Topical Steroids
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Drugs Acting On Skin And Mucous Membranes
Glucocorticoids are used topically for a large variety of dermatological conditions. They bene fit by virtue of their anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, vasoconstrictor and antiproliferative (for scaling lesions) actions.
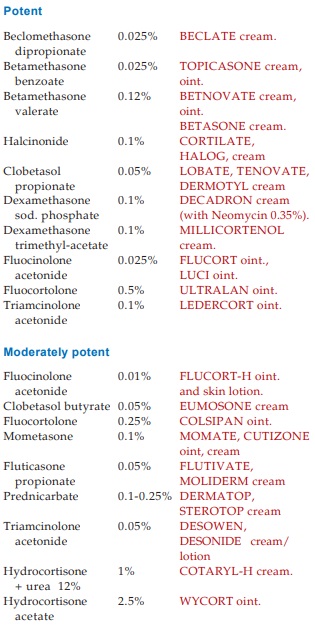
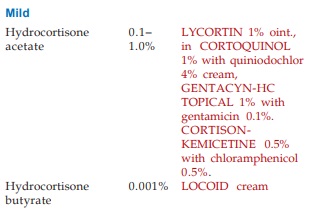
TOPICAL STEROIDS
Glucocorticoids are used
topically for a large variety of dermatological conditions. They bene fit by
virtue of their anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, vasoconstrictor and
antiproliferative (for scaling lesions) actions. The intensity of action
depends on the extent of absorption to the deeper layers, thus lipophilicity of
the compound determines potency to a great extent. Fluorinated compounds and
lipid soluble esters, e.g. hydrocortisone butyrate are potent. The available
preparations may be roughly graded as:
General Guidelines For The Use Of Topical Steroids
(i) Penetration of the
steroid at different sites differs markedly—high at axilla, groin, face, scalp
and scrotum; medium at limbs and trunk: low at palm, sole, elbow and knee.
Areas of high penetration easily develop adverse effects—potent preparations
should be avoided. Areas of low penetration do not generally respond to milder
agents.
(ii) Absorption into
the skin also depends on the nature of lesion—high in atopic and exfoliative dermatitis,
low in hyperkeratinized and plaque forming lesions. Milder drugs should be used
of acute lesions, stronger ones reserved for chronic lesions.
(iii) Choice of
vehicle is important. Lotions and creams (to some extent) are better for exudative
lesions—they allow evaporation, have a cooling, drying and antipruritic effect.
Sprays and gels are appropriate for hairy regions. Ointments form an occlusive
film and are good for chronic, scaly conditions.
(iv) Occlusive
dressing markedly enhances absorption of the steroid (as much
as 10 fold), retains moisture and results in maceration of the horny layer.
Chronic, hypertrophied lesions may be occluded intermittently (12 hours at a
time). Continuous occlusion promotes bacterial and fungal growth.
(v) Absorption is
greater in infants and young children—milder agents should be used. Routine use
of potent steroids is not justified. Very potent preparations should be
restricted to severe inflammatory conditions, unresponsive eczema, psoriasis,
etc., and that too only for short periods till the lesion resolves. The mildest
preparation that will control the lesion should be used.
(vi) Use of potent
preparations should be short term or intermittent to prevent adverse effects and
tachyphylaxis. Sudden discontinuation should be avoided. Upon improvement a
less potent preparation may be substituted or the steroid may be alternated
with an emollient till the lesion resolves.
(vii) More than 2 applications a day do not afford additional benefit. Generally twice daily application is satisfactory.
A combination of
steroid with an antimicrobial may be used for—impetigo, furunculosis, secondary
infected dermatoses, napkin rash, otitis externa, intertriginous eruptions.
Local Adverse Effects Of Topical Steroids
Thinning of epidermis
Dermal changes—atrophy Telangiectasia, Striae Easy bruising Hypopigmentation
Delayed wound healing Fungal and bacterial infections
Related to the potency
of preparation and duration of treatment; skin of face is more susceptible.
Potent haloginated steroids not to be used on face.
Systemic Adverse Effects Of Topical Steroids
Adrenal pituitary
suppression can occur if large amounts are applied repeatedly. Infants and children
are particularly susceptible. Rarely, Cushing’s syndrome has been reported.
With proper use, the systemic risks are minimal.
Popular Combinations
Are:
Containing Neomycin
(0.3–0.5%): BECLATEN, BETASONEN, COLSIPANN, DECADRON, KENACOMB, KENALOGS SKIN,
TOPICASONE.
Containing Chinoform
or Quiniodochlor (3–4%): BECLATE-C, BETASONE-C, BETNOVATE-C,
CORTOQUINOL, FLUCORT-C
Containing Gentamicin
(0.1%): GENTICYN-HC TOPICAL, DERMOTYL-G, LOBATE-G
Containing
Chloramphenicol (1%): CORTISON-KEMICETINE
Containing Providone iodine (1%): ECZO BETADINE
Containing Miconazole (2%): FLUCORTMZ,
TENOVATE-M
Containing
Clotrimazole (1%): CLOBEN
