Asafoetida
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Resins
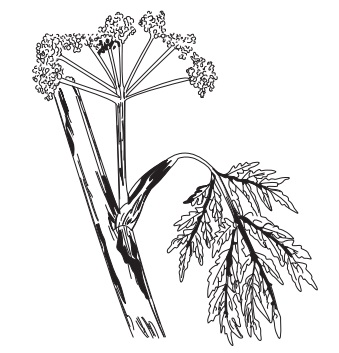
Asafoetida is an oleo-gum resin obtained as an exudation by incision of the decapitated rhizome and roots of Ferula asafoetida L, F. foetida, Royel, F. rubricaulis Boiss, and some other species of Ferula, belonging to family Apiaceae.
ASAFOETIDA
Synonyms
Devil’s dung; food of the gods; asafoda; asant; hing (Hindi).
Biological Source
Asafoetida is an oleo-gum resin obtained as an exudation by
incision of the decapitated rhizome and roots of Ferula asafoetida L, F. foetida, Royel, F. rubricaulis Boiss, and some
other species of Ferula, belonging to family Apiaceae.
Geographical Source
The plant grows in Iran, Turkestan and Afghanistan (Karam
and Chagai districts).
Collection
The plant is a perennial branching, 3 m high herb
possessing large schizogeneous ducts and lysigenous cavities containing milky liquid.
Upon exudation and drying of the liquid, Asafoetida is obtained. For the
collection of the drug the upper part of the root is laid bare and the stem cut
off close to the crown in March–April. The exposed surface is covered by a
dome-shaped structure made of twigs and earth. After separating each slice,
exudation of oleo-gum-resin, present as whitish gummy resinous emulsion in the
schizogenous ducts of the cortex of the stem, takes place. It hardens on the
cut surface which is collected, packed in tin-line cases and exported. Removal
of the exudation and exposure of fresh surface proceeds until the root is
exhausted. The yield is usually soft enough to agglomerate into masses when
packed.
Characteristics
Asafoetida occurs as a soft solid mass or irregular lumps or
‘tears’, sometimes almost semiliquid. Tears are rounded or flattened and about
5–30 mm in diameter, grayish-white or dull yellow or reddish brown in colour.
Asafoetida mass is mixed with fruits, fragments of root,
sand and other impurities. Asafoetida has a strong garlic-like (alliaceous)
odour and a bitter, acrid and alliaceous taste. When triturated with water, it
makes a milky emulsion. It should not have more than 50% of matter insoluble in
alcohol (90%) and not more than 15% of ash.
Chemical Constituents
Asafoetida contains volatile oil (4–20%), resin (40–65%),
and gum (25%). The garlic-like odour of the oil is due to the presence of
sulphur compounds. The main constituent of the oil is isobutyl propanyl
disulphide (C6H16S2). The three sulphur
compounds, such as, 1-methylpropyl-1-propenyl disulphide,
l-(methylthio)-propyl-1-pro-penyl disulphide, and l-methyl-propyl
3-(methylthio)-2-propenyl disulphide have also been isolated from the resin; the
latter two have pesticidal properties. The flavour is largely due to
R-2-butyl-l-propenyl disulphide and 2-butyl-3-methylthioallyl disulphide (both
as mixtures of diastereoisomers).
The drug also contains a complex mixture of sesquiterpene
umbelliferyl ethers mostly with a monocyclic or bicyclic terpenoid moiety.
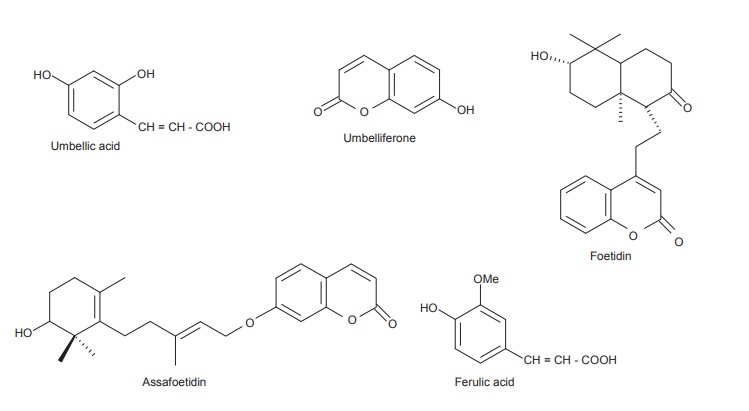
Resin consists of ester of asaresinotannol and ferulic acid, pinene, vanillin
and free ferulic acid. On treatment of ferulic acid with hydrochloric acid, it
is converted into umbelliferone (a coumarin) which gives blue fluorescence with
ammonia.
Asafoetida also contains phellandrene, sec-butylpropenyl
disulphide, geranyl acetate, bornyl acetate, α-terpineol, myristic acid, camphene,
myrcene, limonene, fenchone, eugenol, linalool, geraniol, isoborneol, borneol,
guaiacol, cadinol, farnesol, assafoetidin, foetidin, etc.
Chemical Tests
1. On trituration with water it
produces a milky emul-sion.
2. The drug (0.5 g) is boiled with hydrochloric
acid (5 ml) for sometime. It is filtered and ammonia is added to the filtrate.
A blue fluorescence is obtained.
3. To the fractured surface add 50%
nitric acid. Green colour is produced.
4. To the fractured surface of the
drug, add sulphuric acid (1 drop). A red colour is obtained which changes to
violet on washing with water.
Uses
Asafoetida is used as carminative, expectorant,
antispas-modic, and laxative as well as externally to prevent bandage chewing
by dogs; for flavouring curries, sauces, and pickles; as an enema for
intestinal flatulence, in hysterical and epileptic affections, in cholera,
asthma, whooping cough, and chronic bronchitis.
Adulteration
Asafoetida is adulterated with gum Arabic, other gum-resins, rosin, gypsum, red clay, chalk, barley or wheat flour, and slices of potatoes.
Allied Drugs
Galbanum and ammoniacum are oleo-gum-resins obtained,
respectively, from Ferula galbaniflua
and Dorema ammoniacum. Galbanum
contains umbelliferone and umbelliferone ethers, up to 30% of volatile oil
containing numerous mono- and sesquiterpenes, azulenes, and sulphur-containing
esters. Ammoniacum contains free salicylic acid but no umbeiliferone. The
major phenolic constituent is ammoresinol. An epimeric mixture of prenylated
chromandiones termed ammodoremin is also present. The volatile oil (0.5%)
contains various terpenoids with ferulene as the major component.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparation known as
Madhudoshantak (Jamuna Pharma).
