Uses of Anticholinesterases
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Cholinergic System And Drugs
In glaucoma: Miotics increase the tone of ciliary muscle (attached to scleral spur) and sphincter pupillae which pull on and somehow improve alignment of the trabeculae so that outflow facility is increased → i.o.t. falls in open angle glaucoma.
USES
1. As miotic
In glaucoma: Miotics
increase the tone of ciliary muscle (attached to scleral spur) and sphincter
pupillae which pull on and somehow improve alignment of the trabeculae so that
outflow facility is increased → i.o.t. falls in open angle glaucoma.
Pilocarpine
is the preferred miotic. The action is rapid and short lasting (4–6 hr); 6–8
hourly instillation is required and even then i.o.t. may fluctuate inbetween.
Diminution of vision, especially in dim light (due to constricted pupil), spasm
of accommodation and brow pain are frequent side effects. Systemic
effects—nausea, diarrhoea, sweating and bronchospasm may occur with higher
concentration eye drops.
Physostigmine
(0.1%) is used only to supplement pilocarpine. Miotics are now 3rd choice
drugs, used only as add on therapy in advanced cases. However, they are
effective in aphakic glaucoma. Pilocarpine (along with other drugs) is used in
angle closure glaucoma as well.
To reverse the effect of mydriatics after refraction testing.
To prevent formation of adhesions between iris and lens or iris
and cornea, and even to break those which have formed due to iritis, corneal
ulcer, etc.—a miotic is alternated with a mydriatic.
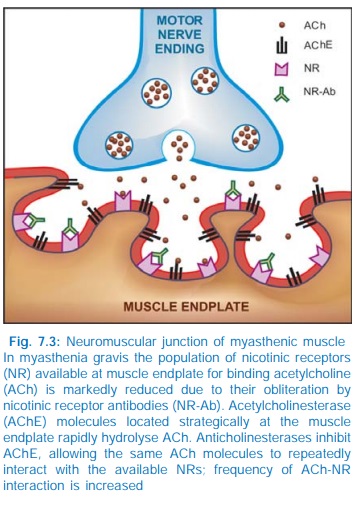
2. Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia
gravis is an autoimmune disorder affecting about 1 in 10,000 population, due to
development of antibodies directed to nicotinic receptors (NR) at the muscle
endplate → reduction in number
of free NM cholinoceptors to 1/3 of normal or less (Fig. 7.3) and
structural damage to the neuromuscular junction → weakness and easy
fatigability on repeated activity, with recovery after rest. Neostigmine and
its congeners improve muscle contraction by allowing ACh released from
prejunctional endings to accumulate and act on receptors over a larger area,
and by directly depolarizing the endplate.
Treatment is usually
started with neostigmine 15 mg orally
6 hourly; dose and frequency is then adjusted according to response. However,
the dosage requirement may fluctuate from time to time and there are often
unpredictable periods of remission and exacerbation. Pyridostigmine is an alternative
which needs less frequent dosing. If intolerable muscarinic side effects are
produced, atropine can be added to block them. These drugs have no effect on
the basic disorder which often progresses; ultimately it may not be possible to
restore muscle strength adequately with antiChEs alone.
Corticosteroids afford considerable
improvement in such cases by their immunosuppressant action. They inhibit
production of NR antibodies and may increase synthesis of NRs. However, their
long term use has problems of its own. Prednisolone 30–60 mg/day induces remission in about 80% of the
advanced cases; 10 mg daily or on alternate days can be used for maintenance
therapy. Other immunosuppressants have also been used with benefit in advanced
cases. Both azathioprine and cyclosporine also inhibit NR-antibody synthesis by
affecting Tcells, but response to the former is slow in onset (takes upto 1
year), while that to the latter is relatively quick (in 1–2 months). Removal of
antibodies by plasmapheresis (plasma
exchange) is another therapeutic approach. Dramatic but short lived improvement
can often be achieved by it in myasthenic crisis.
Myasthenic crisis is characterized by
acute weakness of respiratory
muscles. It is managed by tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.
Generally, i.v. methylprednisolone pulse therapy is given while antiChEs are
withheld for 2–3 days followed by their gradual reintroduction. Most patients
can be weaned off the ventilator in 1–3 weeks. Plasmapheresis hastens recovery.
Thymectomy produces gradual
improvement in majority of cases.
Even complete remission has been obtained. Thymus may contain modified muscle
cells with NRs on their surface, which may be the source of the antigen for
production of antiNR antibodies in myasthenic patients.
Overtreatment with antiChEs also produces weakness by causing persistent depolarization
of muscle endplate: this is called cholinergic
weakness. Late cases with high antiChE
dose requirements often alternately
experience myasthenic and cholinergic weakness and these may assume crisis proportions.
two types of weakness require opposite treatments. They can be differentiated
by edrophonium test—

Diagnostic tests for myasthenia gravis
Ameliorative
test: Edrophonium 2–10 mg
injected slowly i.v. improves
muscle strength only in myasthenia gravis and not in other muscular
dystrophies.
Provocative
test: Myasthenics are highly
sensitive to dtubocurarine; 0.5 mg
i.v. causes marked weakness in them but is ineffective in nonmyasthenics. This
test is hazardous: facilities for positive pressure respiration must be at hand
before performing it.
Demonstration of anti-NR antibodies in plasma or muscle biopsy
specimen is a more reliable test.
Postoperative Paralytic
Ileus/Urinary Retention This can be relieved by 0.5–1 mg s.c. neostigmine,
provided no organic obstruction is present.
Postoperative Decurarization Neostigmine 0.5–2.0 mg i.v., preceded by atropine to block
muscarinic effects, rapidly reverses muscle paralysis induced by competitive
neuromuscular blockers.
Cobra Bite Cobra venom has a
curare like neurotoxin. Though
specific antivenom serum is the primary treatment, neostigmine + atropine
prevent respiratory paralysis.
Belladonna Poisoning Physostigmine 0.5–2 mg i.v.
repeated
as required is the specific antidote for poisoning with belladonna or other anticholinergics.
It penetrates bloodbrain barrier and antagonizes both central and peripheral
actions. However, physostigmine often itself induces hypotension and
arrhythmias; is employed only as a last resort. Neostigmine does not block the
central effect, but is less risky.
Other Drug Overdosages Tricyclic antidepressants,
phenothiazines and many antihistaminics have additional anticholinergic property.
Overdose symptoms and coma produced by these drugs are partly antagonized by
physostigmine. It also appears to have a modest nonspecific arousal effect in
CNS depression produced by diazepam or general anaesthetics, but is rarely
used.
Alzheimer’s Disease Characterized by progressive dementia, is a neurodegenerative disorder, primarily affecting cholinergic neurones in the brain. Various measures to augment cholinergic transmission in the brain have been tried. The relatively cerebroselective antiChEs tacrine, rivastigmine, donepezil and galantamine have been approved for clinical use.
Related Topics
