Distinctive Features of Corticosteroids
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Corticosteroids
Hydrocortisone (Cortisol) acts rapidly but has short duration of action. In addition to primary glucocorticoid, it has significant mineralocorticoid activity as well.
DISTINCTIVE FEATURES
The relative potency
and activity of different natural and synthetic corticosteroids employed
systemically is compared in Table 20.1.
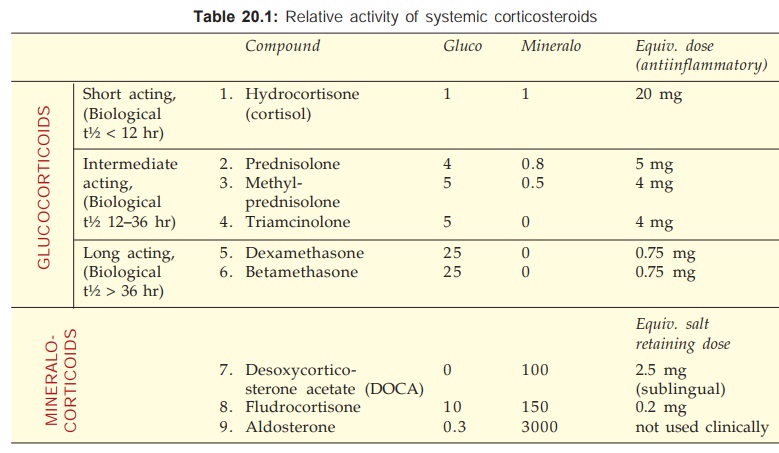
1. Hydrocortisone (Cortisol)
Acts rapidly but has short duration of action. In addition to
primary glucocorticoid, it has significant mineralocorticoid activity as well.
Used for:
Replacement
therapy—20 mg morning + 10 mg afternoon orally.
Shock,
status asthmaticus, acute adrenal insufficiency—100 mg i.v. bolus + 100 mg 8
hourly i.v. infusion.
Topically
(see Ch. No. 64) and as suspension for
enema in ulcerative colitis (see Ch.
No. 48).
LYCORTINS,
EFCORLIN SOLUBLE 100 mg/2 ml inj. (as hemisuccinate for i.v. inj.) WYCORT,
EFCORLIN 25 mg/ml inj (as acetate for i.m./intraarticular inj.). PRIMACORT 100,
200, 400 mg/vial inj.
2. Prednisolone
It is 4 times more potent than hydrocortisone, also more selective glucocorticoid,
but fluid retention does occur with high doses. Has intermediate duration of
action: causes less pituitaryadrenal suppression when a single morning dose or
alternate day treatment is given. Used for allergic, inflammatory, autoimmune
diseases and in malignancies: 5–60 mg/day oral, 10–40 mg i.m., intraarticular;
also topically.
DELTACORTRIL,
HOSTACORTINH, 5, 10 mg tab, 20 mg/ml (as acetate) for i.m., intraarticular
inj., WYSOLONE, NUCORT, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40 mg tabs.
3. Methylprednisolone
Slightly more potent and more selective than prednisolone: 4–32 mg/
day oral. Methylprednisolone acetate has been used as a retention enema in
ulcerative colitis.
Pulse therapy with
high dose methylprednisolone (1 g infused i.v. every 6–8 weeks) has been tried
in nonresponsive active rheumatoid arthritis, renal transplant, pemphigus, etc.
with good results and minimal suppression of pituitaryadrenal axis.
SOLUMEDROL
Methylprednisolone (as sod. succinate) 40 mg, 125 mg, 0.5 g (8 ml) and 1.0 g
(16 ml) inj, for i.m. or slow i.v. inj.
The
initial effect of methylprednisolone pulse therapy (MPPT) is probably due to
its anti-inflammatory action, while long term benefit may be due to temporary
switching off of the immunodamaging processes as a consequence of lymphopenia
and decreased Ig synthesis.
4. Triamcinolone
Slightly more potent than prednisolone but highly selective
glucocorticoid: 4–32 mg/day oral, 5–40 mg i.m., intraarticular injection. Also
used topically.
KENACORT,
TRICORT 1, 4, 8 mg tab., 10 mg/ml, 40 mg/ml (as acetonide) for i.m.,
intraarticular inj., LEDERCORT 4 mg tab.
5. Dexamethasone
Very potent and highly selective glucocorticoid. Long acting, causes
marked pituitaryadrenal suppression, but fluid retention and hypertension are
not a problem.
It
is used for inflammatory and allergic conditions 0.5–5 mg/day oral. Shock,
cerebral edema, etc. 4–20 mg/day i.v. infusion or i.m. injection. Also used
topically.
DECADRON,
DEXONA 0.5 mg tab, 4 mg/ml (as sod. phosphate) for i.v., i.m. inj., 0.5 mg/ml
oral drops; WYMESONE, DECDAN 0.5 mg tab, 4 mg/ml inj.
6. Betamethasone
Similar to dexamethasone, 0.5–5 mg/ day oral, 4–20
mg i.m., i.v. injection or infusion, also topical.
BETNESOL,
BETACORTRIL, CELESTONE 0.5 mg, 1 mg tab, 4 mg/ml (as sod. phosphate) for i.v.,
i.m. inj., 0.5 mg/ml oral drops. BETNELAN 0.5 mg, 1 mg tabs.
Dexamethasone
or betamethasone are preferred in cerebral edema and other states in which
fluid retention must be avoided.
7. Desoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)
It has only mineralocorticoid activity. Used occasionally
for replacement therapy in Addison’s disease: 2–5 mg sublingual, 10–20 mg i.m.
once or twice weekly.
In
DOCABOLIN 10 mg/ml inj (along with nandrolone).
In
addition a number of topically active
glucocorticoids have been developed.
Beclomethasone
dipropionate budesonide, etc. are used by inhalation in asthma, as spray in
nasal allergy, as well as for skin and mucous membrane lesions (see Ch. No. 16).
Fluocinolone
acetonide, fluocortolone, clobetasol propionate and esters of betamethasone,
dexamethasone, triamcinolone are described in Ch. No. 64.
Related Topics
