Turmeric
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Resins
Turmeric is the dried rhizome of Curcuma longa Linn. (syn. C.domestica Valeton)., belonging to family Zingiberaceae.
TURMERIC
Synonyms
Saffron Indian; haldi (Hindi); Curcuma; Rhizoma cur-cumae.
Biological Source
Turmeric is the dried rhizome of Curcuma longa Linn. (syn. C.domestica
Valeton)., belonging to family Zingiberaceae.
Geographical Source
The plant is a native to southern Asia and is cultivated
extensively in temperate regions. It is grown on a larger scale in India,
China, East Indies, Pakistan, and Malaya.
Cultivation
Turmeric plant is a perennial herb, 60–90 cm high with a short stem and tufted leaves; the
rhizomes, which are short and thick, constitute the turmeric of commerce. The
crop requires a hot and moist climate, a liberal water supply and a
well-drained soil. It thrives on any soil-loamy or alluvial, but the soil
should be loose and friable. The field should be well prepared by ploughing and
turning over to a depth of about 30 cm and liberally manured with farmyard and
green manures. Sets or fingers of the previous crop with one or two buds are
planted 7 cm deep at distance of 30–37 cm from April to August. The crop is
ready for harvesting in about 9–10 months when the lower leaves turn yellow.
The rhizomes are carefully dug up with hard picks, washed, and dried.
Characteristics
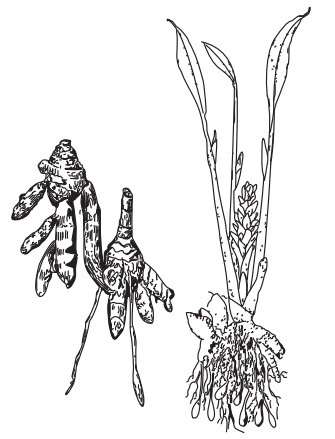
The primary rhizomes are ovate or pear-shaped, oblong or
pyriform or cylindrical, and often short branched. The rhizomes are known as
‘bulb’ or ‘round’ turmeric. The sec-ondary, more cylindrical, lateral branched,
tapering on both ends, rhizomes are 4–7 cm long and 1–1.5 cm wide and called as
‘fingers’. The bulbous and finger-shaped parts are separated and the long
fingers are broken into convenient bits. They are freed from adhering dirt and
fibrous roots and subjected to curing and polishing process. The curing
consists of cooking the rhizomes along with few leaves in water until they become
soft. The cooked rhizomes are cooled, dried in open air with intermittent
turning over, and rubbed on a rough surface. Colour is deep yellow to orange,
with root scar and encircling ridge-like rings or annulations, the latter from
the scar of leaf base. Fracture is horny and the cut surface is waxy and
resinous in appearance. Outer surface is deep yellow to brown and
longitudinally wrinkled. Taste is aromatic, pungent and bitter; odour is
distinct.
Microscopy
The transverse section of the rhizome is characterized by
the presence of mostly thin-walled rounded parenchyma cells, scattered vascular
bundles, definite endodermis, few layers of cork developed under the epidermis,
and scattered oleoresin cells with brownish contents. The epidermis is
consisted of thick-walled cells, cubical in shape, of various dimensions. The
cork cambium is developed from the sub-epidermal layers and even after the
development of the cork, the epidermis is retained. Cork is generally composed
of four to six layers of thin-walled brick-shaped parenchymatous cells. The
parenchyma of the pith and cortex contains grains altered to a paste, in which
sometimes long lens shaped unaltered starch grains of 4–15 μm diameter are
found. Oil cells have suberised walls and contain either orange-yellow globules
of a volatile oil or amorphous resinous masses. Cortical vascular bundles are
scattered and are of a collateral type. The vascular bundles in the pith region
are mostly scattered and they form discontinuous ring just under the
endodermis. The vessels have mainly spiral thickenings and only a few have
reticulate and annular structure.
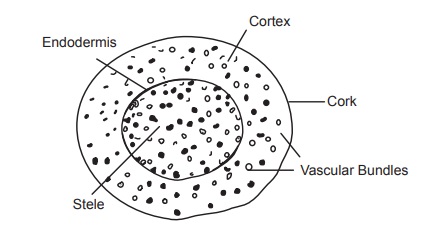
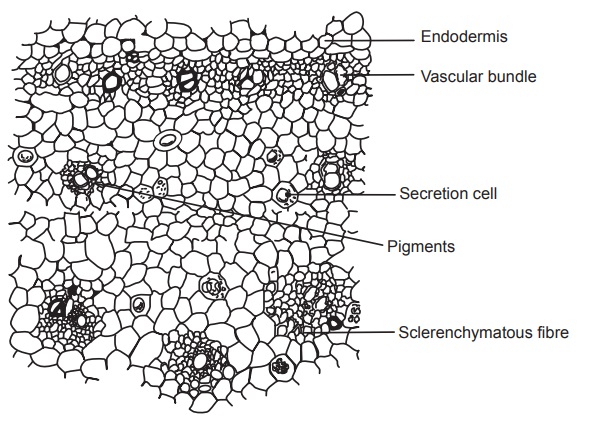
Transverse section of turmeric rhizome
Chemical Constituents
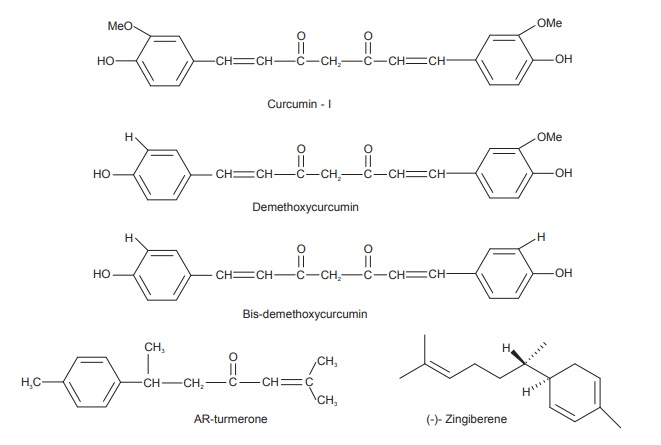
Turmeric contains yellow colouring matter called as
curcuminoids (5%) and essential oil (6%). The chief constituent of the
colouring matter is curcumin I (60%) in addition with small quantities of
curcumin III, curcumin II and dihydrocurcumin. The volatile oil contains mono-
and sesquiterpenes like zingiberene (25%), α-phellandrene, sabinene, turmerone,
arturmerone, borneol, and cineole. Choleretic action of the essential oil is
attributed to β-tolylmethyl carbinol.
The volatile oil also contains α- and β-pinene, camphene, limonene,
terpinene, terpinolene, caryophyllene, linalool, isoborneol, camphor, eugenol,
curdione, curzerenone, curlone, AR-curcumenes, β-curcumene, γ-curcumene. α- and β-turmerones,
and curzerenone.
Chemical Tests
1. Turmeric powder on treatment with
concentrated sulphuric acid forms red colour.
2. On addition of alkali solution to Turmeric
powder red to violet colour is produced.
3. With acetic anhydride and
concentrated sulphuric acid Turmeric gives violet colour. Under UV light this
colour is seen as an intense red fluorescence.
4. A paper containing Turmeric extract
produces a green colour with borax solution.
5. On addition of boric acid a
reddish-brown colour is formed which, on addition of alkalies, changes to
greenish-blue.
6. A piece of filter paper is
impregnated with an alcohol extract, dried, and then moistened with boric acid
solution slightly acidified with hydrochloric acid, and redried. Pink or
brownish-red colour is developed on the filter paper which becomes deep blue on
addition of alkali.
Uses
Turmeric is used as aromatic, antiinflammatory, stomachic,
uretic, anodyne for billiary calculus, stimulant, tonic, car minative, blood
purifier, antiperiodic, alterative, spice, colouring agent for ointments and a
common household remedy for cold and cough. Externally, it is used in the form
of a cream to improve complexion. Dye-stuff acts as a cholagogue causing the
contraction of the gall bladder. It is also used in menstrual pains. Curcumin
has choleretic and cholagogue action and is used in liver diseases. Curcumin is
a nontoxic authorized colour, heat resistant and sensitive to changes in pH.
Curcuminoids have antiphlogistic activity which is due to inhibition of
leukotriene biosynthesis. ar-Turmerone has antisnake venom activity and blocks
the haemorrhagic effect of venom.
Adulteration
The genuine drug is adulterated with the rhizomes of Acorus calamus.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
J.P. Nikhar oil, J.P. Kasantak (Jamuna Pharma), Diabecon, Purian (Himalaya Drug
Company), and Respinova (Lupin Herbal Laboratory).
