Capsicum
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Resins
Capsicum consists of the dried, ripe fruits of Capsicum minimum and Capsicum annum Linn., belonging to family Solanaceae.
CAPSICUM
Synonyms
Chillies; cayenne pepper; red peppers; Spanish pepper; mirch
(Hindi); capsicum fruits; Fructus Capsici.
Biological Source
Capsicum consists of the dried, ripe fruits of Capsicum minimum and Capsicum annum Linn.,
belonging to family Solanaceae.
Geographical Source
Capsicum is native of America and cultivated in tropical
regions of India, Japan, southern Europe, Mexico, Africa (Kenya, Tanzania, and
Sierra Leone), and Sri Lanka.
Cultivation and Collection
Capsicum is cultivated mostly as a rainfed crop. In the
Gangetic area, it is a cold weather crop. The crop is raised on a variety of
soils, for example, ordinary red loams, black soils and clayey loams. Good
drainage is essential and water-logging is detrimental. Seedlings are first
raised in a nursery. Seeds obtained from selected pods and mixed with ashes are
sown by broadcasting. Germination occurs in about a week. The field is ploughed
and manured with compost. The field is irrigated once a day until the plants
are established. Flowering starts when the plants are 2.5–3.5 months old. Dew
and heavy rain at flowering time are injurious. Ripe and nearly ripe fruits are
picked at intervals of 5, 10, and 20 days.
The fruits are picked as they become fully ripe. The quality
of the drug is in part determined by its colour. The unripe fruits fade to pale
buff upon drying. The fruits are dried in sun, graded by colour; occasionally
oil is rubbed on the fruits to give glossiness to the pericarps. Most of the
calices and pedicels are removed.
Characteristics
Capsicum is 5–12 cm long, 2–4 cm wide, globular, ovoid, or
oblong in shape, pericarp is shrievelled, orange or red in colour, pedicel is
prominent and bent. The calyx is toothed. The amount of calices and pedicels
should not exceed beyond 3%. Internally the fruits are divided into two halve
parts by a membranous dissepiment to which the seeds are attached. The seeds
are reniform, flattened, 3–4 mm long, with a coiled embryo and oily endosperm.
Capsicum has characteristic odour and an intense pungent taste.

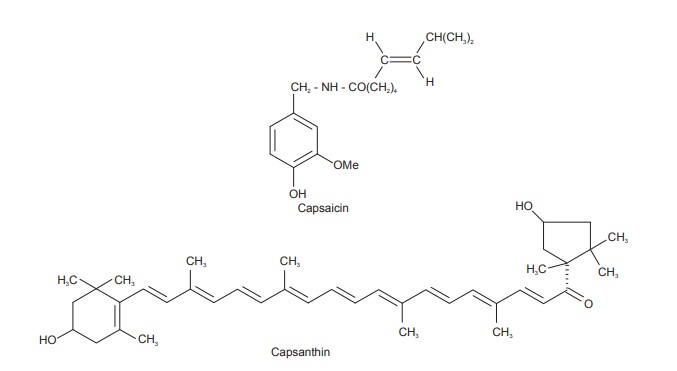
Chemical Constituents
Capsicum contains fixed oils (4–16%), oleoresin,
carotenoids, capsacutin, capsico (a volatile alkaloid), thiamine, volatile oil
(1.5%), and ascorbic acid (0.2%). The resin con-tains an extremely pungent
principle, capsaicin, (decylenic vanillyl amide) (about 0.5%). Capsaicin
retains its char-acteristic pungency in a dilution of 1 part in 10 million
parts with water. Capsanthin is the main carotenoid of red fruits. It also
occurs as monoester and diester along with cryptocapsin. Other carotenoids
include zeaxanthin. capsorubrin, rubixanthin, phylofluene,
capsanthin-5,6-epoxide, capsanthin-3.6-epoxide, lutein, cryptoxanthin, α- and β-carotenes, capsorubin, and few
xanthophylls. The carbohydrates reported in chilies
are fructose, galactose, sucrose, etc. Tocopherol (vitamin E) is present in
trace amounts (~2.4 mg/100 g).
Uses
Capsicum has been used externally as stimulant, counter
irritant, rubefacient, in sore throat, scarlatina, hoarseness, and yellow
fever; internally it is used as carminative, stomachic, dyspepsia, and
flatulence. In the form of ointment, plaster and medicated wool it is used for
the relief of rheumatism and lumbago. Capsaicin is used for the treatment of
migraine and cluster headache, and for some patients with neurogenic ladder
dysfunction.
Allied Drugs
Japanese Chillies (C.
frutescens) are about 3–4 cm long. They
are usually free from pedicels and calices and have a bright red pericarp.
They possess about one-quarter of the pungency of the African Chillies.
Bombay Capsicums (C. annuum). The pericarp is thicker and tougher than in the chillies, and the pedicel is frequently bent. They are much less pungent than African chillies.
Natal Capsicums are larger than the Bombay variety,
being up to 8 cm long. They have a
very bright red, transparent pericarp. They are much less pungent than chillies.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Deepact (Lupin Herbal Laboratory) and Capsigyl-D (Shalaks), a topical
antirheumatic cream.
