Areca Nuts
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Alkaloids
Areca nuts are the seeds of Areca catechu Linn., belonging to family Palmaceae.
ARECA NUTS
Synonyms
Betal nuts; Pinang; Semina Areacae, Supari (Hindi).
Biological Source
Areca nuts are the seeds of Areca catechu Linn., belonging to family Palmaceae.
Geographical Source
The tree is cultivated in tropical India, Sri Lanka, Malay
States, South China, East Indies, Philippine Islands and parts of East Africa
(including Zanzibar and Tanzania). In India it is cultivated in the coastal regions
of southern Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Bengal and Assam.
Cultivation and Collection
Areca palm is mostly propagated by seeds. The palm requires
a moist tropical climate for luxuriant growth; it is very sensitive to drought.
It grows in areas with heavy rainfall in between temperature of 15–38°C. It is
cultivated in plains, hill slopes and low lying valleys. The seeds are
collected from 25–50 years old trees.
Areca nut is a handsome palm with a tall, slender stem
crowned by large elegant leaves. Each tree contains about 100 fruits per year
which are detached by means of bamboo poles and the seeds extracted. The
pericarp is fibrous and surrounds a single seed which is easily separated. The
seeds are usually boiled in water with the addition of a little lime and dried.
Characteristics
Areca nuts are about 2.5 cm in length, bluntly rounded,
conical in shape and 2–3 cm wide at the base. The testa is brown and marked
with a network of small depressed lines. The ruminate endosperm is opal-white. Patches
of a silvery coat, the inner layer of the pericarp, occasionally adhere to the
testa. The deep-brown testa is marked with a network of depressed fissures; the
colour of the testa is due to the presence of tannin. In the centre basal part
of the endosperm, the small embryo is situated and an external pale area
indicated its position. The seed is very hard, has a faint cheese-like odour
when broken and an astringent, acrid taste.
Chemical Constituents
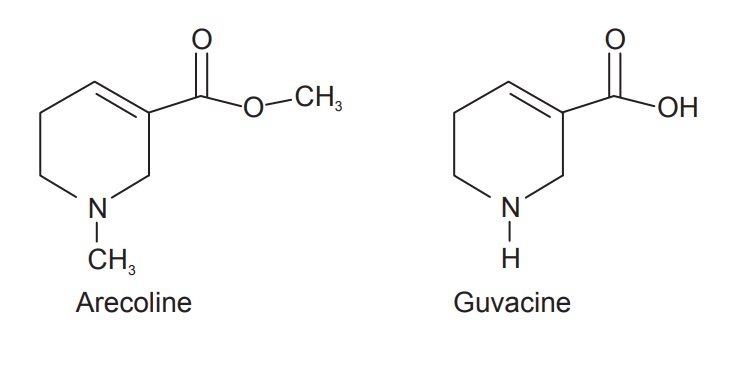
Areca nut contains a number of alkaloids of a piperidine
series, such as arecoline (methyl ester of arecanine), arecaine (N-methyl
guvacine), guvacine (tetrahydronicitinic acid), arecaidine, guvacoline,
arecolidine, leucocyanidine, (+)-catechin, (-)-epicatechin, procyanidins A-l,
B-l and B-2; phthalic, lauric, myristic, palmitic and stearic acids, β-sitosterol and choline. Arecoline is present in about 0.1–0.5% yield and is medicinally important. In addition to
alkaloids, areca nuts contain fat (14%) and amorphous red tannin (15%) known as
areca red of phlobaphene nature. The fat consists mainly of the glycerides of
lauric, myristic and oleic acids.
Uses
Powdered Areca is used as anthelmintic, taenifuge and
vermifuge for dogs. It has aphrodisiac action and useful in urinary disorders,
as nervine tonic and emmenagogue. The chewing of Areca nut may cause mouth
cancer.
Substituents and Adulterants
Nuts from other plants, such as, Areca caliso, A. concinna, A.
ipot, A. laxa, A. nagensis, A. triandra, Caryota cumingii and Heterospathe elata are used as substituents
for Areca nuts.
Sago palm nuts (Metroxylon
species), dried tapioca (Manihot esculenta), and slices of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) form cheap adulterants that are mixed with
slices of Areca nuts and prove a serious menace affecting the industry. Nuts of
Caryota urens, cut to various shapes
and sizes resembling genuine Areca nuts, and coated with concentrated Areca nut
extract kali, form the principal
adulterant. Adultera-tion above 10% significantly increases the fibre content
of the sample, which can be used as a measure of detecting adulteration.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Himplasia (Himalaya Drug Company), Khadiradi bati (Baidyanath) and Pigmento
(Charak Pharma Pvt. Ltd.).
