Dioscorea
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Glycosides
Dioscorea is the dried rhizome of several species of Dioscorea like D. villosa, D. prazeri Prain and Burk; D. composite; D. spiculiflora; D. deltoidea and D. floribunda, belonging to family Dioscoreaceae.
DIOSCOREA
Synonym
Yam.
Biological Source
Dioscorea is the dried rhizome of several species of Dioscorea like D. villosa, D. prazeri Prain and Burk; D. composite; D. spiculiflora;
D. deltoidea and D. floribunda, belonging
to family Dioscoreaceae.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in North America, Mexico, India
(Hima-layas from Kashmir and Punjab up to an altitude of 3,000 m), Nepal and
China.
Cultivation and Collection
It is a perennial climber growing to 3 m. The plant prefers
sandy, loamy and clay soils and requires well-drained soil. The plant prefers
acid, neutral and basic (alkaline) soils. It can grow in semishade or no shade.
It requires moist soil. It can be cultivated in three methods, by sowing seeds
or stem cuttings or by tubercles. Seeds are sown in the month of March to April
in a sunny position in a warm green house and only just covered. It germinates
in one to three weeks at 20°C. The seedlings are taken out as soon as they are
large enough to handle and grown on in a green house for their first year.
Transplanted in late spring as the plant comes into new growth. Basal stem
cuttings are done in the summer. Division is done in the dormant season, never
when in growth. The plant will often produce a number of shoots, the top 5–10
cm of the root below each shoot can be potted up to form a new plant whilst the
lower part of the root can possibly be eaten.
Tubercles (baby tubers) are formed in the leaf axils. These
are harvested in late summer and early autumn when about the size of a pea and
coming away easily from the plant. They should be potted up immediately in
individual pots in a greenhouse or cold frame and transplanted out in early
summer when in active growth.
Characteristics
The colour of the plant is slightly brown, odourless with
bitter taste and vary in size.
Microscopy
The transverse section of the drug when observed under the
microscope shows the absence of epidermis, the cork is made up of few layers
and next to cork it has corical parenchymatous tissue with thin wall. The major
part of the drug is occupied by stele and consists of collateral type of
fibrovascular bundles. The drug has indistinguishable endodermis and pericycle.
Chemical Constituents
The roots contain diosgenin (4–6%) a steroidal sapogenin and
its glycoside smilagenin, epismilagenin and beta isomer yammogenin. It also
contains sapogenase (enzyme), phenolic compounds and starch (75%).
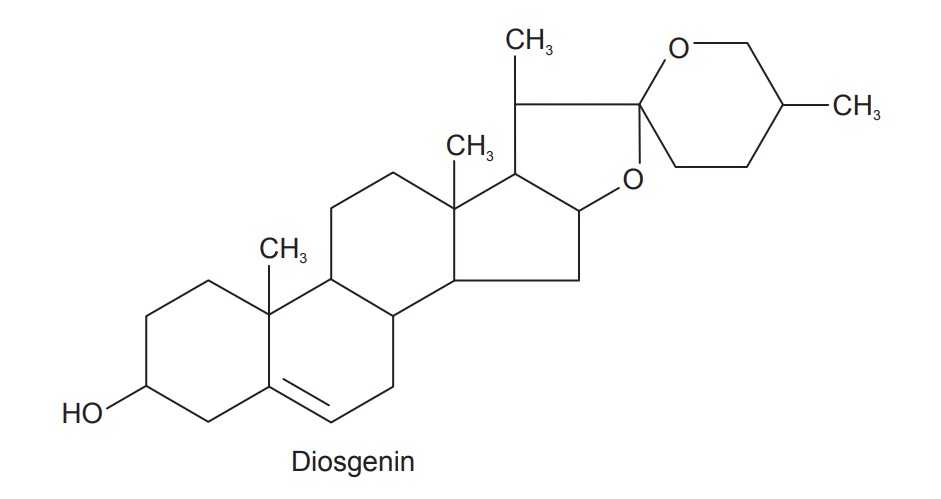
Uses
It is a main source of diosgenin. This is widely used in
modern medicine in order to manufacture progesterone and other steroid drugs.
These are used as contraceptives and in the treatment of various disorders of
the genitary organs as well as in a host of other diseases such as asthma and
arthritis.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Explode (Herbotech Pharmaceuticals).
