Classification of Sedatives and Hypnotics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Sedatives and Hypnotics
Sedatives and hypnotics are classified on the basis of their chemical structure, as follows:
CLASSIFICATION Sedatives and hypnotics are classified on the basis of their chemical structure, as follows: Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Acyclic hypnotics containing nitrogen Cyclic hypnotics containing nitrogen Alcohols and aldehydes Acetylene derivatives Miscellaneous Inorganic salts Acids and esters Antihistaminic and anticholinergic agents Suphones Plant extracts Endogenous substances Other opioids: morphine, pethidine Neuroleptics: chlorpromazine, triflupromazine 8. Newer agents Barbiturates are further classified on the basis of duration of their action. a. Long-acting barbiturates (6 h or more than 6 h) b. Intermediate-acting barbiturates (3–6 h) c. Short-acting barbiturates (less than 3 h) d. Ultra short-acting barbiturates (15 min) Triazolo benzodiazepines a. Urethanes b. Ureides c. Carbamates d. Amides a. Piperidinediones Inorganic salts KBr, magnesium sulphate Acids and esters Tryptophan, 5-hydroxy tryptophan Etomidate c. Antihistamines and anticholinergics d. Sulphones Toxic-not used e. Plant extracts of Radix valerianae Rauwolfia serpentina Avana sativa Glandula lupuli f. Endogenous substances: peptides1. Barbiturates
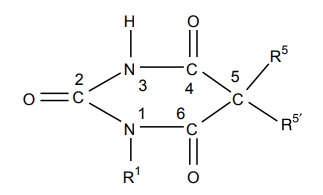
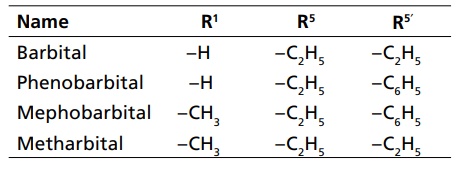
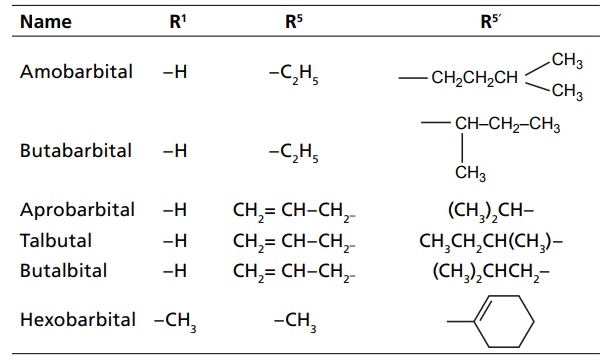
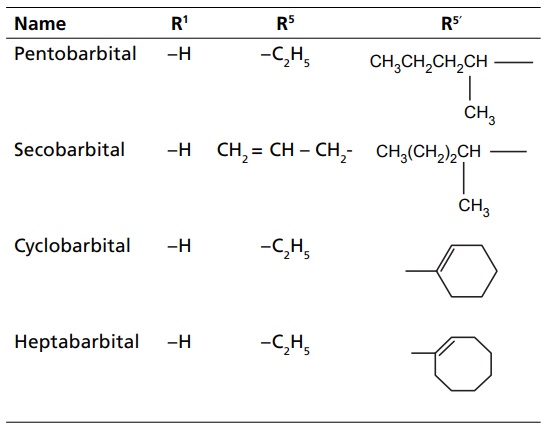
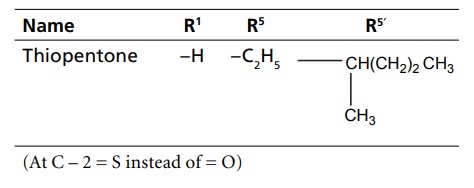
2. Benzodiazepines
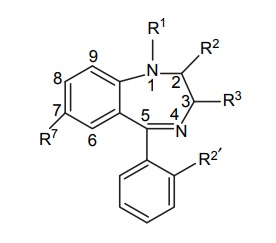
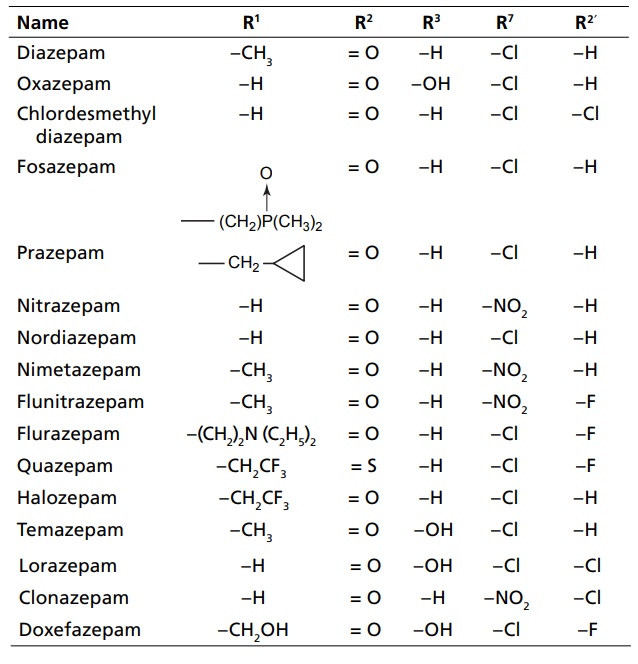
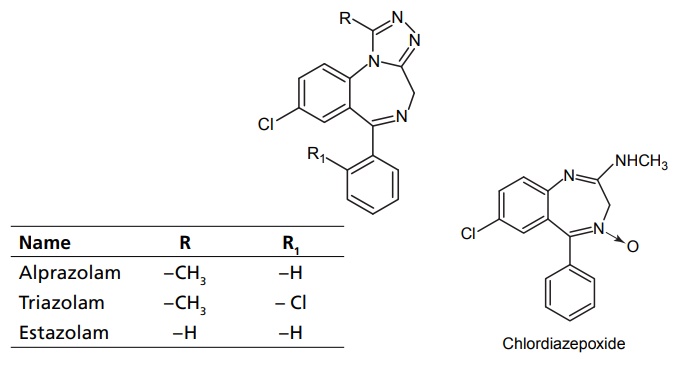
3. Acyclic hypnotics containing nitrogen (acyclic ureides)
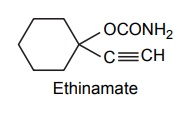
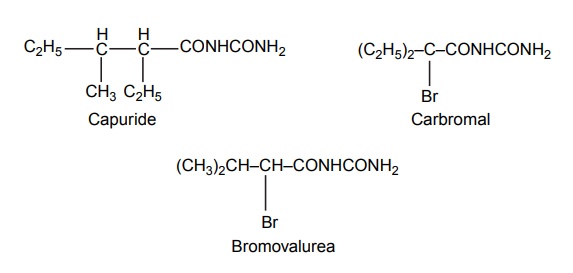
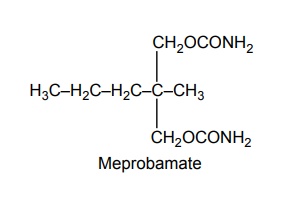
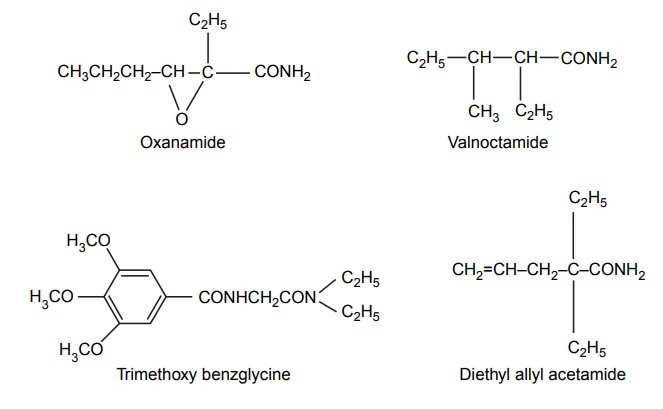
4. Cyclic hypnotics containing nitrogen
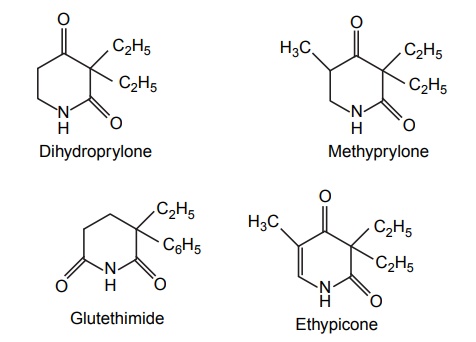
b. Quinazolinones
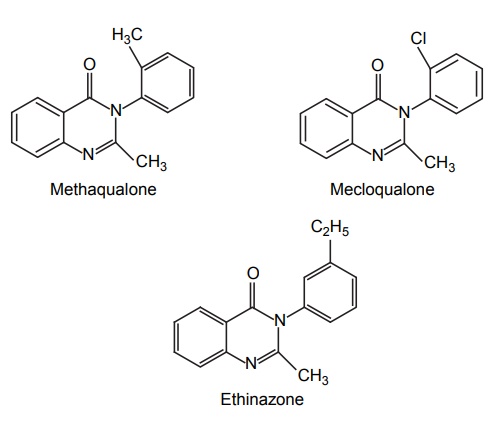
5. Alcohols and aldehydes
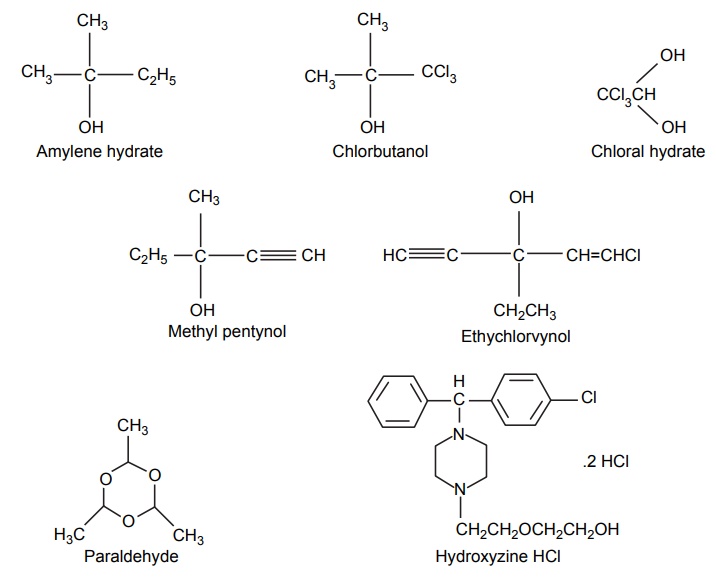
6. Actylene derivatives
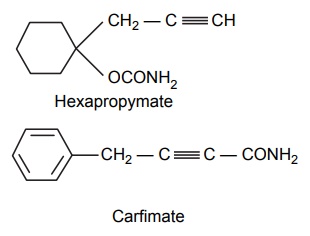
7. Miscellaneous
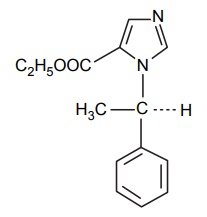
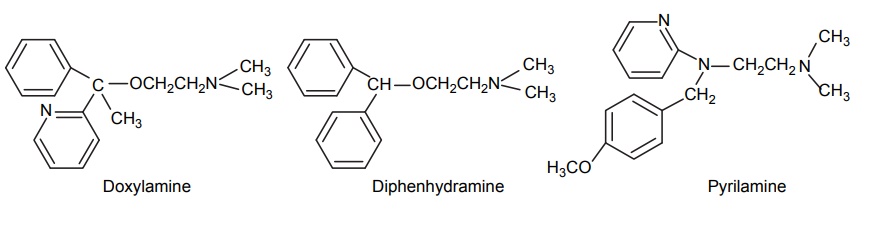
8. Newer agents
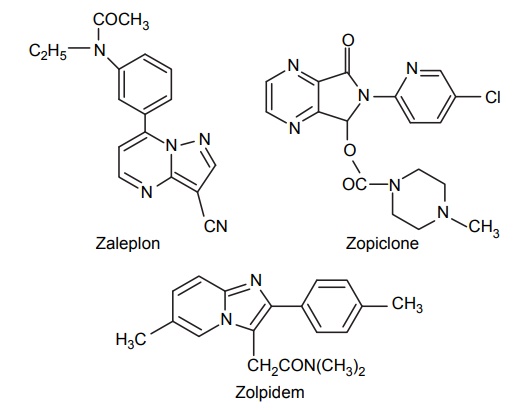
Related Topics
