Garlic
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Volatile Oils
Garlic is the ripe bulb of Allium sativum Linn., belonging to family Liliaceae.
GARLIC
Synonyms
Allium; Lasan (Hindi).
Biological Source
Garlic is the ripe bulb of Allium sativum Linn., belonging to family Liliaceae.
Geographical Source
Garlic occurs in central Asia, southern Europe, and United
States. It is widely cultivated in India.
Cultivation and Collection
The cultivation of Garlic is similar to that of onion. It is
generally grown as an irrigated crop throughout the year. It can be grown under
a wide range of climatic conditions but it succeeds best in mild climates
without extremes of heat and cold. It is grown on a wide variety of soils. It
requires a rich well-drained clay loam to grow well. The land is well ploughed
to a fine tilth, beds, and channels are made. Garlic is planted during
October–November in plains and during February–March in the hills. The cloves
are separated and pressed lightly into the soil. Garlic requires heavy
manuring.
Characteristics
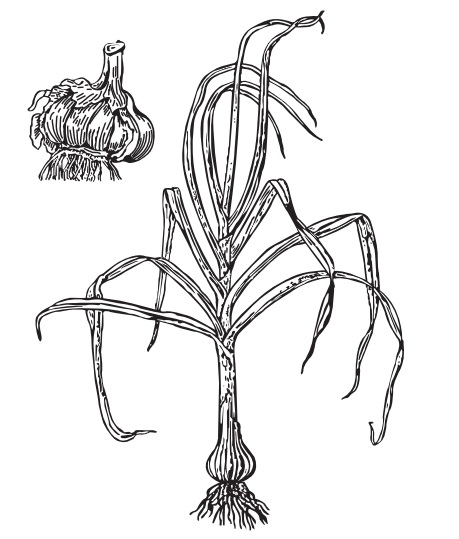
It is a perennial herb having bulbs with several cloves,
enclosed in a silky white or pink membraneous envelope.
Chemical Constituents
Allicin, a yellow liquid responsible for the odour of
garlic, is the active principle of the drug. It is miscible with alcohol,
ether, and benzene and decomposes on distilling. The other constituents
reported in Garlic are alliin, volatile and fatty oils, mucilage and albumin.
Alliin, another active principle, is odourless, crystallized from water acetone
and practically insoluble in absolute alcohol, chloroform, acetone, ether, and
benzene. Upon cleavage by the specific enzyme alliinase, an odour of garlic
develops, and the fission products show antibacterial action similar to
allicin. Essential oil (0.06–0.1%) contains allyl propyl disulphide, diallyl
disulphide, and allicin. γ-Glutamyl peptides are isolated from
the Garlic. The amino acids present in the bulb are leucine, methionine,
S-propyl-L-cysteine, S-propenyl-L-cysteine, S-methyl cysteine, S-allyl cysteine
sulphoxide (alliin), S-ethyl cysteine sulphoxide, and S-butyl-cysteine
sulphoxide.
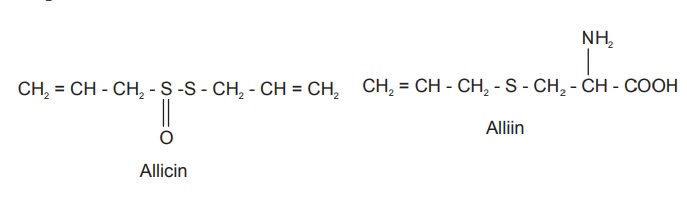
Uses
Garlic is carminative, aphrodisiac, expectorant, stimulant,
and used in fevers, coughs, febrifuge in intermittent fevers, respiratory
diseases such as chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, whooping cough, and
tuberculosis. It is also used in atherosclerosis and hypertension.
In Germany, garlic is consumed as a complement in the diet
of hyperlipidemic patients and for the prophylaxis of the vascular changes
induced by ageing. The garlic can cause gastrointestinal distress and alters
breath and skin odour. Garlic or its constituents exhibit various biological
activities, such as antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antitumor, and
antidiabetic effects.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Lasuna (Himalaya Drug Company) and Lashunadi bati (Baidyanath).
Related Topics
