Strophanthus
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Glycosides
Strophanthus consists of dried ripe seeds of Strophanthus kombe Oliv. deprived of their awns belonging to family Apocynaceae.
STROPHANTHUS
Synonyms
Kombe Seeds, Strophanti Semina, Semen Strophanthi,
Strophanthus Seeds.
Biological Source
Strophanthus consists of dried ripe seeds of Strophanthus kombe Oliv. deprived of their awns belonging to family Apocynaceae.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in East Africa near lakes of Nyasaland
and Tanganyika, Portuguese, Cameroon. The tribal are using this seeds as arrow
poison.
Cultivation and Collection
The plants are large, woody climbers, climbing on the large
trees in the forests of Africa. Fruit consists of two divergent follicles which
are dehiscent and many seeded. Each follicle is 30 cm long, 2.5 cm broad,
tapering both at the apex and base. Mature and ripe fruits are collected in the
month of June–July. After collection epicarp and fleshy mesocarp are removed
and seeds separated from yellow-brown leathery endocarp and awns. Seeds are
washed and dried. The seeds are derived from anatropous ovules.
Characteristics
The name Strophanthus
is derived from the Greek strophos (a
twisted cord or rope) and anthos (a
flower), thus expressing the chief peculiarity of its appearance, the limb of
the corolla being divided into five, long, tail-like segments.
The official description of the seeds is lance-ovoid,
flat-tened and obtusely edged; from 7 to 20 mm in length, about 4 mm in breadth
and about 2 mm in thickness; externally of a light fawn colour with a distinct
greenish tinge, silky lustrous form, a dense coating of flat-lying hairs (S. Kombe) bearing on one side a ridge
running from about the centre to the summit; fracture short and somewhat soft,
the frac-tured surface whitish and oily; odour heavy when the seeds are crushed
and moistened; taste very bitter.
Microscopy
Epidermis consists of elongated, polygonal, tabular cells
and lignified covering trichomes. Next to epidermis collapsed layer of
parenchyma cells are present that contain calcium oxalate crystals. Thin walled
endosperm contains aleurone grains and fixed oil.
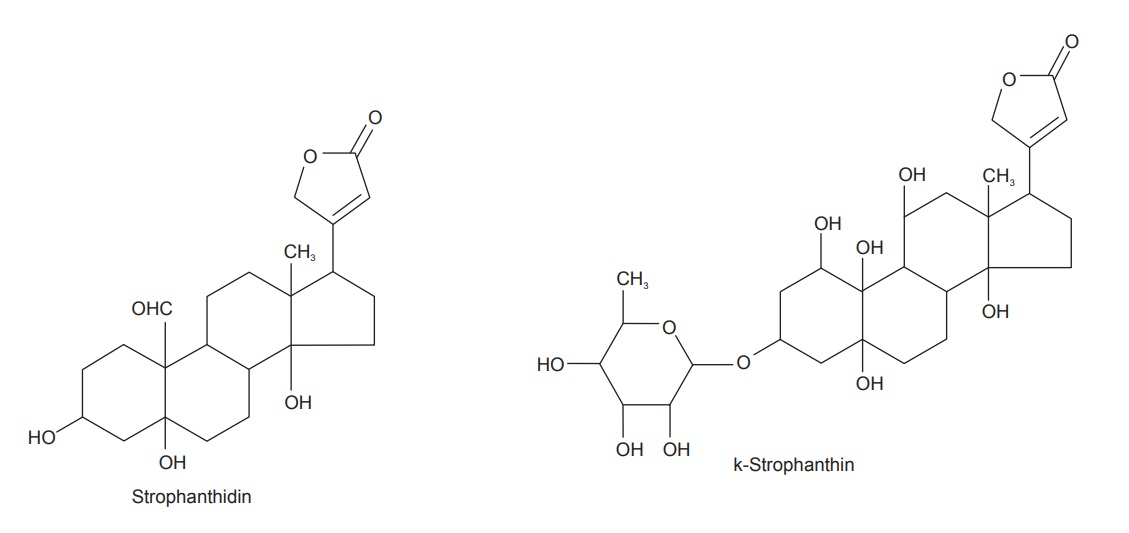
Chemical Constituents
The drug contains 8–10% cardiac glycosides known as
k-strophanthin. k-strophanthin is a mixture of three gly-cosides, cymarin,
k-strophanthin P and k-strophanthoside, which differ only through attached
sugars and on hydrolysis yields same aglycone strophanthidin. It contains a
sugar cymarose that is methoxy digitoxose which gives positive reaction for
Keller–Killiani test. The drug also contains mucilage, resin, fixed oil,
choline, trigonelline, and kombic acid—an acid saponin.
Uses
The use of strophanthus in medicine is for its influence on
the circulation, especially in cases of chronic heart weakness. As its action
is same as that of digitalis, it is often useful as an alternative or adjuvant
to the drug. Believed to have greater diuretic power, it is esteemed of greater
value in cases complicated with dropsies. Unlike digitalis it has no cumulative
property.
Substituents and Adulterants
The S. kombe is
commonly adulterated with S. hispidus, S.
nicholsoni, S. gratus, S. courmontii, S.
emini, S. sarmentosus, etc.
S. hispidus has a shape, colour, similar to that
of the S. kombe, it consist of k- strophanthin. S. nicholsoni has a whitish
seed; the trichomes form a tangled surface covering. The calcium oxalates are
absent in both embryo and the seed coats. S.
gratus are brown in colour, and has a glabrous appearance to the naked
eyes. It reveals the presence of small warty trichomes when observed under the
microscope. S. courmontii has a brownish tinge and has a similar character to that of the genuine drug. It can be
distinguished due to its small size, lanceolate shape and less bitter taste.
