Cell Organelles and its Function
| Home |Chapter: HAP - Structure of Cell: Components and its Function
Organelles are specialized structures inside the cell that perform specific functions—just like organs in the human body. Most organelles are membrane-bound and are suspended in the cytoplasm.
CELL ORGANELLES
Organelles are specialized structures
inside the cell that perform specific functions—just like organs in the human
body. Most organelles are membrane-bound and are suspended in the cytoplasm.
Major
organelles include:
Nucleus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus,
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Centrosome, and components of the Cytoskeleton.
1. NUCLEUS
The nucleus was discovered by Robert
Brown (1831).
It is the largest and most important
organelle in eukaryotic cells and serves as the control center of
the cell.
Structure
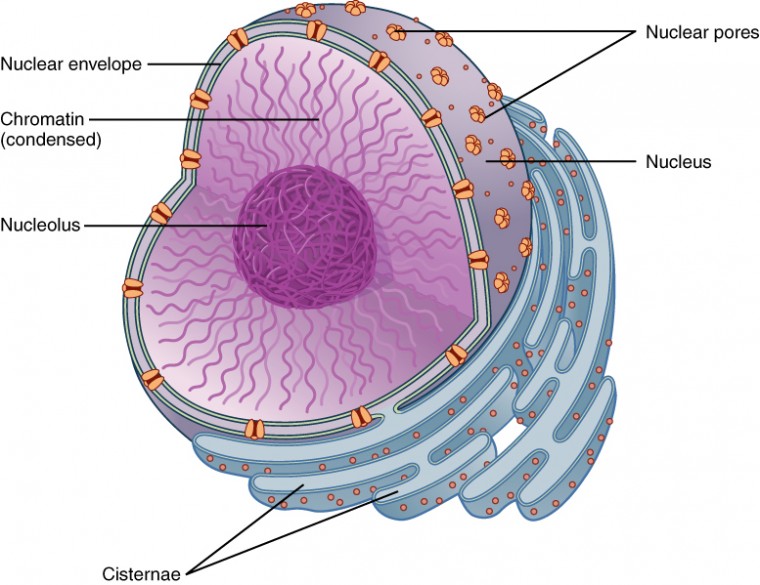
- Surrounded
by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
- Contains:
- Nucleolus – site of ribosome formation
- Chromatin – DNA + proteins
- Nuclear
pores – allow
exchange of materials
- Nucleoplasm – fluid inside the nucleus
Functions of Nucleus
- Stores genetic
material (DNA).
- Controls
protein synthesis.
- Regulates
cell growth and cell division.
- Transfers
hereditary information to the next generation.
- Essential
for cell reproduction—cells without a nucleus cannot divide.
2. MITOCHONDRIA
Discovered by Albert von Kolliker.
Known as the “Powerhouse of the Cell”
because they produce ATP (energy).
Structure
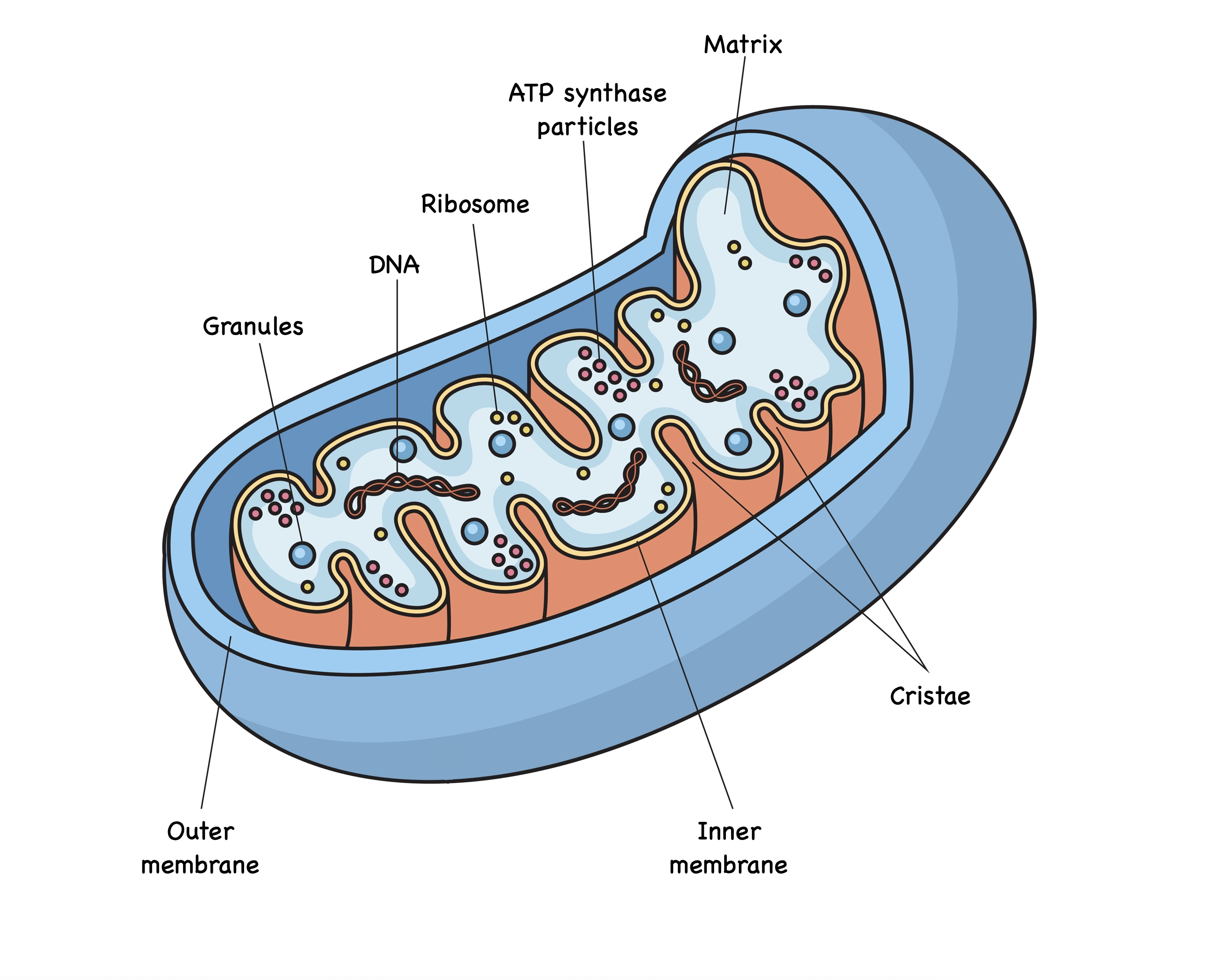
- Double
membrane organelle.
- Inner
membrane folded into cristae.
- Contains
its own DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes.
- Found
abundantly in energy-demanding tissues like muscle and liver.
Functions
- Produces
ATP through cellular respiration.
- Helps
regulate metabolism.
- Plays an
important role in cell death (apoptosis).
- Detoxifies
ammonia in liver cells.
- Essential
for hormone synthesis (testosterone, estrogen).
- Helps in
formation of certain blood components.
3. RIBOSOMES
Discovered by George E. Palade (1955).
Ribosomes are non-membrane organelles
made of RNA and proteins.
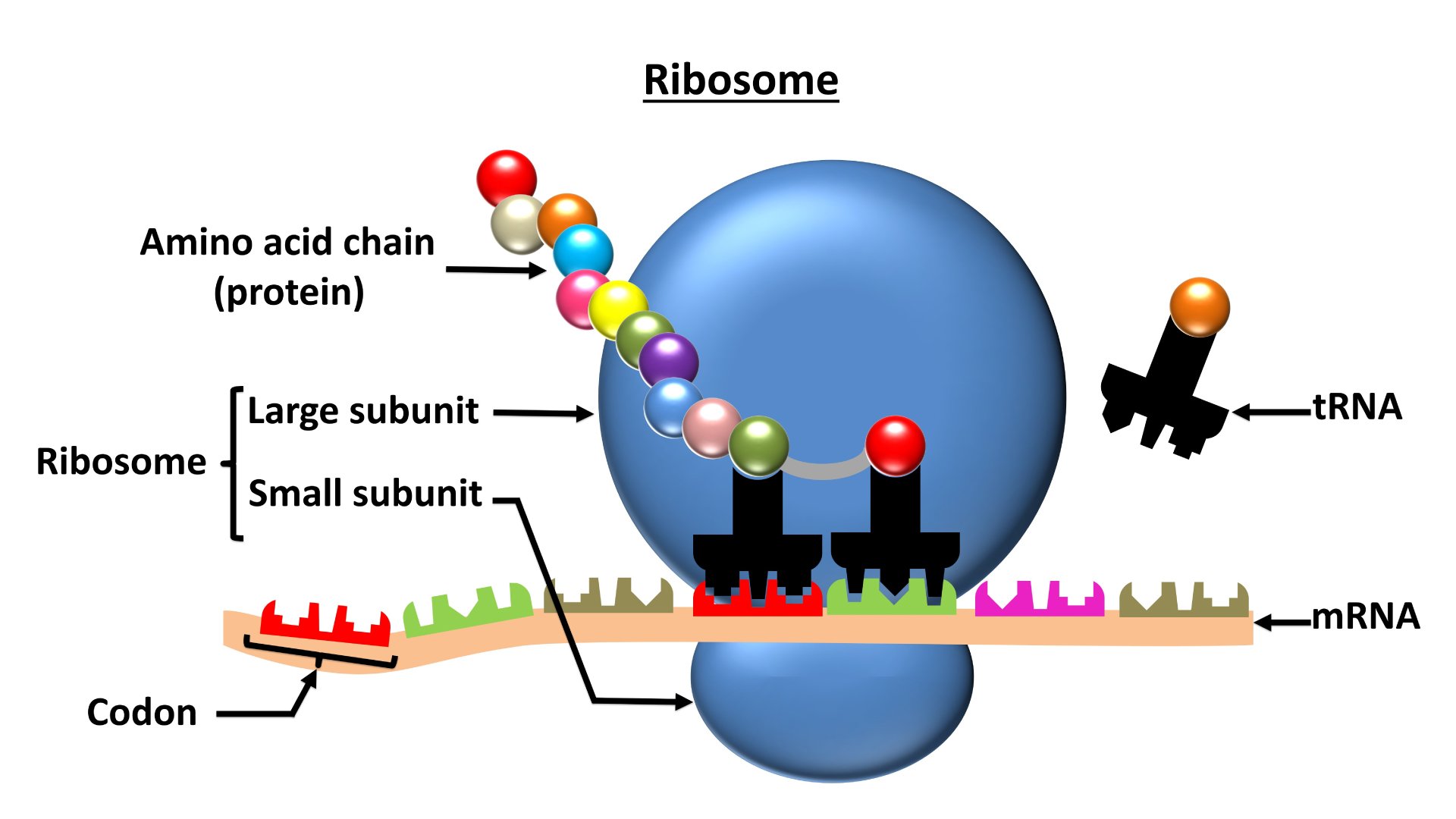
Types
- 70S
ribosomes – found in
prokaryotes
- 80S
ribosomes – found in
eukaryotes
Functions
- Site of protein
synthesis.
- Convert
genetic code (mRNA) into amino acid chains using tRNA.
- Essential
for formation of enzymes, hormones, and structural proteins.
4. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
The ER is a network of membranes forming
channels throughout the cell.
It provides transportation, storage, and manufacturing functions.
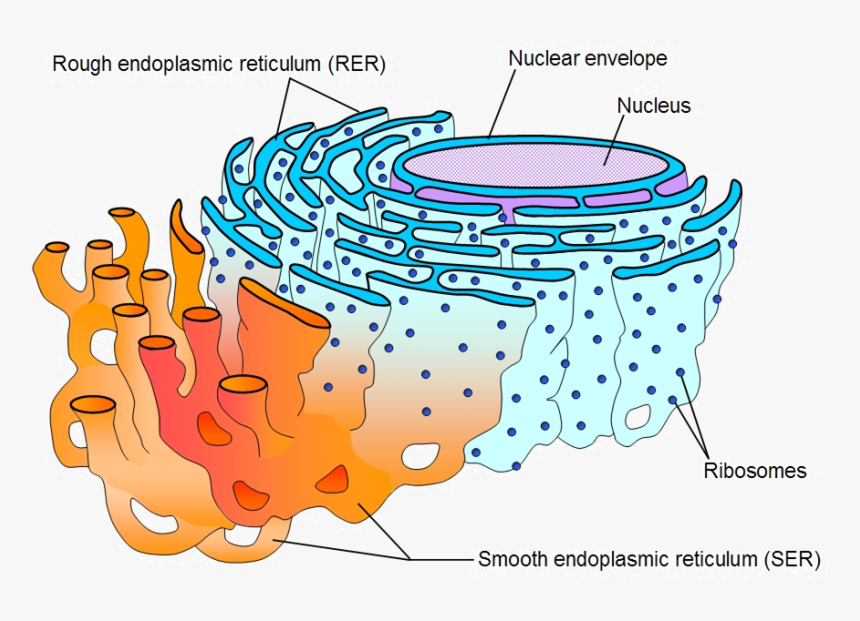
There are two types:
i. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
- Has ribosomes
on its surface (appears rough).
- Involved
in protein synthesis.
- Helps in protein
folding and sorting.
ii. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
- No
ribosomes (appears smooth).
- Involved
in:
- Lipid,
phospholipid, and cholesterol synthesis
- Production
of steroid hormones
- Carbohydrate
metabolism
- Detoxification of drugs in liver cells
- Storage
and release of calcium ions in muscle cells
5. GOLGI BODIES (GOLGI APPARATUS)
Discovered by Camillo Golgi (1898).
Appears as a stack of flattened membranes
called cisternae.
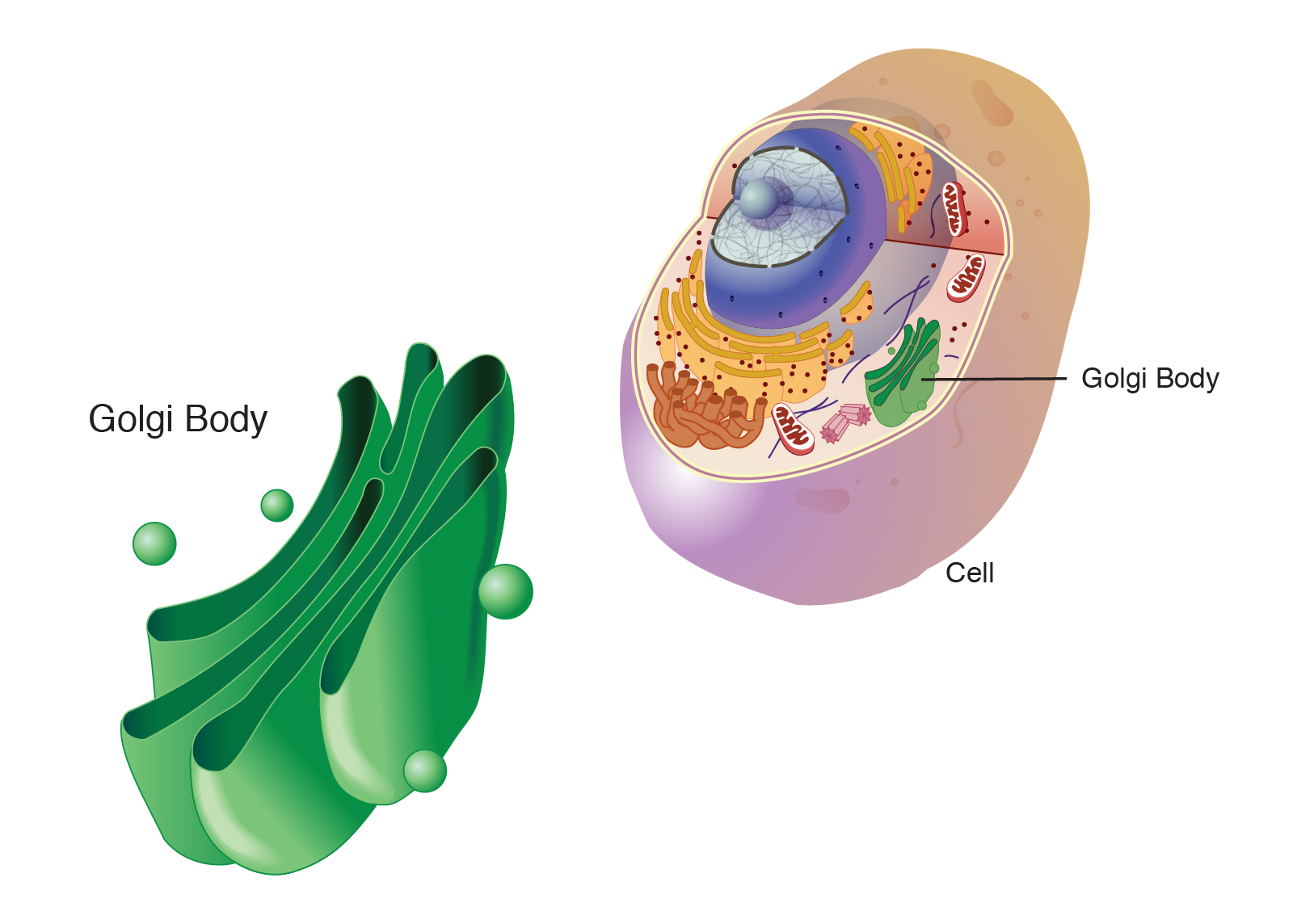
Two Faces
- Cis-face: Receiving side
- Trans-face: Shipping side (releases vesicles)
Functions
- Packages
and modifies proteins and lipids.
- Forms lysosomes.
- Produces glycoproteins
and glycolipids.
- Helps
form complex carbohydrates.
- Important
in forming plant cell walls.
6. LYSOSOMES
Discovered by Christian de Duve (1955).
Known as “Suicide bags of the cell”
because they contain powerful digestive enzymes.
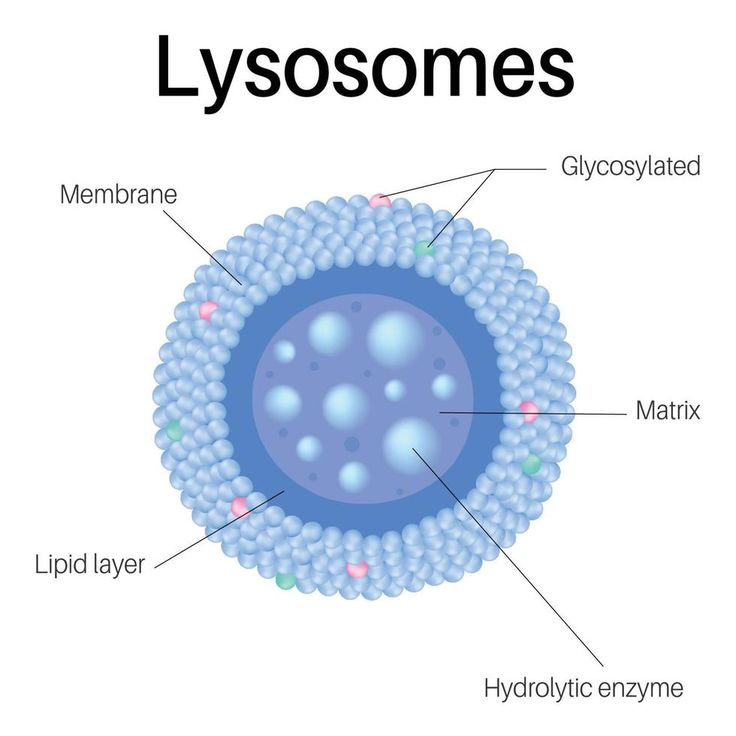
Functions
- Break
down waste materials (autophagy).
- Digest
materials taken in from outside (heterophagy).
- Destroy
harmful substances.
- Release
enzymes outside the cell (exocytosis) when needed.
Lysosomes protect the cell by ensuring
harmful substances are broken down safely.
7. CYTOSOL AND CYTOSKELETON
Cytosol
The fluid portion of the cytoplasm where
chemical reactions occur.
Functions:
- Site of
metabolic reactions.
- Helps
transport molecules.
- Supports
signal transduction pathways.
Cytoskeleton
A network of protein fibres providing
structural support.
Types of Cytoskeleton Fibers
|
TYPE |
FUNCTION |
|
Microfilaments |
Help in muscle contraction, cell
movement, maintain cell shape |
|
Microtubules |
Provide rigidity, help in organelle
movement, form spindle fibers |
|
Intermediate Filaments |
Provide strength, help in cell-to-cell
connection |
8. PEROXISOMES
Discovered by Christian de Duve.
Small, spherical membrane-bound organelles
containing the enzyme catalase.
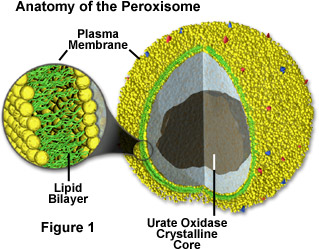
Functions
- Break
down hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) into water + oxygen.
- Protect
cells from oxidative damage.
- Perform β-oxidation
of fatty acids.
- Important
in detoxification reactions.
9. CENTROSOME AND CENTRIOLES
The centrosome is located near the
nucleus and contains a pair of centrioles.
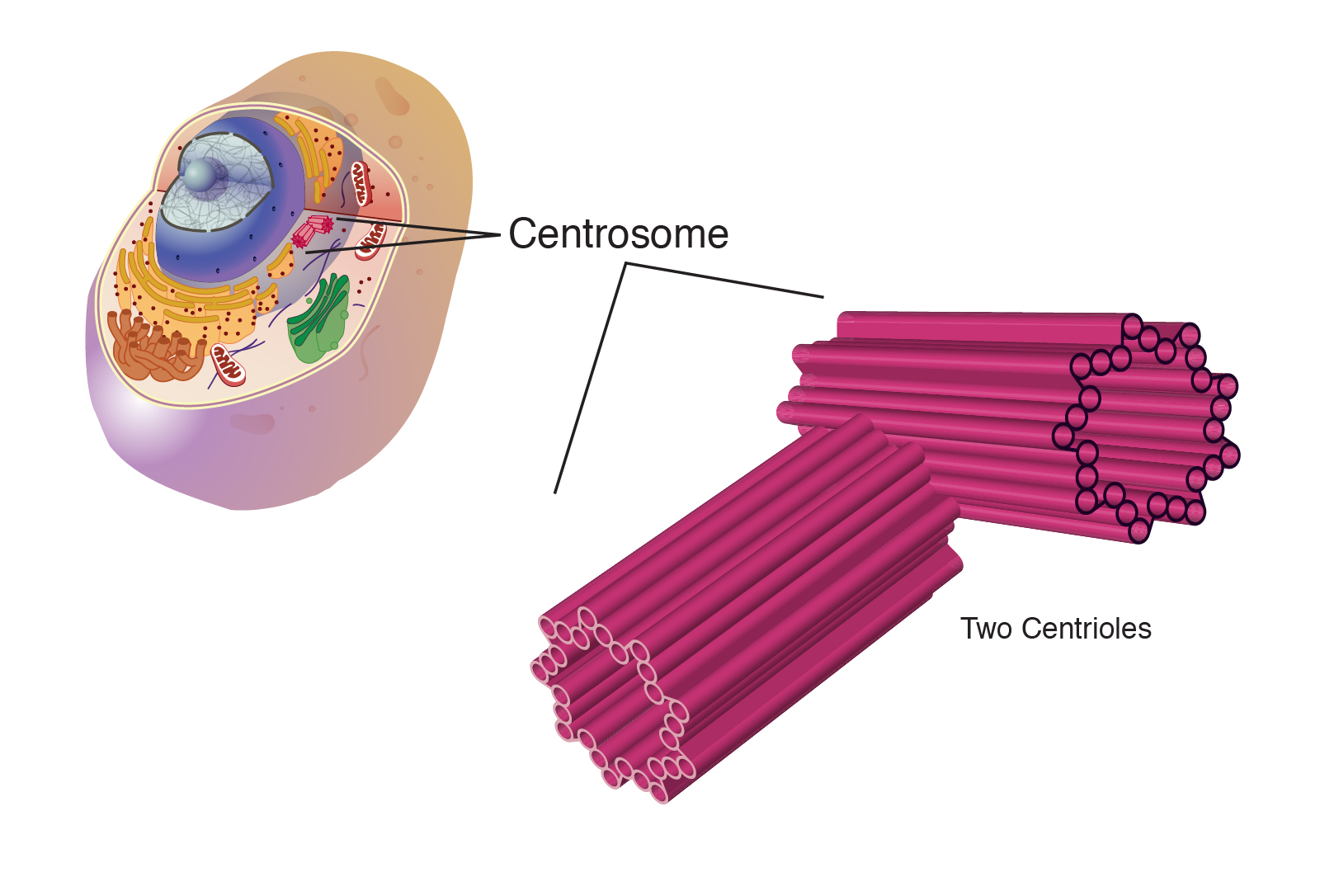
Functions
- Organizes
microtubules.
- Forms the
mitotic spindle during cell division.
- Helps
with chromosome movement during mitosis.
Centrioles are essential for maintaining
the internal organization and support of the cell.
10. CELL EXTENSIONS
Some cells have structures that extend from
the plasma membrane for movement or increasing surface area.
Types of Cell Extensions
|
EXTENSION |
DESCRIPTION |
FUNCTION |
|
Microvilli |
Small finger-like projections |
Increase surface area for absorption
(e.g., intestines) |
|
Cilia |
Hair-like projections that beat in
coordination |
Move substances across surfaces (e.g.,
mucus in respiratory tract) |
|
Flagella |
Long tail-like structure |
Movement of the entire cell (e.g., sperm
cell) |
