Future Developments in Memo and Conclusion
| Home | | Pharmacovigilance |Chapter: Pharmacovigilance: MEMO in the United Kingdom
Dispensed prescribing data collection in MEMO is labour-intensive and expensive.
FUTURE DEVELOPMENTS IN MEMO
Dispensed
prescribing data collection in MEMO is labour-intensive and expensive. The
automated capture of computerised dispensed prescribing data has been
investigated in five test pharmacies, a method that could eventually become
Tayside wide or Scottish wide (McGilchrist and MacDonald, 1996). Of 200 000
prescription items from which data were collected using this methodology, a comparison
with a sample of duplicate data collected by MEMO in the usual way showed that
there was agreement for 98% of the items.
CONCLUSION
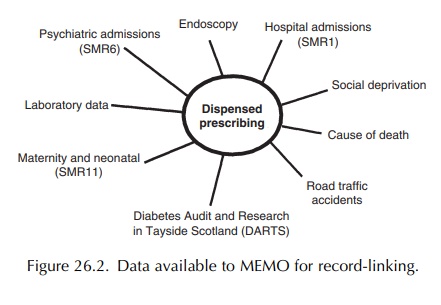
In conclusion, MEMO is a comprehensive record-linkage system
that can be used for the detection and quantification of serious drug toxicity,
outcomes research and pharmacoeconomic studies. The reali-sation of disease
management also strengthens the capabilities of MEMO. Figure 26.2 summarises
the record-linked data sets that are available in MEMO.
Related Topics
