Spontaneous Reporting System (SRS) in Japan
| Home | | Pharmacovigilance |Chapter: Pharmacovigilance: Pharmacovigilance and Risk Management in Japan
The Japanese SRS was created in 1967. In the early developing stage of Japanese SRS, the reports were sent from dozens of ‘designated medical institu-tions’ to the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
SPONTANEOUS REPORTING SYSTEM
(SRS) IN JAPAN
The
Japanese SRS was created in 1967. In the early developing stage of Japanese
SRS, the reports were sent from dozens of ‘designated medical institu-tions’ to
the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MHW, renamed the Ministry of Health, Labour
and Welfare, MHLW in 2000). Since 1984, reports were also sent from ‘designated
pharmacies.’ For the first few years after implementation of the SRS, the
annual number of ADR reports was only in the hundreds. However, with the
increase in the number of ‘designated medical institutions’ and ‘designated
pharmacies,’ the number of ADR reports steadily increased to reach around 1500
per annum by the early 1990s (Table 31.1.). After a further expansion of the
system in 1997, the MHW (MHLW) received around 5000 reports per annum from
health professionals in all of the medical institutions and all of the
pharmacies. Following the recent amendment of the PAL in 2002, doctors,
dentists, pharmacists and other health professionals now have a legal duty to
report an ADR when judged to be necessary to prevent the onset or spread of the
risk of harm to public health or hygiene (Pharmaceu-tical affairs law,
enforcement ordinance and enforcement regulations, 2003).
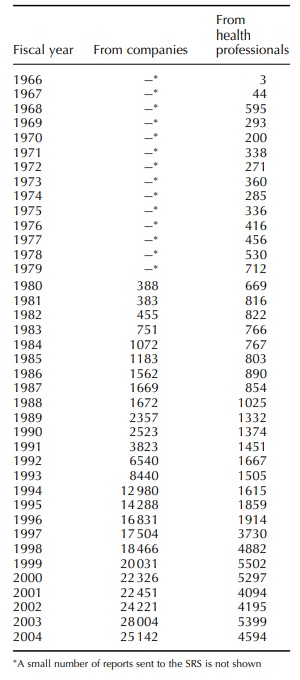
Since
1967, the MHW has received ADR reports sent via
drug companies as well as reports directly from the doctors. However, until
1979 the annual number of reports was less than 500. In 1979 the ministerial
ordinance ‘Enforcement Regulations on the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law’ (Article
62-2) made drug companies duty bound to send the ADR reports to the MHW.
Thereafter the number of ADR reports gradually increased until the late 1980s
when the increase accelerated significantly. The number of domestic reports per
annum exceeded 17 000 in 1997 when the duty of the drug companies to send the
ADR reports to the regulatory body was clearly stipu-lated in PAL (Article
77-4-2), and ICH-E2A guideline and its expedited reporting criteria were
implemented for the approved drugs. The number of ADR reports has consistently
been around 25 000 per annum over the 3-year period since 2002 (Table 31.1.).
Electronic submission of safety reports with E2B/M2 format has been mandatory
since October 27 in 2003. At the start, in 2003, 25% of submitted reports were
via elec-tronic data interchange (EDI); however, the fraction of EDI was
increased to 83% being employed by 73 companies in August 2005.
Related Topics
