Anatomy
| Home |Chapter: HAP - Scope of Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy is the branch of science that deals with the structure of the human body and the relationship between its parts. It helps us understand where organs are located and how they are arranged.
ANATOMY
Anatomy is the branch of science that deals
with the structure of the human body and the relationship between
its parts. It helps us understand where organs are located and how they are
arranged.
SCOPE & TYPES OF ANATOMY
1. Gross Anatomy (Macroscopic Anatomy)
Study of structures visible to the naked
eye.
Types of Gross Anatomy:
- Surface
Anatomy: Study of
external body features.
- Regional
Anatomy: Study of
structures in specific regions (e.g., head, neck, chest).
- Systemic
Anatomy: Study of
organ systems like skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, etc.
Divisions of Systemic Anatomy:
|
Division |
Study Area |
|
Spanchnology |
Organs |
|
Osteology |
Bones |
|
Myology |
Muscles |
|
Arthrology |
Joints |
|
Neurology |
Nervous system |
|
Cardiology |
Heart |
|
Ophthalmology |
Eyes |
|
Otology |
Ears |
|
Odontology |
Teeth |
|
Pulmonology |
Lungs |
|
Endocrinology |
Endocrine glands |
|
Haematology |
Blood |
|
Nephrology |
Kidneys/excretory system |
|
Gynaecology |
Female reproductive system |
|
Embryology |
Growth and development of embryos |
2. Microscopic Anatomy
Structures that cannot be seen without a
microscope.
- Cytology: Study of cells
- Histology: Study of tissues
3. Clinical Anatomy
Useful in medical practice; includes:
- Pathological
Anatomy: Study of
structural changes due to disease
- Radiographic
Anatomy: Study of
internal structures using X-ray, CT, MRI
- Molecular
Biology: Study of
structures at sub-cellular level
TYPES OF BASIC ANATOMICAL TERMS
1. Anatomical Position
This is the standard reference position for
describing the human body:
- Body
standing upright
- Face
forward
- Arms at
side
- Palms
facing forward
- Feet
together
All anatomical terms (like anterior,
posterior, medial, lateral) refer to the body in this position.
2. Anatomical Directional Terms
Used to locate one structure in relation to
another.

Table: Anatomical Directional Terms
|
Term |
Description |
|
Anterior (Ventral) |
Toward front of body |
|
Posterior (Dorsal) |
Toward back of body |
|
Superior (Cranial) |
Above another structure |
|
Inferior (Caudal) |
Below another structure |
|
Lateral |
Away from midline |
|
Medial |
Toward midline |
|
Proximal |
Near point of attachment |
|
Distal |
Away from point of attachment |
|
Superficial |
Close to body surface |
|
Deep |
Away from body surface |
|
Cranial |
Toward head |
3. Anatomical Regional Terms

These terms describe specific body regions
such as:
- Cranium
(head)
- Thorax
(chest)
- Abdomen
- Brachium
(arm)
- Antebrachium
(forearm)
- Carpus
(wrist)
- Digits
(fingers/toes)
- Thigh,
leg, ankle, etc.
ANATOMICAL TERMS OF BODY PLANES (POSITION)
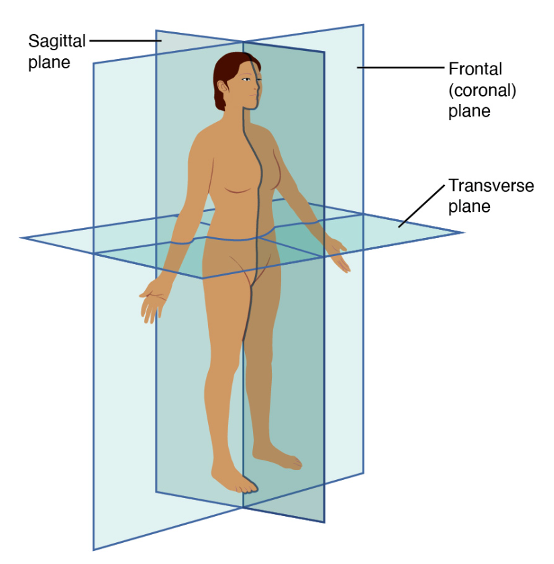
To study the human body accurately,
imaginary flat surfaces called planes are used. These planes help
describe sections or cuts through organs and the whole body.
1. Sagittal Plane
- A
vertical plane dividing the body into right and left portions.
- If it
divides the body exactly into equal right and left halves, it is the mid-sagittal
(median) plane.
- If the
division is unequal, it is called a para-sagittal plane.
2. Frontal (Coronal) Plane
- A
vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior
(back) portions.
3. Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
- A
horizontal plane that divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior
(lower) portions.
- Commonly
used in CT and MRI scanning.
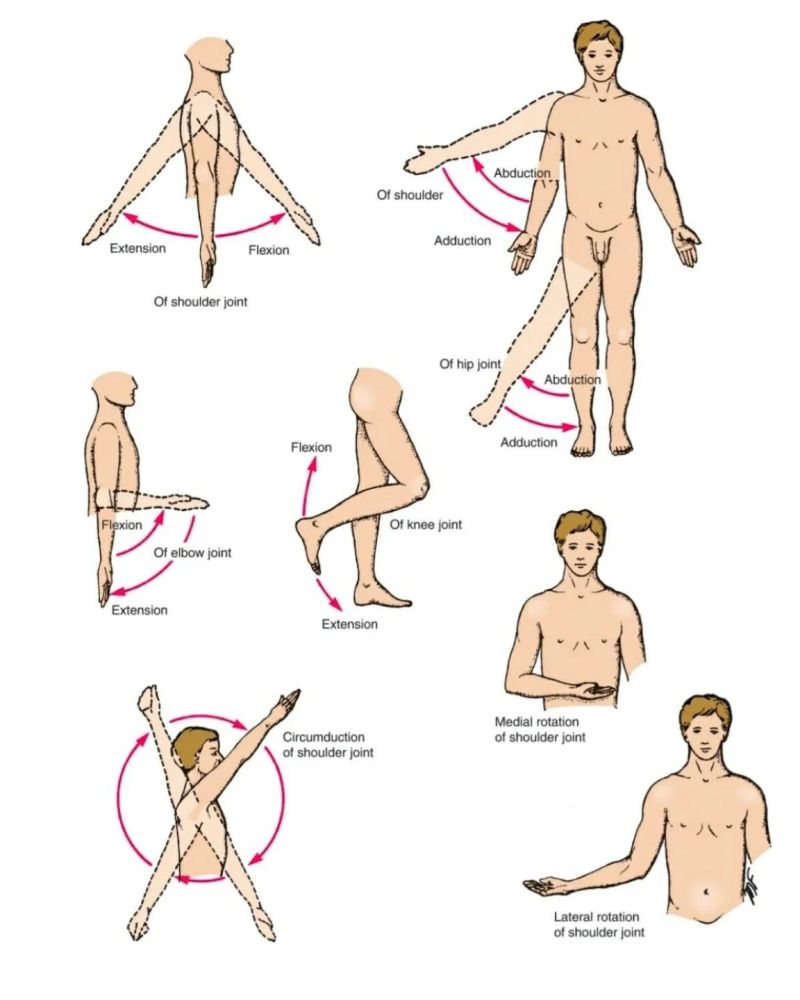
ANATOMICAL TERMS OF MOVEMENT AT JOINTS
Movements at joints help us understand how
bones and muscles work together. These terms describe how body parts move
relative to their normal position.
Basic Movement Terms
|
Movement |
Description |
|
Adduction |
Movement towards the body’s
midline. |
|
Abduction |
Movement away from the midline. |
|
Circumduction |
Circular movement combining flexion,
extension, abduction, and adduction. |
|
Medial Rotation |
Turning a limb toward the midline
of the body. |
|
Lateral Rotation |
Turning a limb away from the
midline. |
|
Pronation |
Rotation of the forearm so the palm
faces backward/downward. |
|
Supination |
Rotation of the forearm so the palm
faces forward/upward (as in anatomical position). |
|
Protraction |
Moving a body part forward (e.g.,
pushing jaw outward). |
|
Retraction |
Moving a body part backward (e.g.,
pulling shoulders back). |
|
Inversion |
Turning the sole of the foot medially
(towards the midline). |
|
Eversion |
Turning the sole laterally (away
from midline). |
Related Topics
