Jalap
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Resins
Jalap consists of dried tuberous roots or tubercles of Ipomoea purga Hayne, belonging to family Convolvulaceae.
JALAP
Synonyms
Radix jalapae, Jalap root, Vera cruz or Mexican Jalap.
Biological Source
Jalap consists of dried tuberous roots or tubercles of Ipomoea purga Hayne, belonging to family Convolvulaceae.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in Mexican Andes, India, West Indies, and
South America.
Collection
The plant is large and twinning perennial herb, and it
pro-duces thin horizontal slender runners. Adventitious roots (fusiform or
napiform roots) are produced from the nodes of the runners. Some of the roots
remain thin but few of them swell due to the storage of starch. These roots are
collected after the rainy season, that is, in May. As a result of unfavourable
environmental conditions they are dried by woodfire in nets. Since the drug is
artificially dried it gains a smoky odour. Some slits are also made on the drug
to facilitate the escape of the moisture.
Characteristics
Jalap is cylindrical, fusiform or napiform, irregularly
oblong about 5 to 10 cm long and 2 to 10 cm wide. It is hard, resinous,
compact, and heavy. The outer surface is dark brown in colour with furrows and
wrinkles and internally it is yellowish grey in colour. Odour is smoky and
taste is sweet and starchy in the beginning and later it is acrid.
Microscopy
Cork is the outermost layer consisting of tabular polygonal
cells which are brown in colour. Just below the cork it has the secondary
phloem. The secondary phloem is formed by the circular cambium and is about 2
mm wide. Inside the cambium it has the secondary xylem. The secondary xylem has
vessels, which are either in small groups or scattered. Latex cells are
present in the phloem tissues arranged longitudinally and form a dark and
resinous point scattered in the drug. The parenchymatous cells contain starch
which are simple, rounded, or in groups of two to four. Small prism types of
calcium oxalate crystals are present in the parenchyma and very few
sclerenchymatous cells are seen in the phelloderm region.
Chemical Constituents
Jalap contains 8 to 12% of glycosidal resin and the other
constituents are mannitol, sugar, β-methyl-aesculetin, phytosterin,
ipurganol, starch and calcium oxalate. Jalap resin is the resinous constituent
that has a soluble portion and an insoluble portion when dissolved in ether.
The soluble portion constitutes to 10%, whereas the remaining is the insoluble
portion. Ether insoluble portion is called convolvulin and the ether soluble
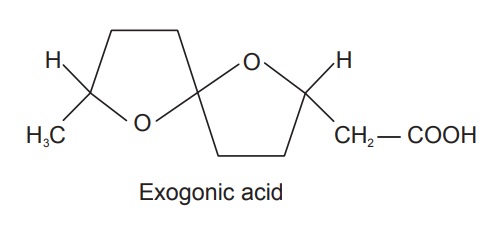
portion is called julapin. Convolvulin is a substance with some 18 hydroxyl
groups esterified with valeric, tiglic, and exogonic acids. Exogonic acid is
3,6-6,9-dioxidodecanoic acid.
Uses
Jalap can stimulate the intestinal secretion, it act as
laxative in small doses and purgative in large doses, and it is also used as
hydragogue cathartic.
