Biosynthesis of Carbohydrates
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Carbohydrates and Derived Products
Carbohydrates are products of photosynthesis, a biologic process that converts electromagnetic energy into chemical energy. In the green plant, photosynthesis consists of two classes of reactions. One class comprises the so-called light reactions that actually convert electromagnetic energy into chemical potential.
BIOSYNTHESIS OF CARBOHYDRATES
Production of Monosaccharides by Photosynthesis
Carbohydrates are products of photosynthesis, a biologic
process that converts electromagnetic energy into chemical energy. In the green
plant, photosynthesis consists of two classes of reactions. One class comprises
the so-called light reactions that actually convert electromagnetic energy into
chemical potential. The other class consists of the enzymatic reactions that
utilize the energy from the light reactions to fix carbon dioxide into sugar.
These are referred to as the dark reactions. The results of both of these types
of reactions are most simply summarized in the following equation:

Although this equation summarizes the overall relationships
of the reactants and products, it gives no clue as to the nature of the
chemical intermediates involved in the process. The elucidation of the
reactions by which carbon dioxide is accepted into an organic compound and
ultimately into sugars with regeneration of the carbon dioxide acceptor was a
major achievement in biosynthetic research. The pathway of carbon in
photosynthesis, as worked out primarily by Calvin and coworkers, is presented
in Figure below.
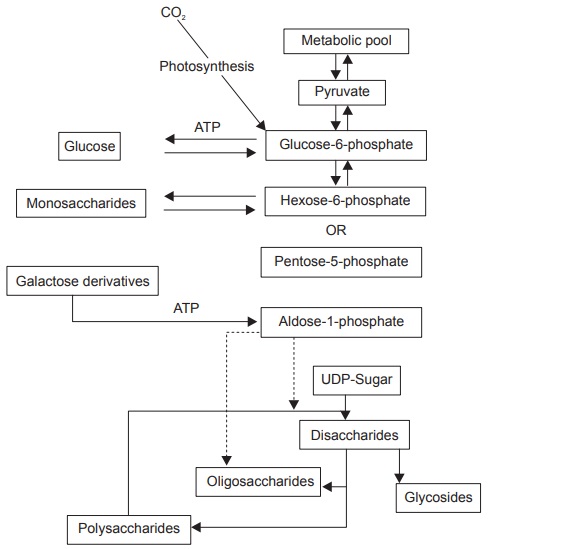
Carbohydrate biosynthesis
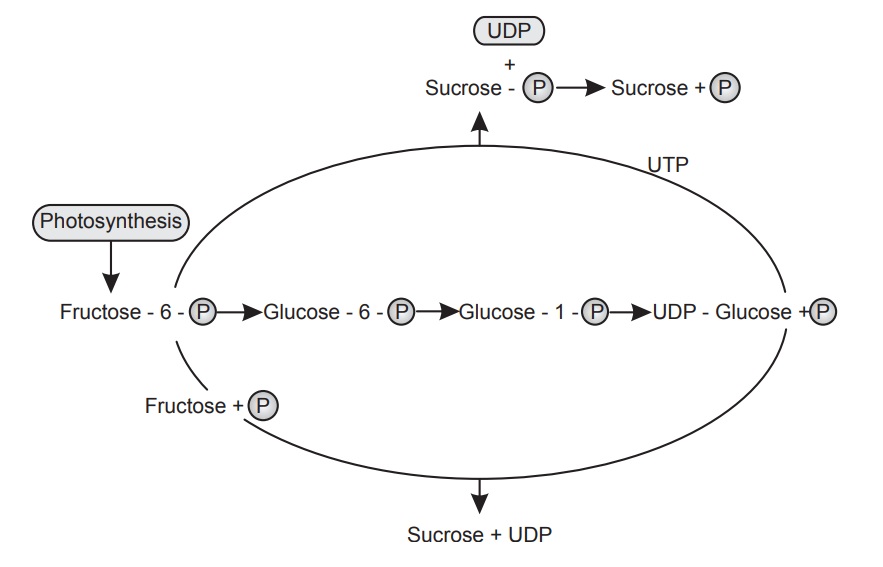
Production
of sucrose
Sucrose is of considerable metabolic importance in higher
plants. Studies have shown that sucrose is not only the first sugar formed in
photosynthesis but also the main transport material. Newly formed sucrose is,
therefore, probably the usual
precursor for polysaccharide synthesis. Although an alternative pathway
consisting of a reaction between glucose 1-phosphate and fructose is
responsible for sucrose production in certain microorganisms, the biosynthesis
of this important metabolite in higher plants apparently occurs as shown in
Figure below.
Fructose 6-phosphate, derived from the photosynthetic cycle,
is converted to glucose 1-phosphate, which, in turn, reacts with UTP to form
UDP-glucose. UDP-glucose either reacts with fructose 6-phosphate to form first
sucrose phosphate and ultimately sucrose, or with fructose to form sucrose
directly. Once formed, the free sucrose may either remain in situ or may be
translocated via the sieve tubes to various parts of the plants. A number of reactions, for example, hydrolysis by
invertase or reversal of the synthetic sequence, convert sucrose to
monosaccharides from which other oligosaccharides or polysaccharides may be
derived.