Organization of Human Body
| Home |Chapter: HAP - Scope of Anatomy and Physiology
The human body is arranged in different structural levels, starting from the simplest chemical units and building up to the complete organism.
ORGANIZATION
OF HUMAN BODY
The human body is arranged in different
structural levels, starting from the simplest chemical units and building up to
the complete organism.
Levels of Structural Organization in the
Human Body
|
Level |
Description |
|
Chemical Level |
Includes atoms, the smallest units of
matter (e.g., Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen). Atoms combine to form molecules
essential for life. |
|
Cellular Level |
Cells are the basic structural and
functional units of life. Some organisms (like Amoeba, Paramecium) exist as
single cells, but humans have many specialized cells. |
|
Tissue Level |
Groups of similar cells working together
to perform a specific function. Examples: Epithelial tissue, Nervous tissue,
Muscle tissue. |
|
Organ Level |
Organs are made of two or more tissues
working together. Example: Heart, Lungs, Brain. |
|
Organ System Level |
A group of organs that perform related
functions, such as the digestive system or respiratory system. |
|
Organism Level |
All organ systems working together to
form one complete living individual. Example: the human body. |
Main Subdivisions of the Human Body
The human body can be divided into several
major parts for easier study:
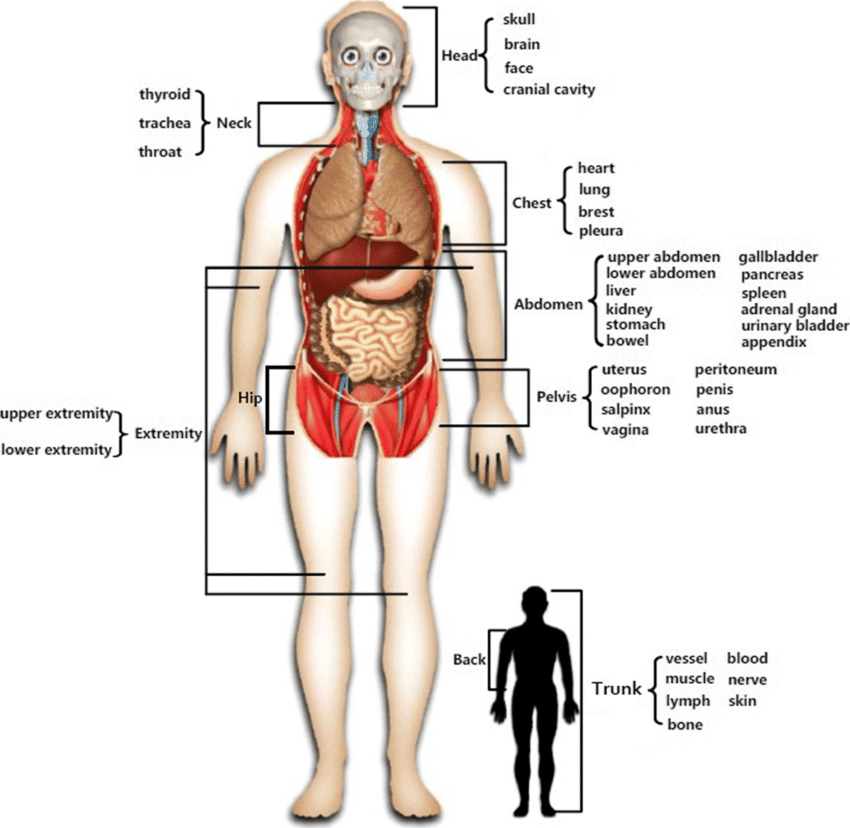
- The Head
- The Trunk
- The
Thorax
- Limbs/Extremities
- The
Abdomen
- Arm
- The
Pelvis
- Forearm
- Thigh
- Leg
- Great Toe
These subdivisions help in anatomical
description and clinical reference.
Related Topics
