Ashwagandha
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Alkaloids
It consists of the dried roots and stem bases of Withania somnifera Dunal, belonging to family Solanaceae.
ASHWAGANDHA
Synonyms
Withania root. Ashwagandha, Clustered Wintercherry.
Biological Source
It consists of the dried roots and stem bases of Withania somnifera Dunal, belonging to family Solanaceae.
Geographical Source
Withania is widely distributed from southern Europe to India
and Africa.
History
The use of ashwagandha in Ayurvedic medicine extends back
over 3,000–4,000 years to the teachings of an esteemed rishi (sage) Punarvasu
Atriya. It has been described in the sacred texts of Ayurveda, including the
Charaka and Sushruta Samhitas where it is widely extolled as a tonic especially
for emaciation in people of all ages including babies, enhancing the
reproductive function of both men and women.
Cultivation and Collection
Withania somnifera are propagated by division, cuttings
or seed. Seed is the best way to
propagate them. Seed sown on moist sand will germinate in 14–21 days at 20°C. Withania somnifera need full sun to partial shade with a well-drained slightly alkaline soil mix. Plants do
best when the soil pH is 7.5–8.0. Soil mix consisting of two parts sandy loam
to one part sand will to better. The plants are allowed to dry thoroughly in
between waterings. In containers, too much water causes root rot. Plants are
fertilized once during the year with a balanced fertilizer.
Characteristics
A low lying plant, often reaching only 1–2 ft, but
occasion-ally 6 ft. It is a perennial, but can be grown as an annual. Plant and
fruits resemble its relatives the ground cherry and Chinese lantern. Young
roots are straight, unbranched and conical and in pieces of different lengths.
Root thickness varies according to age and usually it is 5–12 mm below crown.
Outer surface is buff to yellow and longitudinally wrinkled. Taste is bitter and
mucilaginous.
Microscopy
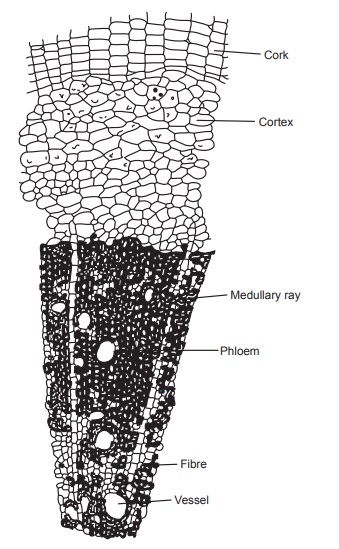
Transverse section of root shows cork exfoliated or crushed;
when present isodiamatric and nonlignified; cork cambium of two to four
diffused rows of cells; secondary cortex about twenty layers of compact
parenchymatous cells; phloem consists of sieve tubes, phloem parenchyma,
companion cells, cambium shows four to five rows of tangentially elongated
cells; secondary xylem hard forming a closed vascular ring separated by
multiseriate medullary rays and a few xylem parenchyma.
Chemical Constituents
The plants contain the alkaloid withanine as the main
constituent and somniferine, pseudowithanine, tropine and pseudotropine,
hygrine, isopellederine, anaferine, anahygrine and steroid lactones. The leaves
contain steroid lactone, commonly known as withanolides.

Uses
All plant parts are used including the roots, bark, leaves,
fruit and seed are used to treat nervous disorders, intestinal infections and
leprosy. Ashwagandha is one of the most widespread tranquillizers used in
India, where it holds a position of importance similar to ginseng in China. It
acts mainly on the reproductive and nervous systems, having a rejuvenative
effect on the body, and is used to improve vitality and aid recovery after
chronic illness. It is also used to treat nervous exhaustion, debility,
insomnia, wasting diseases, failure to thrive in children, impotence,
infertility; multiple sclerosis, etc. Externally it has been applied as a
poultice to boils, swellings and other painful parts. Withania is considered as
an adaptogen and so is used in number of diseases.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Abana, Geriforte, Mentat, Mentat syrup, Reosto, Tentex forte, AntiStress
Massage Oil, Nourishing Baby Oil, Nourishing Skin Cream, Anxocare, Galactin
Vet, Geriforte Aqua, Geriforte Vet, Immunol, Speman forte Vet, Tentex forte
Vet, Ashvagandha tablet (Himalaya Drug Company), Balarishta (Baidyanath),
Aswagandha tablet (BAPS AMRUT).
