Teratogenicity
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Adverse Drug Effects
It refers to capacity of a drug to cause foetal abnormalities when administered to the pregnant mother. The placenta does not strictly constitute a barrier and any drug can cross it to a greater or lesser extent.
TERATOGENICITY
It refers to capacity of a drug to cause foetal abnormalities when administered to the pregnant mother. The placenta does not strictly constitute a barrier and any drug can cross it to a greater or lesser extent. The embryo is one of the most dynamic biological systems and in contrast to adults, drug effects are often irreversible. The thalidomide disaster (1958–61) resulting in thousands of babies born with phocomelia (seal like limbs) and other defects focused attention to this type of adverse effect.
Drugs can affect the foetus at 3 stages—
§ Fertilization and implantation—conception to 17 days—failure of pregnancy which often goes unnoticed.
§ Organogenesis—18 to 55 days of gestation— most vulnerable period, deformities are produced.
§ Growth and development—56 days onwards developmental and functional abnormalities can occur, e.g. ACE inhibitors can cause hypoplasia of organs, specially lungs and kidneys; NSAIDs may induce premature closure of ductus arteriosus.
The type of malformation depends on the drug as well as the stage of exposure to the teratogen. Foetal exposure depends on the blood level and duration for which the drug remains in maternal circulation. The teratogenic potential of a drug is to be considered against the background of congenital abnormalities occurring spontaneously, which is ~ 2% of all pregnancies. Majority of implicated drugs are low grade teratogens, i.e. increase the incidence of malformations only slightly, which may be very difficult to detect, confirm or refute. Nevertheless, some drugs have been clearly associated with causing foetal abnormalities in human beings. These are listed in the box. However, only few mothers out of those who receive these drugs during the vulnerable period will get a deformed baby, but the exact risk posed by a drug is difficult to estimate.
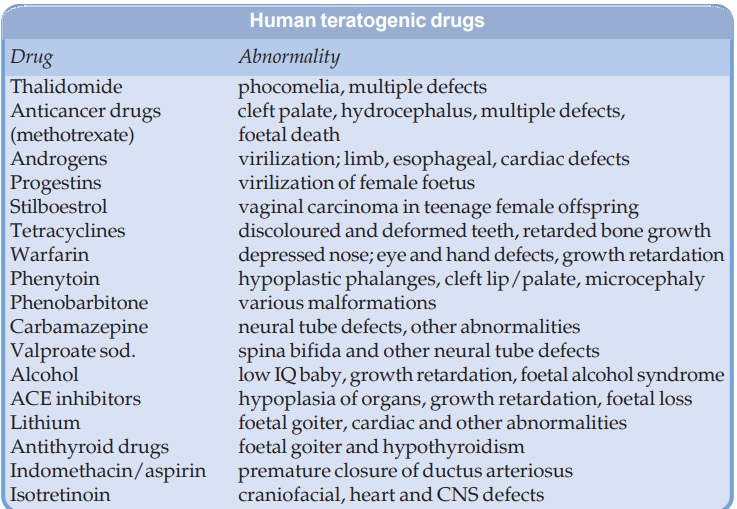
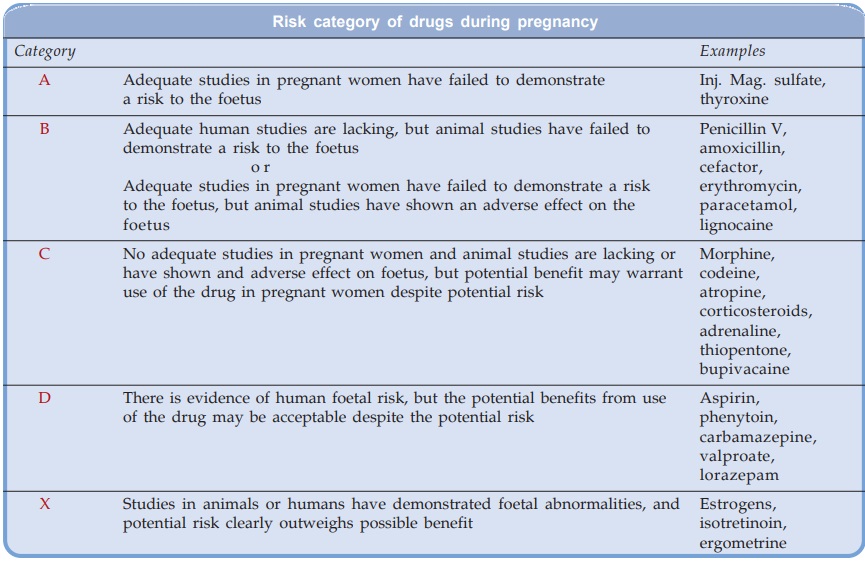
The USFDA has graded the documentation of risk for causing birth defects into five categories (see box).
It is, therefore, wise to avoid all drugs during pregnancy unless compelling reasons exist for their use regardless of the assigned pregnancy category, or presumed safety.
Frequency of spontaneous as well as drug induced malformations, especially neural tube defects, may be reduced by folate therapy during pregnancy.
Related Topics
