Opium
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Alkaloids
Opium is the air dried milky latex obtained by incision from the unripe capsules of Papaver somniferum Linn, or its variety P. album Decand., belonging to family Papaveraceae.
OPIUM
Synonyms
Crude Opium; Raw Opium; Gum Opium; Afim; Post.
Biological Source
Opium is the air dried milky latex obtained by incision from
the unripe capsules of Papaver somniferum
Linn, or its variety P. album Decand.,
belonging to family Papaveraceae.
Opium is required to contain not less than 10% of morphine
and not less than 2.0% of codeine. The thebaine content is limited to 3%.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in Turkey, Russia, Yugoslavia, Tasmania,
India, Pakistan, Iran, Afghanistan, China, Burma, Thailand and Laos. In India,
Opium is cultivated in M.P. (Neemuch) and U.P. for alkaloidal extraction and
seed production.
History
The cultivation of opium dates back to 3400 B.C. in
Mesopotamia and by 1300 B.C. Egyptians began the cultivation of opium thebaicum.
Hippocrates ‘the father of medicine’, (460–357 B.C.) prescribed drinking the
juice of the white poppy mixed with the seed of nettle and also acknowledged
its use as narcotic and styptic in internal diseases. It was Alexander the
Great, who introduced opium to India and Persia. During the 17th century
tobacco smoking was introduced in China, which resulted in its extensive. In
1800 control on opium supply and prices was brought and in 1805 Friedrich W.
Seiturner (German pharmacist) isolated and identified the chief chemical
constituent of opium. The compound isolated was named morphium (morphine) after
Morpheus, the god of dreams. Eventually many other constituents like codeine
(1832) and papaverine (1848) were also isolated and identified. Due to the
uncontrolled use of opium in china (late 18th century) the imperial court had
to ban its use. The United States in 19th century made easy availability of the
opium preparations and the ‘patent medicines’. Later on during the war, the
Union Army were provided with enough amount of opium pills, laudanum, morphine
sulphate, etc., which made opium addiction known as the ‘army disease or the
‘soldier’s disease’.
By 1870s, substitute for morphine by acetylating morphine
were prepared and in 1898 a German company manufactured 3, 6-diacetylmorphine
(Heroin) in bulk quantity. In December 1914, Harrison Narcotics Act which
called for control of each phase of the preparation and distribution of
medicinal opium, morphine, heroin, cocaine, and any new derivative with similar
properties, was enforced by the United States Congress. The Federal Controlled
Substances Act of 1970 is the redefined act of the Har-rison Act. In 1999,
opium was declared as the Bumper crop of Afghanistan by producing 75% of
world’s heroin. In December 2002 the U.K. government under the health plan,
will make heroin available free on National Health Service to all those with a
clinical need for it.
Cultivation and Collection
Opium is cultivated under license from the government. Its
seeds are sown in October or March in alluvial soil. After germination of seeds
snow falls. In spring the thin plant attains the height of 15 cm. Fertilizers
are used for better crop. The poppy of first crop blossoms in April or May and
the capsule mature in June or July. When the capsules are about 4 cm in
diameter, the colour changes from green to yellow; they are incised with a
knife about 1 mm deep around the circumference between midday and evening. The
knife, known as a ‘nushtur’ bears narrow iron spikes which are drawn down the
capsule to produce several longitudinal cuts. The incision must not penetrate
into the interior of the capsule otherwise latex will be lost. The latex tube
opens into one another. The latex, which is white in the beginning, immediately
coagulates and turns brown. Next morning it is removed by scrapping with a
knife and transferred to a poppy leaf. Each capsule is cut several times at
intervals of two or three days. After collection the latex is placed in a
tilted vessel so that the dark fluid which is not required may drain off. By
exposure to air the opium acquires a suitable consistency for packing. The
dried latex is kneaded into balls, wrapped in poppy leaves and dried in shade.
The principal commercial varieties of Opium are Turkish Opium, Indian Opium,
Chinese Opium, Yugoslavian Opium and Persian Opium.
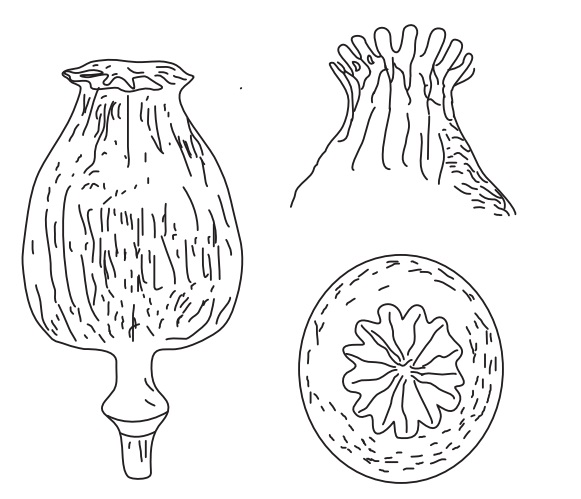
Characteristics
Opium occurs in rounded or flattened mass which is 8–15 cm
in diameter and weighing from 300 g to 2 kg each. The external surface is pale
or chocolate-brown, texture is uniform and slightly granular. It is plastic
like when fresh and turns hard and brittle after sometime. Fragment of poppy
leaves are present on the upper surface. Internal surface is coarsely
granular, reddish-brown, lustrous; odour is characteristic; taste is bitter and
distinct. Opium is intended only as a starting material for the manufacture of
galenical preparations and is not dispensed as such.
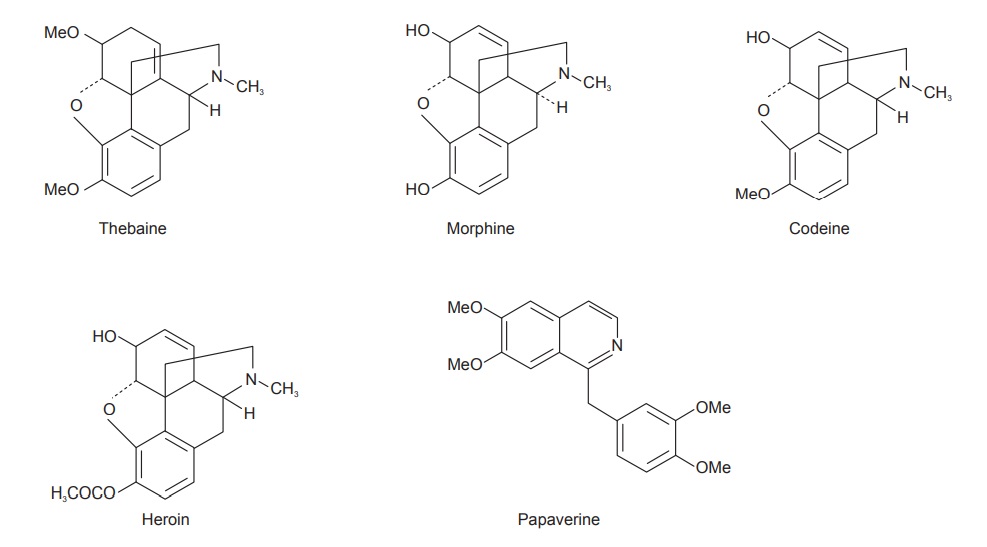
Chemical Constituents
Opium contains about 35 alkaloids among which morphine
(10–16%) is the most important base. The alkaloids are combined with meconic
acid. The other alkaloids isolated from the drug are codeine (0.8–2.5%),
narcotine, the-baine (0.5–2%). noscapine (4–8%), narceine and papaverine
(0.5–2.5%). Morphine contains a phenanthrene nucleus. The different types of
alkaloids isolated are:
1. Morphine
Type: Morphine,
codeine, neopine, pseudo or oxymorphine,
thebaine and porphyroxine. Morphine consists of alkaloids which has
phenanthrene nucleus whereas those of the papaverine group has
benzyliso-quinoline structure. Protopine and hydrocotamine are of different
structural types. The morphine molecule has both a phenolic and an alcoholic
hydroxyl group and acetylated form is diacetyl morphine or heroin. Codeine is
ether of morphine (methyl-morphine). Other morphine ethers which are used
medicinally are ethylmorphine and pholcodine.
2. Phthalide
Isoquinoline Type: Hydrocotarnme,
narcotoline, 1-narcotine, noscapine,
oxynarcotine, narceine, and 5’-O-demethyl-narcotine.
3. Benzyl
Isoquinoline Type: Papaverine,
dl-laudanine, lau-danidine, codamine and laudanosine.
4. Cryptopine
Type: Protopine,
cryptopine.
5. Unknown
Constituents:
Aporeine, diodeadine, meconidine, papaveramine and lanthopine.
The
drug also contains sugars, sulphates, albuminous compounds, colouring matter
and moisture. In addition to these anisaldehyde, vanillin, vanillic acid, β-hydroxystyrene, fumaric acid, lactic acid, benzyl alcohol,
2-hydroxycinchonic acid, phthalic acid, hemipinic acid, meconin and an odorous
compound have also been reported.
Chemical Tests
Aqueous extract of Opium with FeCl3 solution
gives deep reddish purple colour which persists on addition of HCl. It
indicates the presence of meconic acid.
Morphine gives dark violet colour with conc. H2SO4
and formaldehyde.
Uses
Opium and morphine have narcotic, analgesic and sedative
action and used to relieve pain, diarrhoea dysentery and cough. Poppy capsules
are astringent, somniferous, soporific, sedative and narcotic and used as
anodyne and emollient. Codeine is mild sedative and is employed in cough
mixtures. Noscapine is not narcotic and has cough suppressant action acting as
a central antitussive drug. Papaverine has smooth muscle relaxant action and is
used to cure muscle spasms. Opium, morphine and the diacetyl derivative heroin,
cause drug addiction.
