Ginkgo
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Glycosides
The leaves of Ginkgo are obtained from the dioeceous tree Ginkgo biloba, belonging to family Ginkgoaceae.
GINKGO
Biological Source
The leaves of Ginkgo are obtained from the dioeceous tree Ginkgo biloba, belonging to family
Ginkgoaceae.
Geographical Source
It is a native to China and Japan and cultivated
ornamentally in many temperate regions.
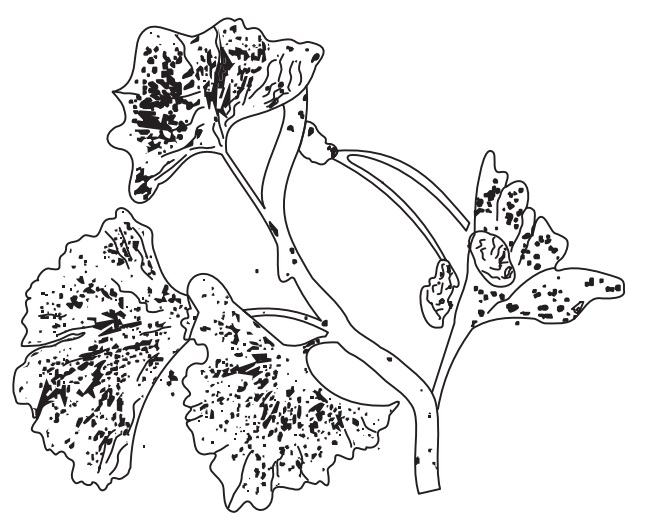
Characteristics
The leaves are bilobed, each lobe being triangular in
outline with a fine radiating, fan-like venation. The leaf is glabrous,
petiolate and has an entire margin.
Chemical Constituents
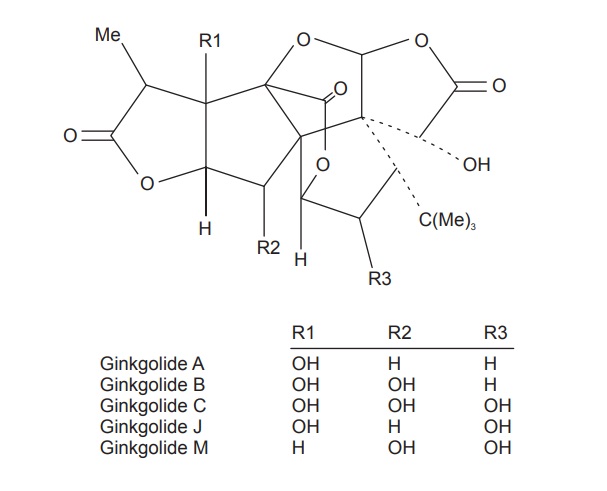
The diterpene lactones and flavonoids possess therapeutic
activity. Five diterpene lactones (ginkgolides A, B, C, J, M ) have been
characterized; these have a cage structure involving a tertiary butyl group and
six 5-membered rings including a spirononane system; a tetrahydrofuran moiety
and three lactonic groups. These compounds are platelet-activating factor (PAF)
antagonists and as they do not react with any other known receptor, their
effect is very specific. A tertiary butyl group is present in the sesquiterpene
bilo-balide; no PAF-antagonist activity has been demonstrated for this
compound.
About 40 flavonoids have now been isolated from the leaves
including glycosides of kaempferol, quercetin and isorhamnetin derivatives. The
tree also synthesizes a number of biflavonoids based on amentoflavone.
Uses
Ginkgo is used as an antiasthmatic and bronchodilator.
Extracts of the leaf containing selected constituents are used for improving
peripheral and cerebral circulation in those elderly with symptoms of loss of
short-term memory, hearing and concentration; it is also claimed that vertigo,
headaches, anxiety and apathy are cured.
