Pyridine derivatives
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antihyperlipidaemic Agents
Antihyperlipidaemic Agents : Pyridine derivatives ; Nicotinic acid - Synthesis and Drug Profile - Structure, Properties, uses, Synthesis, Assay, Storage, Dosage forms, Dose
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Pyridine derivatives
i. Nicotinic acid
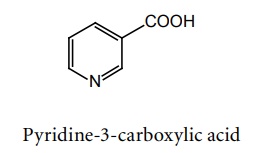
Mode of action: Nicotinic acid inhibits the lipolysis of triglycerides by hormone sensitive lipase, which reduces transport of the free fatty acids to liver and decreases hepatic triglycerides synthesis. Reduction of triglycerides synthesis decreases the production of hepatic VLDL.
Metabolism: Nicotinic acid is a B-complex vitamin that is converted to nicotinamide, NAD+, and NADP+. The latter two compounds are coenzymes, and required for the oxidation/reduction reaction in a variety of biochemical pathways. Nicotinic acid is metabolized to a number of inactive compounds, including nicotinuric acid and N-methylated derivatives
Properties and uses: It is a white, crystalline powder and it dissolves in dilute solutions of the alkali hydroxides and carbonates, soluble in boiling water and in boiling alcohol, sparingly soluble in water. It is used as an antihyperlipidaemic agent.
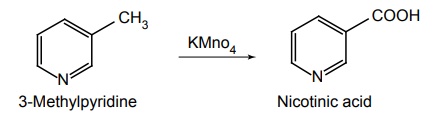
Synthesis
Method I: From 3-Methyl pyridine
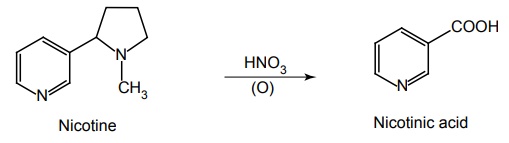
Method II: From Nicotine
Assay: Dissolve the sample in water and titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, using phenolphthalein solution as indicator. End point is the appearance of a pink colour.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light.
Dosage forms: Nicotinic acid tablets I.P., B.P.
Related Topics
