Cannabis
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Resins
Cannabis consists of dried flowering tops of the pistillate plants of Cannabis sativa Linn., belonging to family Cannabinaceae.
CANNABIS
Synonyms
Indian hemp, Indian cannabis, hashish, bhang, ganja, charas,
Cannabis indica, marihuana.
Biological Source
Cannabis consists of dried flowering tops of the pistillate
plants of Cannabis sativa Linn.,
belonging to family Cannabinaceae.
Geographical Source
Cannabis occurs in India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Iran,
Central America, United States, East Africa, South Africa, and Asia Minor.
Cultivation and Collection
Cannabis is an annual dioecious herb, which is cultivated by
seed sowing method. The seeds are sown on seedbeds in the month of August and after
a month the seedlings are transplanted into the open field. The male plants,
which have attained the maturity, are taken and shaken over the female plants
so as to facilitate pollination. The flowering tops of female plants are
collected in February or March. They are made into bundles and treated under
the foot to form flat masses. The flat masses are dried under the shade to
obtain ‘ganja’. In India the tops are treated to form rounded masses called as
‘ganja’.
Cannabis Products
The following products are prepared from Cannabis. Ganja: It contains up to 10% of its
fruits, large foliage
leaves and stems over 3 cm. It is known as Flat or Bombay ganja when 30 cm
long pieces of the herb are made into bundles
and pressed. Round or Bengal ganja is prepared by rolling the
wilted tops between the hands. Ganja is legally produced only by a few licensed
growers in Bengal and southern India. The seeds are sown in rows about 1.3 m
apart and male plants are discarded. The resinous tops of the unfertilized
plants are cut about 5 months after sowing and pressed into cakes. The yield is
nearly 120 kg per acre.
Bhang or Hashish: It consists of the larger leaves and
twigs of both male and female plants.
It is smoked with or without tobacco. It is unfit for medicinal use owing to
deficiency of resin. It is also taken in the form of an electuary made by digestion
with melted butter.
Charas: It is the crude resin obtained by
rubbing the tops between the hands
and beating them on a piece of cloth. This is an inferior product. It may be
collected by beating the flowering tops in coarse cotton cloths spread on the
ground. A greenish-brown soft mass adheres, and may be purified by pressing it
through the cloths. The resin is scraped off. It is mixed with many smoking
mixtures.

Morphology
Cannabis occurs in flattened, rough, dull dusky green
masses. The dried resin is hard, brittle, and does not stick. The flat-ganja is
flattened mass of a dull green colour. The odour is very marked in the fresh
drug and becomes faint afterwards; taste is slightly bitter.
The flat- or Bombay ganja occurs in agglutinated flattened
masses of a dull green or greenish-brown colour. The resin is not sticky but
hard and brittle; the odour, which is very marked in the fresh drug, is faint.
The drug has a slightly bitter taste. The lower digitate leaves of the plant
are not found in the drug. The thin, longitudinally furrowed stems bear simple
or lobed; stipulate bracts which subtend the bracteoles, enclosing the pistil
late flowers. The bracts are stipulate and the lamina may be simple or
three-lobed. The bracteole enclosing each flower is simple.
Microscopy
The resin is secreted by numerous glandular hairs. The head is usually eight-celled and the pedicel multiseriate or unicellular. Corrigan and Lynch, a reagent consisting of vanillin in ethanolic sulphuric acid, stains the cannabis glands a deep reddish-purple. Abundant conical, curved, unicellular hairs are also found, many having cystoliths of calcium carbonate in their enlarged bases. These cystolith hairs are not confined solely to the genus Cannabis. Cluster crystals of calcium oxalate are abundant, particularly in the bracteoles.
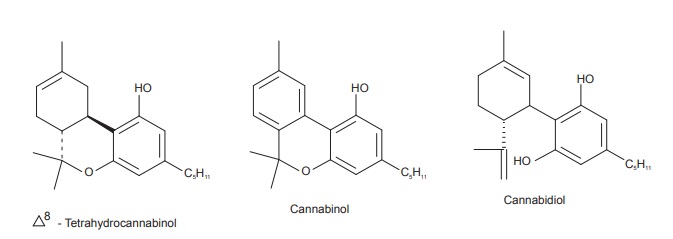
Chemical Constituents
Cannabis consist of 15 to 20% resin, the resins are
amorphous, semisolid, brown coloured, soluble in ether, alcohol, and carbon
disulphide. The most important active constituents present in cannabis are:
cannabidiol, cannabidolic acid, cannabinol, cannabichromene, and
trans-tetrahydrocannbinol. Cannabis also contains Cannabidiolic acid,
cannabidiol A 9, tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabinol A9, Tetrahydrocannabinol
(THC), volatile oil, trigonelline, and cholene.
Uses
Cannabis resin is tonic, sedative, analgesic, intoxicant,
stomachic, antispasmodic, antianxiety, anticonvulsant, antitussive, and
narcotic. Cannabis causes only pshycic dependence and act upon the nervous
system.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparation known as
Bilwadi churna (Baidyanath).
