Nonsedative H1-antihistamines (H1-antagonists)
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antihistamines
Antihistamines - > Nonsedative H1-antihistamines (H1-antagonists) - > 1. Cetirizine (Zirtin, Cetin, Cetzine) 2. Loratadine (Alaspan, Lorfast) 3. Epinastine 4. Rocastine - Synthesis and Drug Profile
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Nonsedative H1-antihistamines (H1-antagonists)
1. Cetirizine (Zirtin, Cetin, Cetzine)
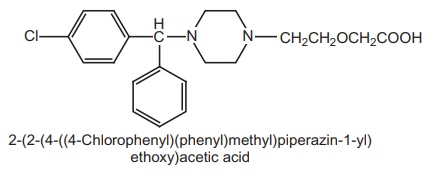
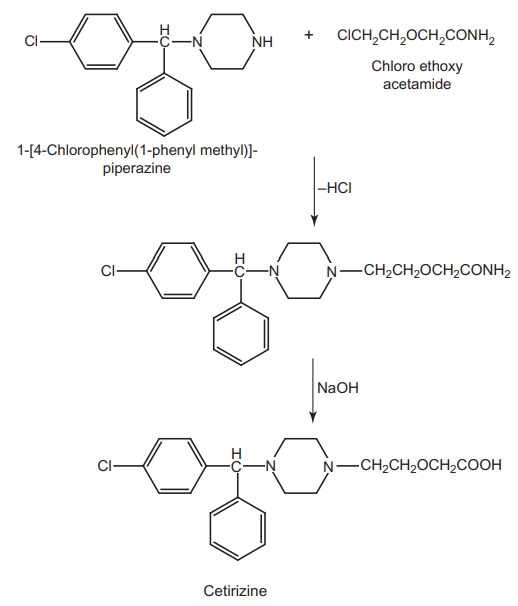
Synthesis
Route I. From: 1-[4-Chlorophenyl
(1-phenylmethyl)]-piperazine
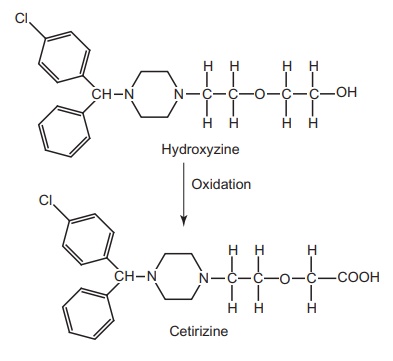
Route II. From: hydroxyzine
Cetirizine
is an acid metabolite formed by the oxidation of primary alcohol of
antihistamine hydroxyzine.
Properties and uses: Cetirizine hydrochloride is a white powder,
soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and methylene chloride. This
is the principal metabolic product of hydroxyzine, the polar acid group
prevents its penetration into the CNS. It is used as an antihistamine to treat
various allergic conditions. Cetrizine is one of the most widely prescribed
H1-antihistamines. It is highly selective in its interaction with various
hormonal binding sites and highly potent as well. Other effects of this drug
include fatigue, dry mouth, pharyngitis, and dizziness.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of water and acetone (1:7) and
titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide to the second point of inflexion and
determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: Usual dose is 5–10 mg thrice/day.
2. Loratadine (Alaspan, Lorfast)
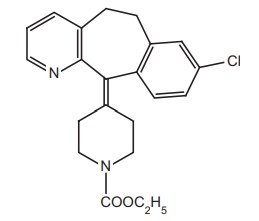
4-(8-Chlor-5,6-dihydro-benzocyclohepta
pyridine-11-ylidene)-1-piperidine carboxylic acid ethylester
Synthesis
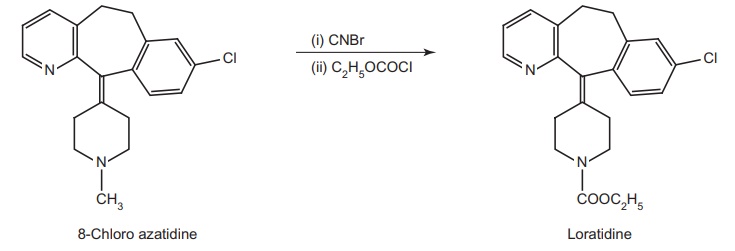
Metabolism: It is a nonsedative antihistaminic drug. The metabolite is
desloratidine (descarboethoxy loratidine) is associated with potentially
cardiotoxic effect.
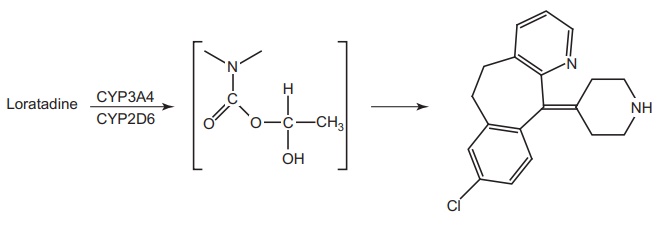
The metabolic
conversion of loratidine to descarboethoxy loratidine occurs via oxidative
process and not via hydrolysis, and both CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 are to be the
isoenzyme catalyzing this oxidative metabolism.
Properties and uses: Loratadine is a white crystalline powder,
practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone and methanol. Loratadine is
an azo isomer of cyproheptadine. The replacement of methyl group of azatadine
(piperidine nitrogen) by corresponding carbomate and introduction of 8-chloro
substitution preserve the antihistaminic action and reduces the CNS effect. The
potency of loratidine is comparable with that of astemizole and greater than of
terfenadine.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in glacial acetic acid and titrate against
0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
3. Epinastine
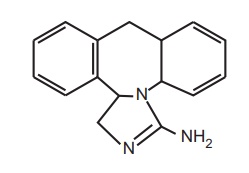
Properties and uses: This is structurally related to the
antidepressant and nonsedative H1-receptor antagonist mianserin. Introduction
of an amidine moiety preserve the antihistamine action and reduce the CNS
effect (sedation).
4. Rocastine
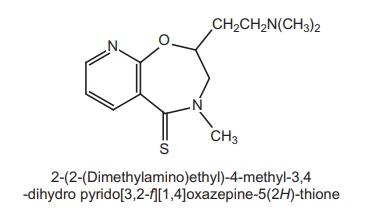
Properties and uses: It is a rapid acting, nonsedating H1-antagonist.
The R-enantiomer was at least 300 times more potent than S-enantiomer.
Related Topics
