
=> Microbial Phage Conversion
=> Microbial Variations [Genetic Manipulation in Microorganisms]
Chapter 7: Microbial Control by Physical and Chemical Methods
=> Introduction
=> Microbial Control by Physical Methods
=> Microbial Control by Chemical Methods
=> Experimental Parameters Influencing the Antimicrobial Agent Activity
Chapter 8: Sterility Testing: Pharmaceutical Products
=> Sterility Testing: Pharmaceutical Products
=> Methods of Sterility Testing: Pharmaceutical Products
=> Sampling: Probability Profile
=> Overall Conclusions
Chapter 9: Immune Systems
=> Immune Systems
=> Types of Specific Immunity
=> Duality of Immune System
=> Immunological Memory
=> Natural Resistance and Nonspecific Defense Mechanisms [or Defensive Mechanisms of Body]
Chapter 10: Microbiological (Microbial) Assays: Antibiotics-Vitamins- Amino Acids
=> Microbiological (Microbial) Assays: Antibiotics-Vitamins- Amino Acids
=> Variants In Assay Profile
=> Types of Microbiological (Microbial) Assays
=> Radioenzymatic [Transferase] Assays
=> Analytical Methods For Microbial Assays
=> Antibiotics Assays - Examples of Pharmaceutical Microbial Assays
=> Assay of Antibiotics by Turbidimetric (or Nephelometric) Methods
Glossary
=> Pharmaceutical Microbiology: Glossary, Technical Words, Terms
=> Pharmaceutical Microbiology: Glossary, Technical Words, Terms
=> Pharmaceutical Microbiology: Glossary, Technical Words, Terms