High ceiling or Loop diuretics - Nonmercurial diuretics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Diuretics
Nonmercurial diuretics : High ceiling or Loop diuretics - i. Bumetanide (Bumex) ii. Furosemide - Synthesis and Drug Profile
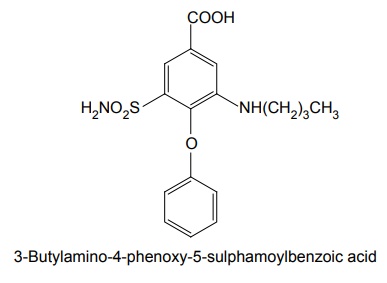
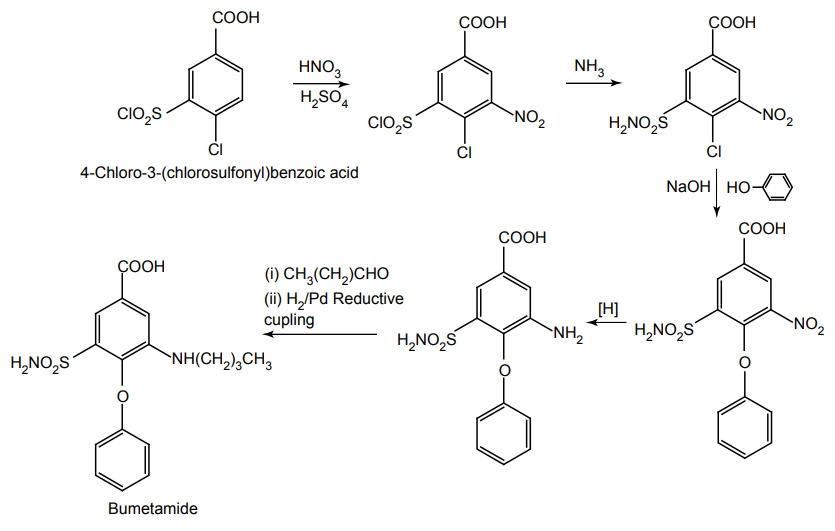
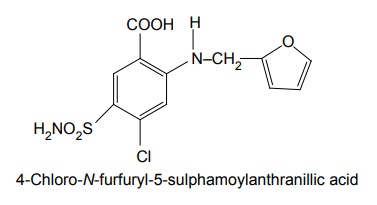
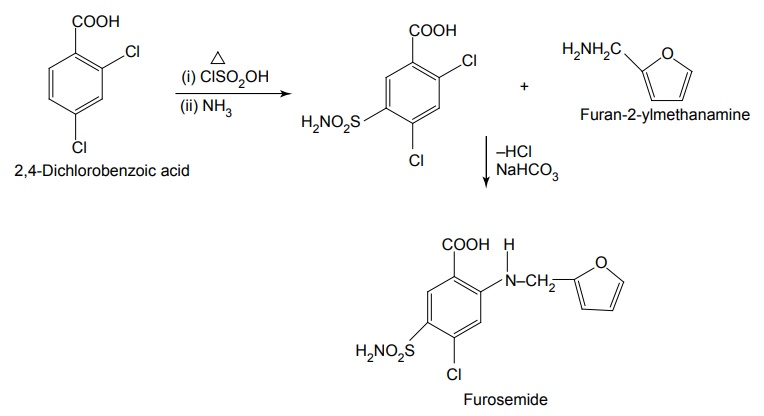
Mode of action: A glycoprotein with 12 membrane-spanning domains has found its function as Na+-K+2Cl–co-transporters. Many epithelia in the loop of henle performing secretory\absorbing functions, loop diuretics attach to the chloride-binding site of these proteins to inhibit transport functions. Synthesis Properties and uses: Bumetanide is a white crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone, alcohol, and dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides, slightly soluble in methylene chloride. It is a 3-aminobenzoic acid, metanilamide derivative that is a potent loop diuretic with efficacy and biochemical effects similar to those of furosemide. Used in chronic congestive heart failure, chronic renal failure, chronic hepatic disease, and in the nephritic syndrome. It is used in the treatment of renal insufficiency and for the control and management of acute drug poisoning. Assay: Dissolve the sample in alcohol and titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide using phenol red solution as indicator until a violet-red colour is obtained. Perform a blank titration. Dose: By oral 0.5 to 2.0 mg once daily. Parenteral: 0.5 to 1.0 mg intravenously. An equivalent dose of bumetanide is only one fortieth that of furosemide, and its bioavailability is about twice. Dosage forms: Bumetanide injection B.P., Bumetanide oral solution B.P., Bumetanide tablets B.P., Bumetanide and slow potassium tablets B.P. Synthesis Properties and uses: Furosemide is a white crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water and in methylene chloride, soluble in acetone and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides, sparingly soluble in ethanol. A diuretic chemically related to the sulphonamide diuretics. It is slightly more potent than the organomercurial agents, is orally effective, and its diuretic action is independent of alterations in body acid-base balance. It is used for the treatment of oedema associated with renal disease, nephritic syndrome, cirrhosis of the liver, and congestive heart failure. Assay: Dissolve the sample in dimethylformamide and titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide using bromothymol blue solution as indicator. Dosage forms: Furosemide tablets I.P., B.P., Co-amilofruse tablets B.P., Furosemide injection B.P.SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Nonmercurial diuretics
High ceiling or Loop diuretics
i. Bumetanide (Bumex)
ii. Furosemide
Related Topics
