Morphan derivatives
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Narcotic Analgesics
Narcotic Analgesics - Morphan derivatives - Synthesis and Drug Profile - a. Pentazocine (Fortstar, Fortwin, Zocin) b. Cyclazocin c. Phenazocine - Structure, Properties, uses, Synthesis, Assay, Storage, Dosage forms, Dose | Synthesis and Drug Profile
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Morphan derivatives
a. Pentazocine (Fortstar, Fortwin, Zocin)
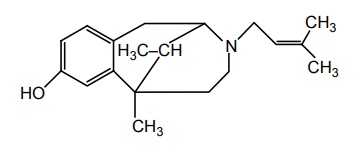
Properties and uses: It is a white or almost white powder sparingly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, and sparingly soluble in methylene chloride. A synthetic analgesic agent, when administered orally in a 50 mg dose, it appears to be equivalent in analgesic effectiveness to 60 mg of codeine. Pentazocine in a parenteral dose of 30 mg or an oral dose of 50 mg is about as effective as 10 mg of morphine in most patients. There is some evidence that the analgesic action resides principally in the (–) isomer, and a dose of 25 mg is approximately equivalent to 10 mg of morphine sulphate.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in ethanol and add 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and determine the end point potentiometrically.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
Dose: By parenteral, 20 to 60 mg (as lactate); usually 30 mg 6 to 8 times/day; daily dose must not exceed 360 mg.
Dosage forms: Pentazocaine injection I.P., Pentazocaine HCl tablets I.P.,Pentazocine capsules B.P., Pentazocine tablets B.P.
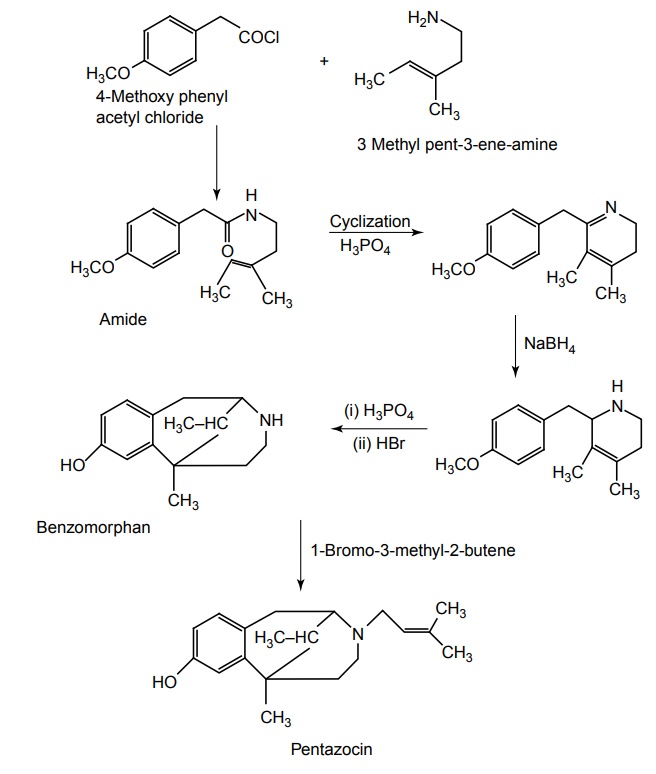
Synthesis
Route I. From: 4-Methoxy phenyl acetyl chloride
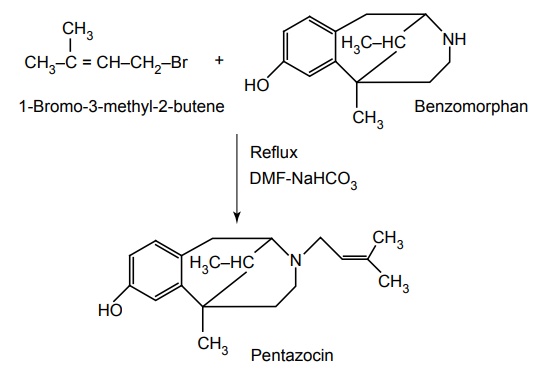
Route II.From: 1-Bromo-3 methyl 2 butene
b. Cyclazocin
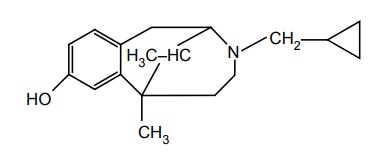
Synthesis
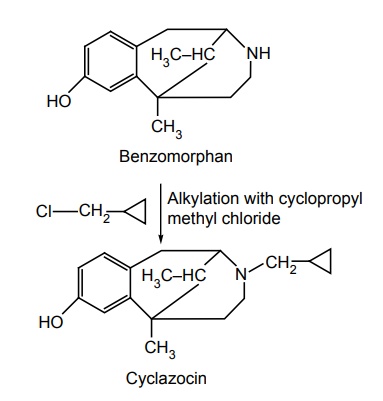
Uses: It is a potent narcotic antagonist that has shown analgesic activity in humans at 1 mg doses.
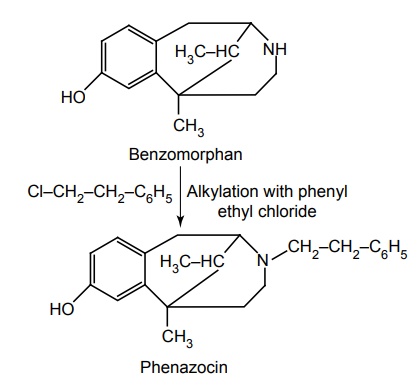
c. Phenazocine
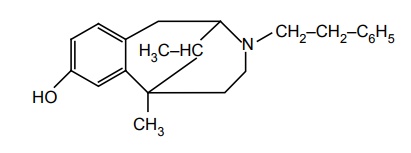
Synthesis
Related Topics
