Osmotic diuretics - Nonmercurial diuretics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Diuretics
Nonmercurial diuretics : Osmotic diuretics : i. Mannitol ii. Urea iii. Glycerine iv. Isosorbide - Synthesis and Drug Profile
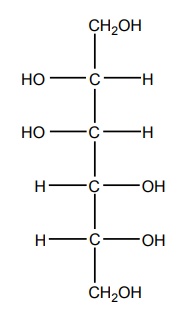
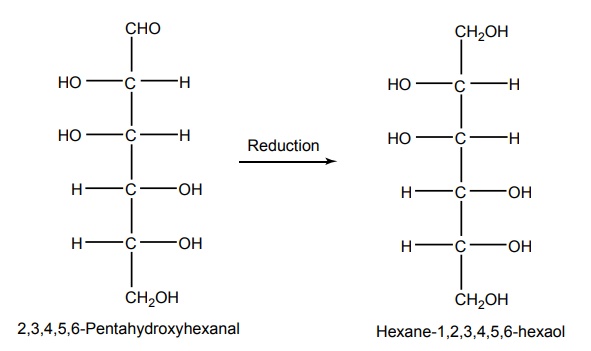
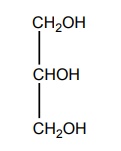
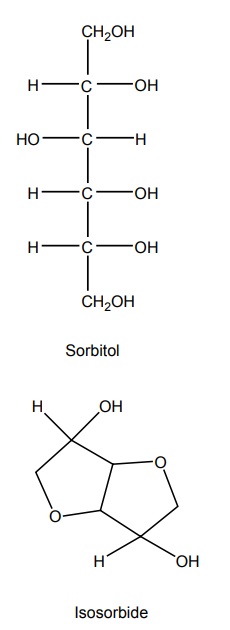
Osmotic diuretics are nonelectrolytes, which are freely filtered at the glomerulus and are not significantly reabsorbed from the tubules, and presence of these agents in the urine causes an increase in the electrolytes and volume flow. Mannitol, urea, glycerol, and isosorbide are the four osmotic diuretics, which are freely filtered through the glomerulus and are insignificantly reabsorbed from the tubules; they mainly induce diuresis by inhibiting sodium and water reabsorption in the PTs and the henle’s loop. Synthesis Properties and uses: Mannitol is a white crystalline powder or granules, soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol. It is most widely used for acute renal failure, cardiovascular operation, and severe traumatic injury with nephrotoxic anticancer agents. Assay: It is assayed by adopting the liquid chromatography technique Dosage forms: Mannitol injection I.P., Mannitol intravenous infusion B.P. NH2CONH2 Properties and uses: It is a colourless white, prisamatic crystals or a white crystalline powder, odourless with a saline taste, soluble in water, alcohol, methanol, or glycerol, but insoluble in chloroform or ether. It is administered intravenously in a solution containing (30% urea +5% to 10% dextrose). Properties and uses: It is used prior to ophthalmological procedures. Glycerine is an orally active diuretic and obtained from the production of soaps and fatty acids through hydrolysis or by hydration of propylene. Properties and uses: Isosorbide is given orally to cause a reduction in intraocular pressure. Isosorbide is prepared by acid dehydration of sorbitol.SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Nonmercurial diuretics
Osmotic diuretics
i. Mannitol
ii. Urea
iii. Glycerine
iv. Isosorbide
Related Topics
