Benzodiazepines
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Tranquillizers
a. Chlordiazepoxide (Cebrum, Cloxide, Librium), b. Oxazepam - Benzodiazepines - Tranquillizers - SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE : Structure, Properties, uses, Synthesis, Assay, Storage, Dosage forms, Dose
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Benzodiazepines
Metabolism is discussed under ‘Sedatives and Hypnotics’ in Next Section.
a. Chlordiazepoxide (Cebrum, Cloxide, Librium)
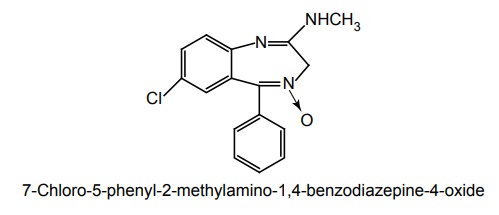
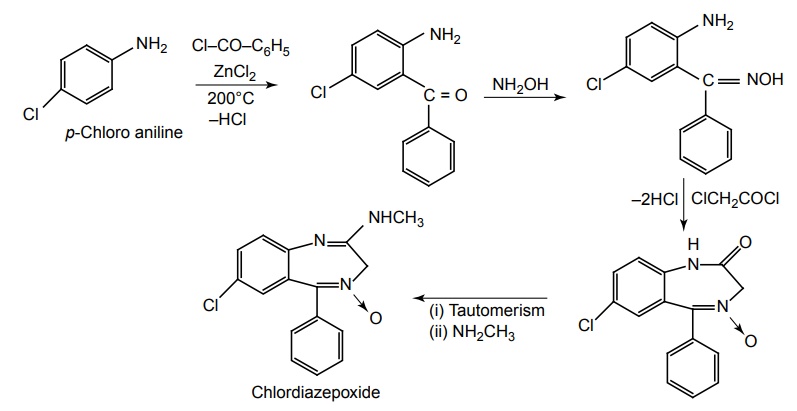
Synthesis
Properties and uses: It is a white or slightly yellow crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in ethanol and soluble in water. Chlordiazepoxide is also available commercially in anxiolytic products combined with anticholinergic and anti-depressant agents. The therapeutic value of these fixed combinations has not been established. Adverse reactions include drowsiness, ataxia, confusion, skin eruptions, oedema, menstrual irregularities, nausea and constipation, EPS and decreased libido. In some patients; blood dyscrasias (agranulocytosis), jaundice, and hepatic dysfunction have occasionally been reported. Used for the relief of anxiety and tension, withdrawal symptoms of acute alcoholism, and also used as sedative as well as muscle relaxant.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in water and titrate with 0.1 M silver nitrate. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight container and protected from light.
Dose: For Anxiety: Adult: 30 mg daily in divided doses, up to 100 mg daily in severe conditions. Elderly and debilitated patients: Dose reduction may be needed. For muscle spasms: Adult: 10–30 mg daily in divided doses. Elderly and debilitated patients: Dose reduction may be needed.
b. Oxazepam
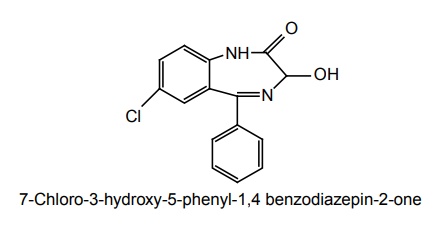
Synthesis and drug profile are discussed under ‘Sedatives and Hypnotics’ in Next Section.
