Body Cavities
| Home |Chapter: HAP - Scope of Anatomy and Physiology
Body cavities are hollow spaces within the body that protect internal organs and allow them to function without interference from one another. They also provide room for organs to expand or move.
BODY
CAVITIES
Body cavities are hollow spaces within the
body that protect internal organs and allow them to function without
interference from one another. They also provide room for organs to expand or
move.
There are two major categories of body
cavities:
1. Dorsal Body Cavity (Posterior)
This cavity protects organs of the nervous
system.
a) Cranial Cavity
- Contains
the brain.
- Formed by
skull bones:
- Front: Frontal bone
- Sides: Temporal bones
- Back: Occipital bone
- Top: Parietal bones
- Bottom: Sphenoid and Ethmoid bones
b) Vertebral (Spinal) Cavity
- Formed by
the vertebral column.
- Contains:
- Spinal
cord
- Spinal
nerve roots
- Protects a major part of the central nervous system.
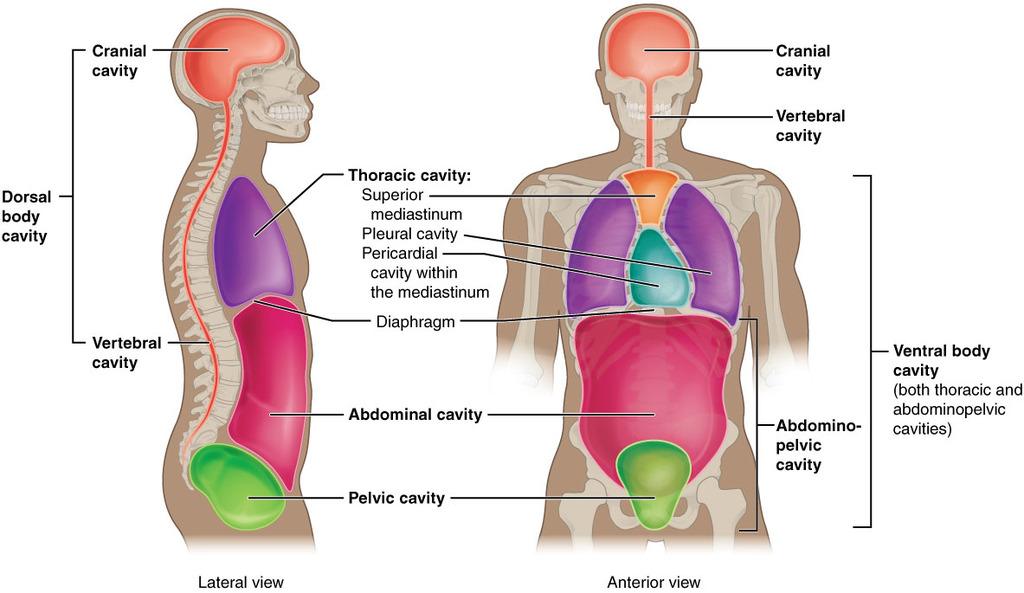
2. Ventral Body Cavity (Anterior)
Located in the front of the body; contains
many vital organs.
a) Abdominal Cavity
- Largest
cavity in the body; oval-shaped.
- Boundaries:
- Superior: Diaphragm
- Anterior: Abdominal muscles
- Posterior: Lumbar vertebrae and muscles
- Lateral: Lower ribs
- Inferior: Continuous with the pelvic cavity
- Lined by peritoneum,
a protective membrane.
b) Thoracic Cavity
- Located
in the upper trunk.
- Boundaries:
- Front: Sternum and rib cartilages
- Sides: Ribs and intercostal muscles
- Back: Thoracic vertebrae
- Top: Structures of neck root
- Bottom: Diaphragm
- Contains
heart, lungs, major blood vessels.
c) Pelvic Cavity
- Funnel-shaped;
continuation of abdominal cavity.
- Boundaries:
- Superior: Abdominal cavity
- Anterior: Pubic bones
- Posterior: Sacrum and coccyx
- Lateral: Hip bones
- Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and lower digestive tract.
Related Topics
