Azole antifungals
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antifungal Agents
Azole antifungals : 1. Miconazole (Micatin, Monistat) and Econazole 2. Ketoconazole (Nizoral) and Terconazole 3. Clotrimazole (Clotrimin, Mycelex) 4. Fluconazole (Syscan, Zocon, Flucos) 5. Butoconazole 6. Bifonazole 7. Zinoconazole
Antifungal Agents - Synthesis
and Drug Profile
Azole antifungals
Mode of action: Azole antifungals inhibit sterol 14-α-demethylase,
a microsomal cytochrome P450-dependent enzyme system, and thus, impair the
biosynthesis of ergosterol for the cytoplasmic membrane and lead to the
accumulation of 14-α-methyl sterols. These methylsterols may disrupt the
packing of aryl chains of phospholipids, the functioning of certain membrane
bound enzyme systems, such as ATPase and enzymes of the electron transport
system, and thus, inhibiting the growth of fungi.
1. Miconazole (Micatin, Monistat) and Econazole
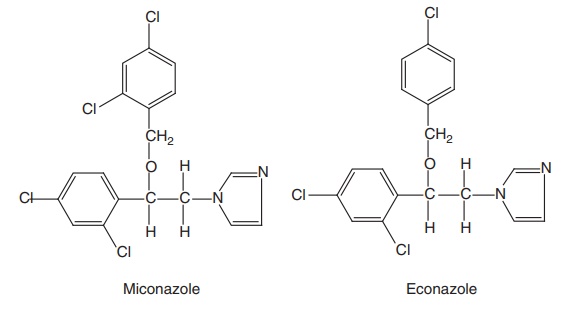
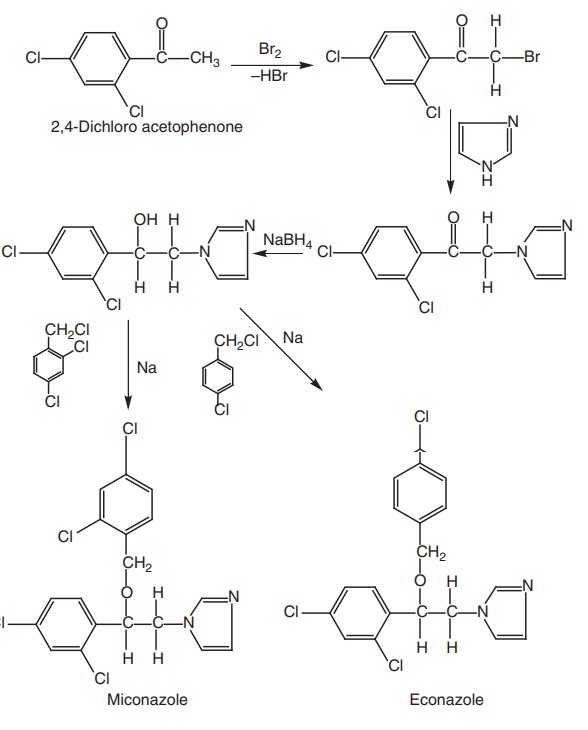
Synthesis
Synthesis of
Miconazole and Econazole
Properties and uses of Miconazole: Miconazole is a white or almost white powder,
very slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, and slightly
soluble in alcohol. It is used as an antifungal agent.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid, with slight
heating, if necessary, and titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the
end point potentiometrically.
Dose: It is to be applied in the vagina at bedtime for seven days, and
200 mg vaginal suppositories for three days therapy.
Dosage forms: Miconazole cream I.P., B.P., Miconazole pessaries I.P., Miconazole tablets I.P., Miconazole and Hydrocortisone cream B.P., Miconazole and Hydrocortisone acetate cream B.P., Miconazole and Hydrocortisone ointment B.P.
Properties and uses of Econazole: Econazole is white or almost white crystalline
powder, very slightly soluble in water, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble
in methylene chloride, and slightly soluble in alcohol. It is used as
antifungal agent.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and titrate with
0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: It is available as a water insoluble cream (1%) to be applied
twice a day.
Dosage forms: Econazole cream B.P., Econazole pessaries B.P.
2. Ketoconazole (Nizoral) and Terconazole
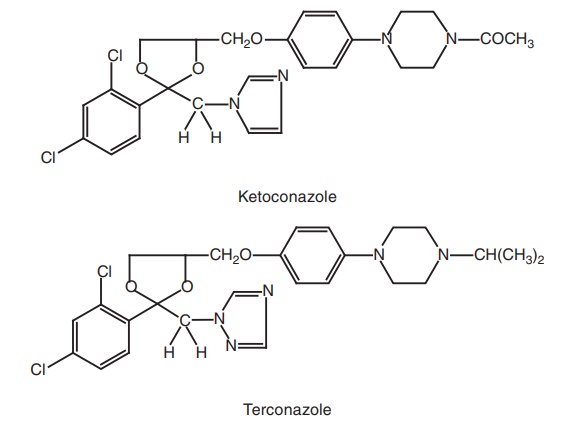
Metabolism of Ketoconazole: It is extensively metabolized by deacetylase of
the microsomal enzymes and all the metabolites are inactive.
Properties and uses of Ketoconazole: Ketoconazole is a white powder, practically
insoluble in water, soluble in methylene chloride and in methanol, sparingly
soluble in alcohol. It is a racemic compound, consisting of the cis-2S, 4R, and cis-2R, 4S isomers. An investigation of the relative potencies of
the four possible diastereomers of ketoconazole against rat lanosterol 1,4α-demethylase
indicated that the 2S, 4R isomer was 2.5 times more active than its 2R, 4S enantiomer and the trans isomers, 2S, 4S, and 2R, 4R are
much less active. Ketoconazole is an imidazole antifungal agent, which is a
highly lipophilic compound. This property leads to high concentrations of
ketoconazole in fatty tissues and purulent exudates. Ketoconazole is active
against Candida spp and Cryptococcus neoformans.
Assay of Ketoconazole: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of anhydrous
acetic acid and methyl ethyl ketone (1:7) and titrate with 0.1 M perchloric
acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: It is administered as 200 mg scored tablets and 2% topical
cream.
Synthesis
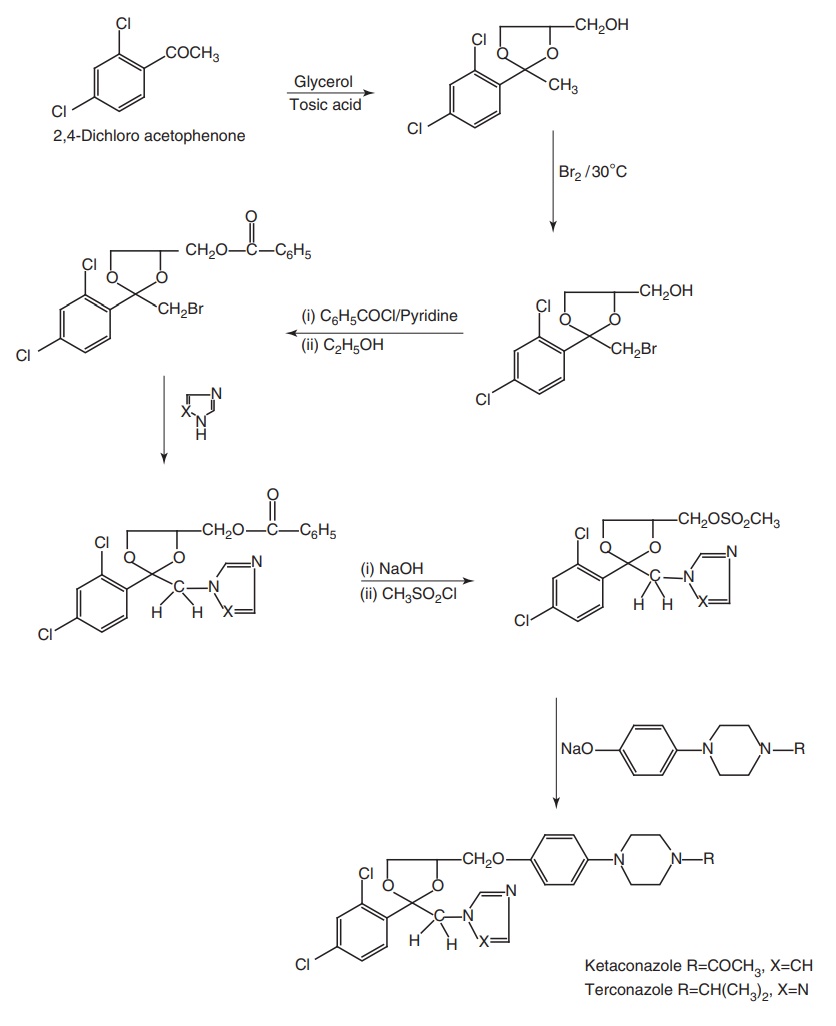
Metabolism of Terconzole: It is metabolized by CYP3A4 on oral
administration.
Properties and uses of Terconzole: Terconazole is a white powder, practically
insoluble in water, soluble in methylene chloride and in acetone, sparingly
soluble in alcohol. It is a triazole derivative that is used exclusively for
the control of Vulvovaginal moniliasis caused
by Candida albicans and other Candida spp.
Assay of Terconzole: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of anhydrous
acetic acid and volumes of methyl ethyl ketone (1:7) and titrate with 0.1 M
perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically at the second point
of inflexion.
Dose: The administered dose is 80 gm vaginal suppository at bedtime
for three days; and 0.4% as vaginal cream for seven days.
3. Clotrimazole (Clotrimin, Mycelex)
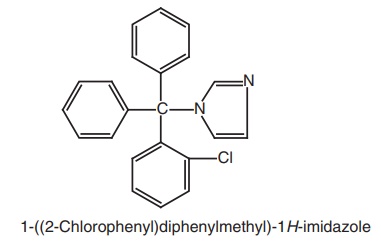
Synthesis

Properties and uses: Clotrimazole is a white or pale yellow
crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol and in
methylene chloride. It is used as an antifungal agent.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and titrate with
0.1 M perchloric acid using naphtholbenzein as indicator until the colour
changes from brownish-yellow to green.
Dose: The administered dose is usually as 100 mg tablet per day at
bedtime for seven days for vaginal infection.
Dosage forms: Clotrimazole cream I.P., B.P., Clotrimazole pessaries I.P., B.P.
4. Fluconazole (Syscan, Zocon, Flucos)

Synthesis
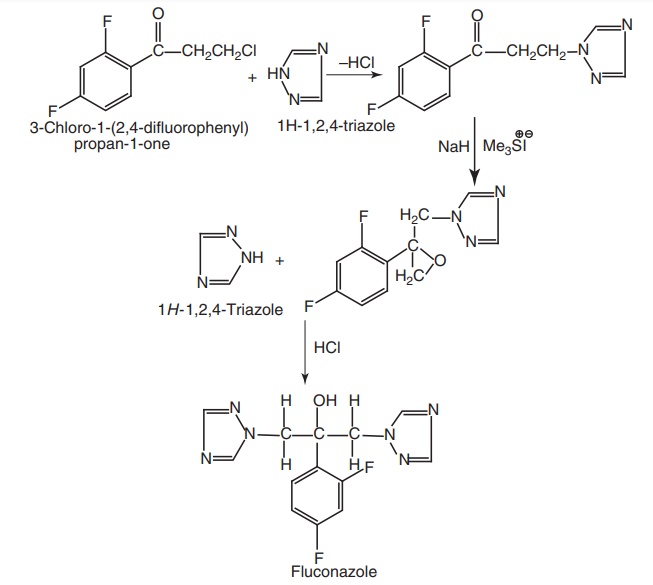
Properties and uses: Flucanazole is a white hygroscopic crystalline
powder, slightly soluble in water, and soluble in methanol and in acetone. It
is a widely used bis-triazole
antifungal agent. It is generally considered to be a fungi-static agent, and it
is principally active against Candida spp
and Cryptococcus spp. Fluconazole has
useful activity against Coccidioides
immitis, and is often used to suppress the meningitis produced by the
fungus.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and titrate with
0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: The administered dose for superficial mucosal candidiasis for
adults is 50 mg daily, which is increased to 100 mg daily. Recommended
treatment duration is 7–14 days; in the case of oropharyngeal candidiasis, 14
days for atrophic oral candidiasis associated with dentures, 14–30 days for
other mucosal candidal infections, including oesophagitis. In the case of
children, more than 4 weeks the loading dose is 6 mg/kg followed by 3 mg/kg
daily.
The
administered dose for dermatophytosis, pityriasis versicolor, and candida
infections for adults is 50 mg daily for up to 6 weeks.
The
administered dose for cryptococcal infections, including meningitis, systemic
candidasis for adults, initially is 400 mg followed by 200–400 mg daily; the
maximum dose is 800 mg daily in the case of severe infections. In the case of
cryptococcal meningitis, usual treatment duration is at least 6–8 weeks and may
also be given via IV infusion. For children more than 4 weeks the dose is 6–12
mg/kg daily; same doses may be given every 72 h in neonates up to 2 weeks and
every 48 h in neonates 2–4weeks old; the maximum dose is 400 mg daily.
5. Butoconazole
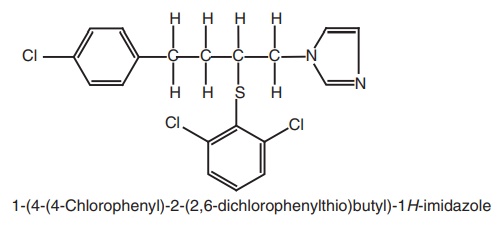
Synthesis
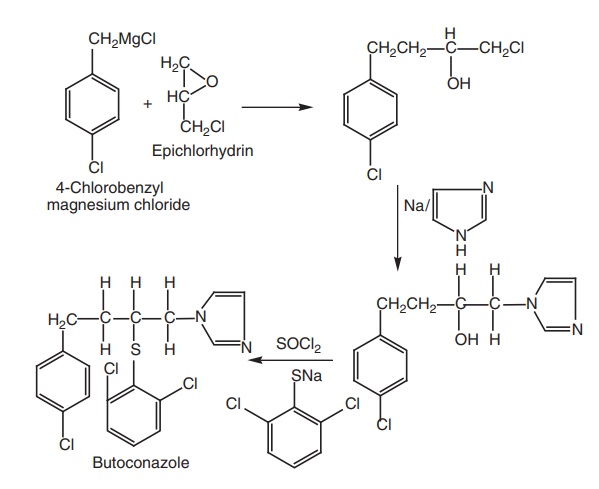
6. Bifonazole
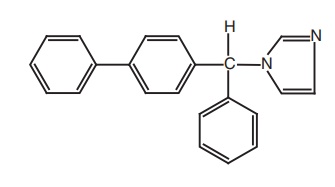
Synthesis
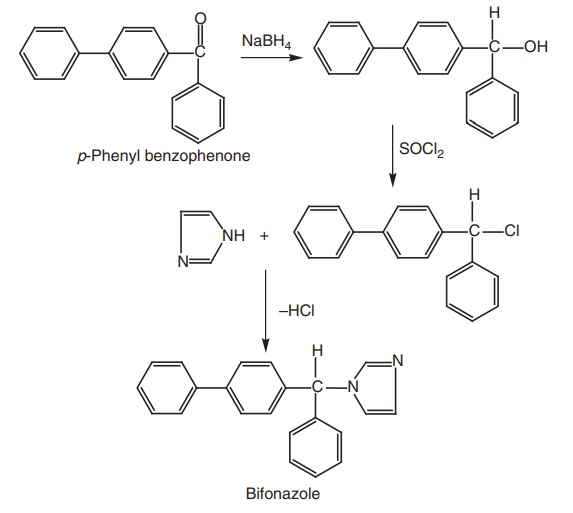
Properties and uses: Bifonazole is a white crystalline powder,
practically insoluble in water, and sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol. It
is used as an antifungal agent.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and titrate with
0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
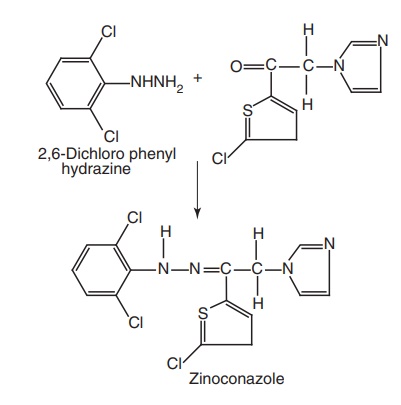
7. Zinoconazole
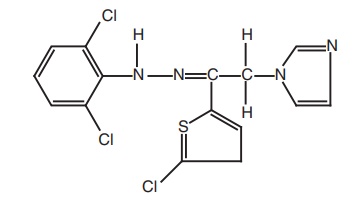
Synthesis:
Related Topics
