Group 10: platinum anticancer agents
| Home | | Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry |Chapter: Essentials of Inorganic Chemistry : Transition Metals and d-Block Meta Chemistry
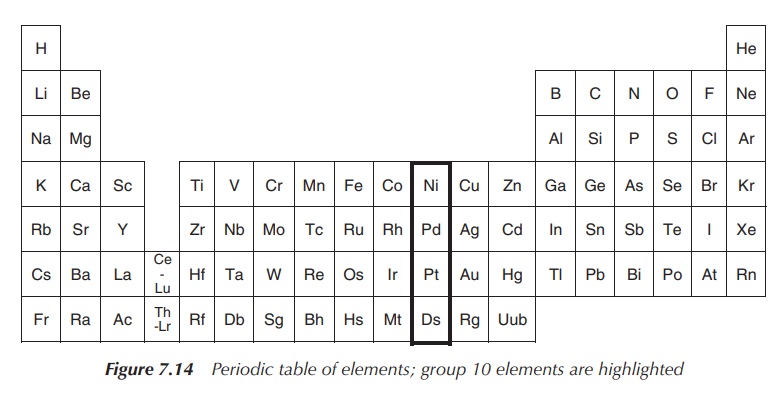
Group 10 of the periodic table of elements consists of the nonradioactive members nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd) and platinum (Pt) as well as the radioactive element darmstadtium (Ds).
Group
10: platinum anticancer agents
Group 10 of the periodic table of elements consists of the
nonradioactive members nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd) and platinum (Pt) as well as
the radioactive element darmstadtium (Ds) (Figure 7.14).
The noble metals palladium and platinum are resistant to
corrosion and can be attacked by O2, F2 and Cl2
only at very high temperatures. Palladium dissolves in hot oxidising acids,
whereas platinum dissolves in only ‘aqua regia’ (1 : 3 mixture of HNO3
and HCl).
Palladium is used as a hydrogenation catalyst, for H2/D2/T2
separation and purification as well as a catalyst in the Wacker process. The
Wacker process, which facilitates the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde,
was the first organopalladium reaction that was applied on an industrial scale.
Platinum is also intensively used as a catalyst, for example, in HNO3
production, as oxidation catalysts, in petroleum reforming, in hydrogenations
and in many more chemical processes, as well as for jewellery.
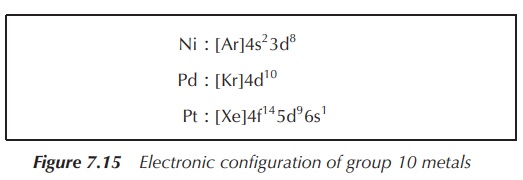
All three nonradioactive elements of group 10 show a high
diversity in their electronic configuration (Figure 7.15).
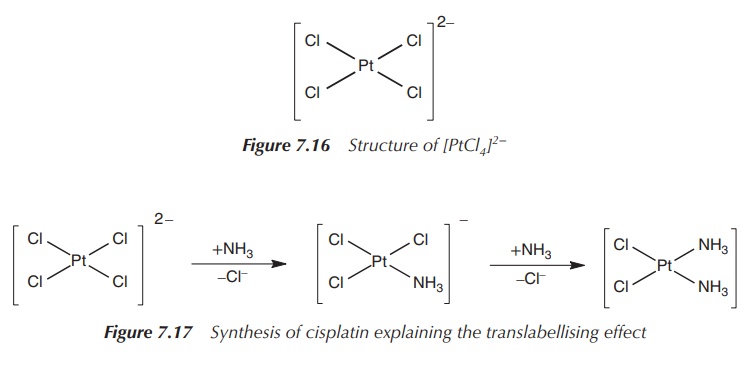
Most stable oxidation states are +II for all three nonradioactive elements, whereas Pt(II) and Pt(IV) are not only stable but also kinetically inert. The bromide and iodide salts of Pt(II) and Pd(II) are insoluble. Pt(II) has an electron configuration of d8, and the square planar geometry is the dominant structure. The [PtCl4]2− anion is an example where this square planar geometry is adapted. It is a stable anion, and indeed most platinum(II) chemistry starts with K2[PtCl4].
[PtCl4]2− is also the
starting material for the synthesis of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)
(cisplatin, CDDP), a widely used chemotherapeutic drug (see Figure 7.16). The
first NH3 ligand is added to any of the four positions around the
central Pt atom, as all four positions are equivalent. The second NH3
will be directed cis to the first NH3 group and cisplatin is
obtained. The reason is that the Cl− ligands have a larger so-called
trans effect than NH3 (Figure 7.17).
The trans effect or trans labellising effect is mainly seen in square planar complexes
and describes the ability of some ligands to direct newly added ligands into
the trans position. The intensity of the trans effect increases in the
following order: F−, H2O, OH− < NH3 < py < Cl− < Br− < I−, SCN−, NO2− < SO32− < CH3− < H−, NO, CO, CN−.
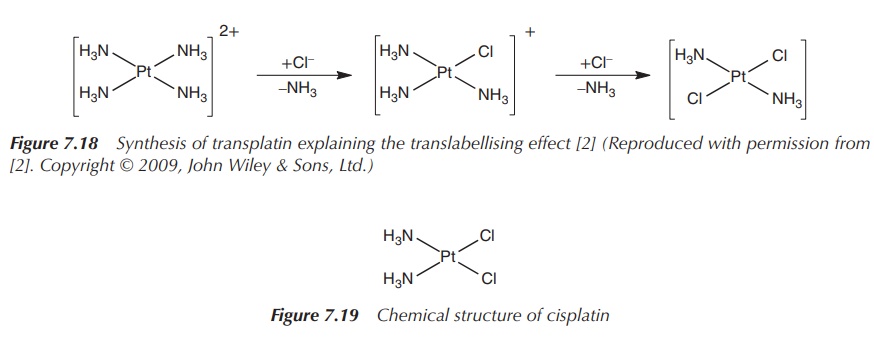
In comparison, if the synthesis is started
from Pt(NH3)42+, transplatin is obtained.
Again, the addition of the first ligand, in this case Cl−, can occur
at any of the four positions. The addition of the second Cl− ligand
will be directed into the trans position by the initial Cl− ligand
as it has a higher trans effect than the NH3 ligand (Figure 7.18).