Transport of Material Across Cell Membrane
| Home |Chapter: HAP - Structure of Cell
Materials move across the membrane by passive or active transport mechanisms.
TRANSPORT OF MATERIAL ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE
Materials move across the membrane by passive
or active transport mechanisms.
1. PASSIVE TRANSPORT
- Does
not require energy.
- Movement
occurs from high concentration →
low concentration.
Types of Passive Transport
a)
Diffusion
Movement of solute molecules from an area of high concentration to low
concentration.
Two types:
- Simple
Diffusion –
substances pass directly through the membrane.
- Facilitated
Diffusion –
substances pass through transport proteins (carrier or channel proteins).
b)
Osmosis
Movement of water molecules from high water concentration to low water
concentration across a selectively permeable membrane.
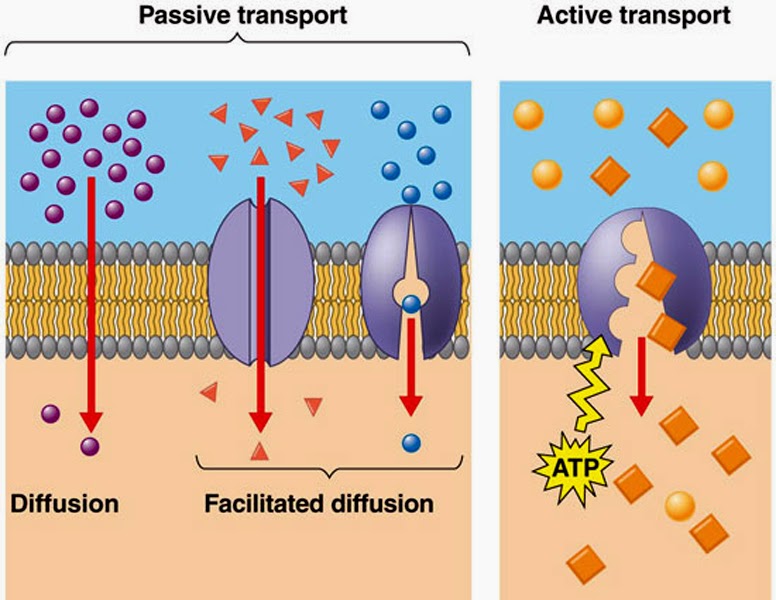
2. ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- Requires
energy (ATP).
- Movement
occurs from low concentration →
high concentration
(against gradient).
Examples:
- Sodium-Potassium
Pump
Maintains ion balance inside nerve and muscle cells.
Bulk Transport
Used for movement of large particles or
liquids.
a) Endocytosis ― Transport into the cell
- Phagocytosis – “cell eating”; uptake of solid
particles.
- Pinocytosis – “cell drinking”; uptake of fluids.
- Receptor-mediated
endocytosis – very
specific uptake using receptors.
b) Exocytosis ― Transport out of the cell
- Used to
release hormones, enzymes, waste, etc.
