Alcohols and Aldehydes
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Sedatives and Hypnotics
Mode of action: These drugs elicit the action and is similar to the mechanism of barbiturates. These are general CNS depressants, which produce profound hypnosis.
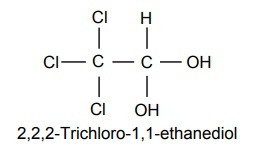
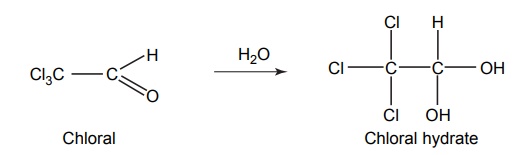
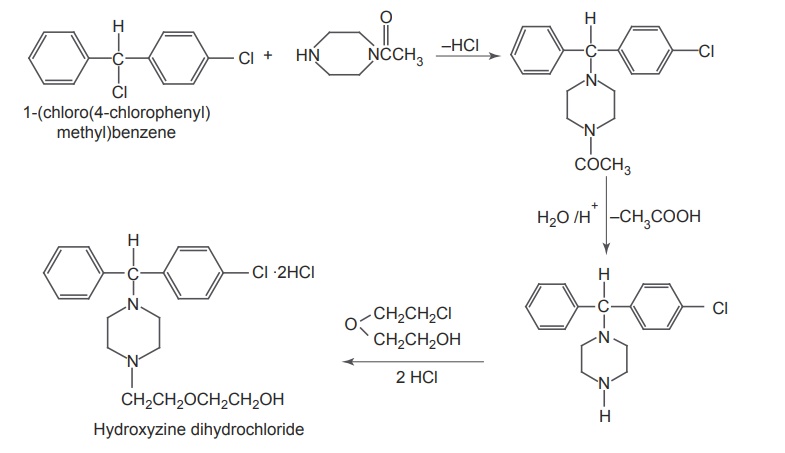
V. Alcohols and Aldehydes Mode of action: These drugs elicit the action and is similar to the mechanism of barbiturates. These are general CNS depressants, which produce profound hypnosis. Metabolism: These are metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme. Chloralhydrate undergoes oxidation to chloral and then to an inactive metabolite, trichloroacetic acid, via aldehyde dehydrogenase, which also is extensively metabolized to aryl glucuronides via conjugation with glucuronic acid and then excreted in urine. Synthesis Properties and uses: Colourless, transparent crystals, very soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. Used principally for the short-term treatment of insomnia, it is used pre-operatively to allay anxiety and to induce sedation/sleep. It is used post-operatively as an adjuvant to opiates and other analgesics to control pain. It has also been used to produce sleep prior to electroencephalogram (EEG) evaluations. It is also effective in reducing anxiety associated with withdrawal of alcohol and other drugs, such as opiates and barbiturates. Assay: Dissolve the sample in water and add 1 M sodium hydroxide solution. Allow to stand for exactly 2 min and titrate with 0.5 M sulphuric acid, using phenolphthalein solution as indicator. Titrate the neutralized solution with 0.1 M silver nitrate, using potassium chromate solution as an indicator. Storage: It should be stored in well closed airtight container. Dose: The usual adult dose is 500–1000 mg for hypnotic and 250 mg for sedative. Synthesis Properties and uses: It also possesses muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant properties apart from CNS depressant action. Adverse effects include suppression of REM sleep, ataxia, and hypotension. Dose: The usual adult dose is 500–1000 mg hypnotic and 100–200 mg sedative. Synthesis Properties and uses: It is a colourless or slightly yellow transparent liquid. It solidifies on cooling to form a crystalline mass. Miscible with alcohol and with essential oils, soluble in water, but less soluble in boiling water, it is exclusively used in the management of hospitalized patients undergoing alcohol withdrawal. Its CNS depressant activity resembles that of alcohol and chloral hydrates. Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light. If the substance has solidified, the whole contents of the container must be liquefied before use. Dosage forms: Paraldehyde injection B.P. 2-(2-(4-[(4-Chloro phenyl) phenyl methyl)-1-Piperazinyl]-ethoxy) ethanol dihydrochloride Synthesis Properties and uses: It is a hygroscopic crystalline powder, white or almost white in colour, freely soluble in water and in alcohol, very slightly soluble in acetone. It is useful in psychosomatic disturbances, nervous tension, and anxiety. Assay: Dissolve the sample in 10 ml of anhydrous acetic acid and 40 ml of acetic anhydride. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid and determine the endpoint potentiometrically. Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light. Dose: Adult: I.M. injection as the hydrochloride in doses of 25–100 mg every 4–6 h; Children: 1 mg per kg body weight I.M for pre and postoperative sedation.1. Chloral hydrate (Noctec)
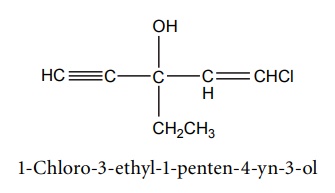
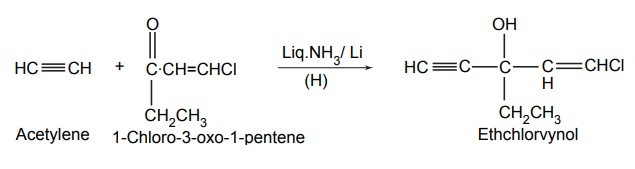
2. Ethchlorvynol (Placidyl)
3. Paraldehyde
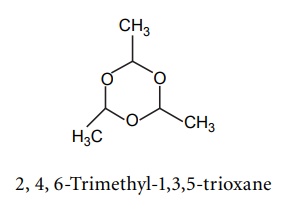
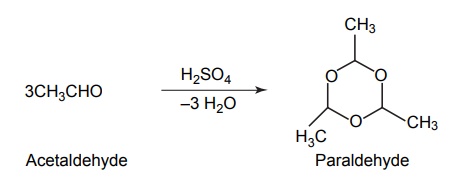
4. Hydroxyzine hydrochloride

Related Topics
