Vaccines
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Vaccines And Sera
Vaccines are antigenic materials consisting of the whole microorganism or one of its products.
VACCINES
Vaccines are antigenic
materials consisting of the whole microorganism or one of its products.
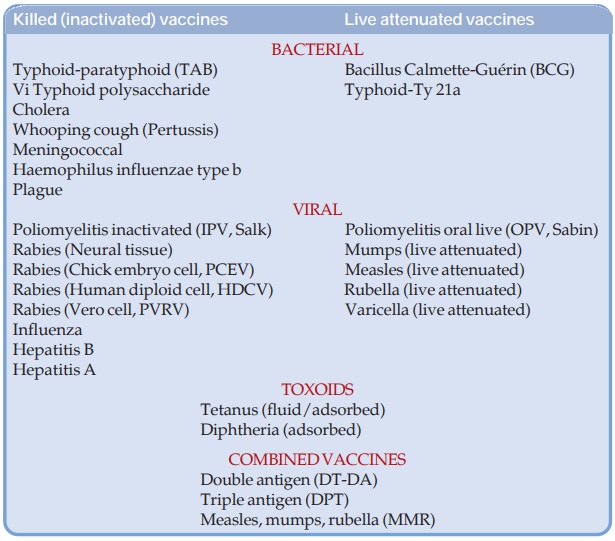
Vaccines are of 3 types:
Killed
(Inactivated) Vaccines: consist of microorganisms killed by heat or
chemicals.
Live
Attenuated Vaccines: consist of live bacteria or viruses which
have been rendered avirulent. They nevertheless grow and multiply in the body
of the host to a limited extent. In individuals with impaired host defence,
e.g.
· Leukaemia or other malignancies, especially those receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy.
· Systemic lupus erythematosus.
· Corticosteroid recipients.
· AIDS and other immune deficiency states.
The limited virulence of organisms in the live vaccine may be sufficient to cause a disease; live vaccines are contraindicated in them.
Two live vaccines, if
not given together, should preferably be administered with a gap of 1 month.
Toxoids: are modified
bacterial exotoxins so that toxicity
is lost but antigenicity is retained. The term ‘vaccine’ is sometimes
restricted to preparations of whole microorganisms and toxoids are enumerated
separately.
Active immunization
with vaccines may fail to ‘take’ during corticosteroid or immunosuppressant
medication and should be avoided. Vaccination should be deferred in the presence
of any acute (especially respiratory) infection and during pregnancy. Antibiotics
added during production of vaccines and present in trace amounts in viral
vaccines may cause reaction in individuals sensitive to these. Egg proteins (in
vaccines prepared on chick embryo) and other materials used for vaccine culture
may be responsible for allergic reactions. Adrenaline injection (1 in 1000)
should be available to control allergic reaction to the vaccine, if it occurs.
The antibodies
developed in response to live or killed vaccines inactivate the bacteria/virus
when it subsequently enters the body, while those induced by toxoids neutralize
the elaborated exotoxin. The latent period between vaccination and development
of immunity and the period for which it lasts depends primarily on the organism,
but varies somewhat in different individuals. Viral vaccines and toxoids
generally afford more prolonged protection than bacterial vaccines. The important
vaccines are described briefly.
Related Topics
