Sulphonamide derivatives - Nonmercurial diuretics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Diuretics
Nonmercurial diuretics :Sulphonamide derivatives - Synthesis and Drug Profile- i. Quinethazone (Hydromox) ii. Chlorthalidone (Hygroton) iii. Metolazone (Diulo, Zaroxolyn) iv. Indapamide v. Xipamide vi. Clorexolone
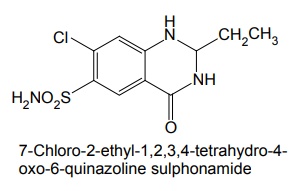
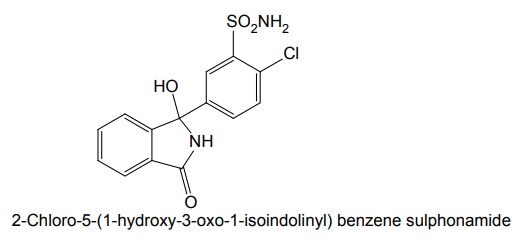
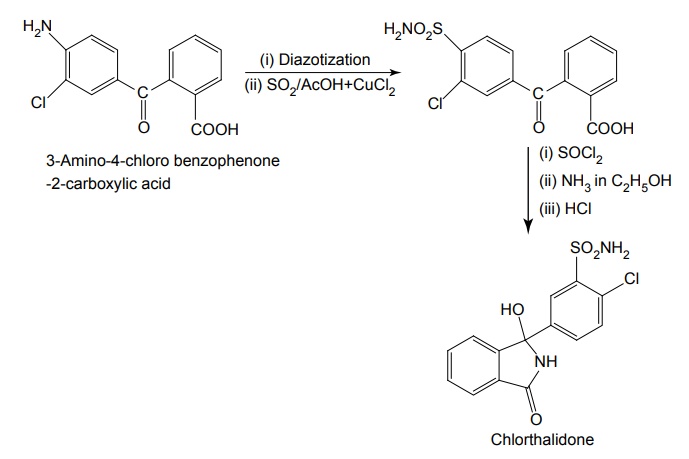
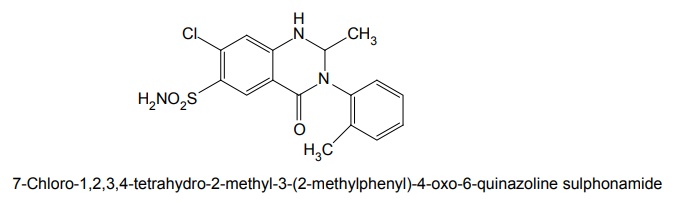
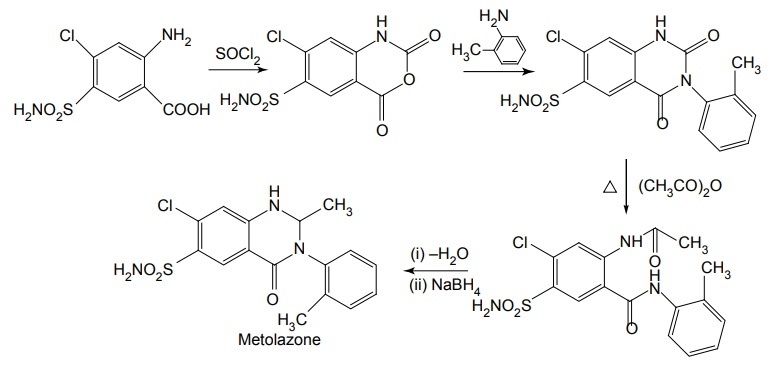
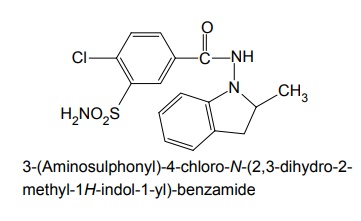
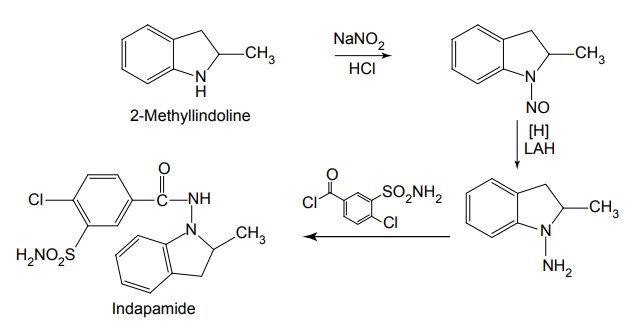
Properties and uses: Quinethazone is a quinazoline derivative with the effect similar to 6-thiazide. It is a yellowish white, odourless, crystalline powder, soluble in water and alcohol and freely soluble in solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates. Replacement of the ring sulphone group in thiazide by carbonyl yields quinazlones. These compounds have same diuretic response as the thiazides. The most potent compound of the series, quinethazone have high Na+/K+ excretion ratio. Used as both diuretics and anti-hypertensive. Synthesis Dose: 50 to 200 mg/day; usually 50 to 100 mg once daily. Synthesis Properties and uses: Chlorthalidone is an orally effective nonthiazide diuretic. It is an adjunct in oedema associated with congestive heart failure and is used in the treatment of oedema associated with obesity, pregnancy, renal disease, hepatic cirrhosis, premenstrual syndrome, and in congestive heart failure. Dose: As diuretic, 50 to 200 mg per day or alternate day; usually 100 mg once daily, as antihypertensive, 100 mg alternate day or 50 mg every day. Properties and uses: Metolazone is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water or alcohol, but soluble in organic solvents. It is a quinazoline derived nonthiazide diuretic, exerts its diuretic effect in the PT and in the cortical segment of the ascending limb of henle or distal convoluted tubule. Patients with non-oedematous, stable chronic renal failure, and high dosage of metazoline increases urine flow significantly. It is used for hypertension and oedema accompanying congestive heart failure. Synthesis Dose: Usual, adult oral dose for oedema of cardiac failure is 5 to 10 mg once daily; oedema of renal disease, 5 to 20 mg once daily; mild essential hypertension, 2.5 to 5 mg once daily. Synthesis Properties and uses: Indapamide is a white powder, practically insoluble in water, and soluble in ethanol. It is an oral diuretic and antihypertensive related to the indolines. Used in oedema associated with congestive heart failure and hypertension. Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique. Dosage forms: Indapamide tablets B.P. v. Xipamide Synthesis Properties and uses: Used in the treatment of hypertension and oedema. Uses: It is effective in the treatment of congestive heart failure and cirrhosis of the liver. SynthesisSYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Nonmercurial diuretics
Sulphonamide derivatives
i. Quinethazone (Hydromox)
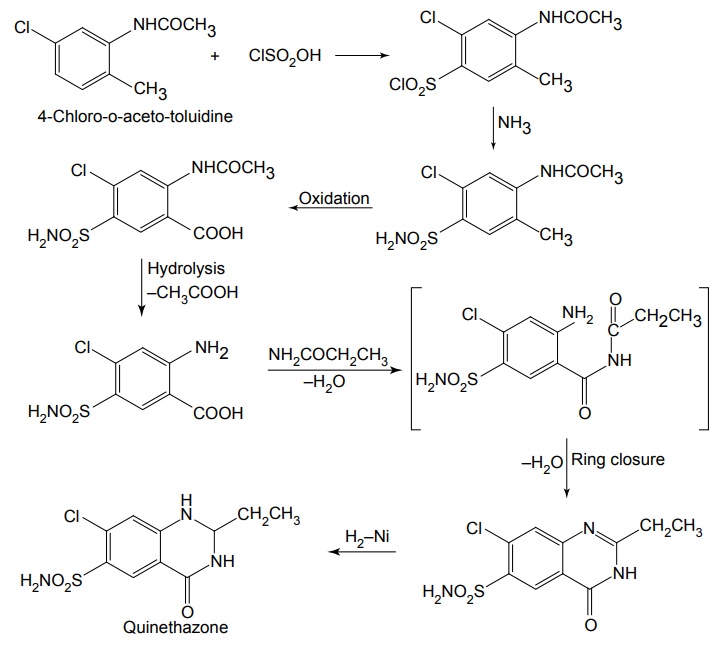
ii. Chlorthalidone (Hygroton)
iii. Metolazone (Diulo, Zaroxolyn)
iv. Indapamide
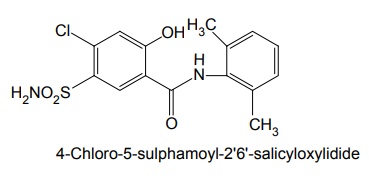
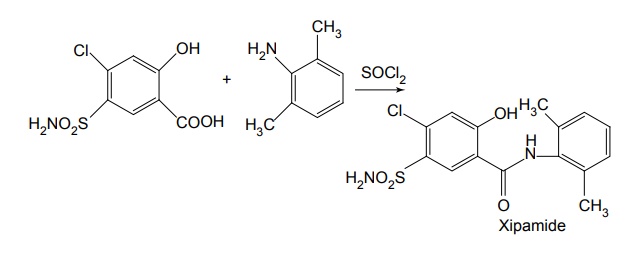
vi. Clorexolone
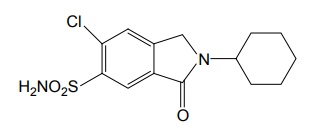
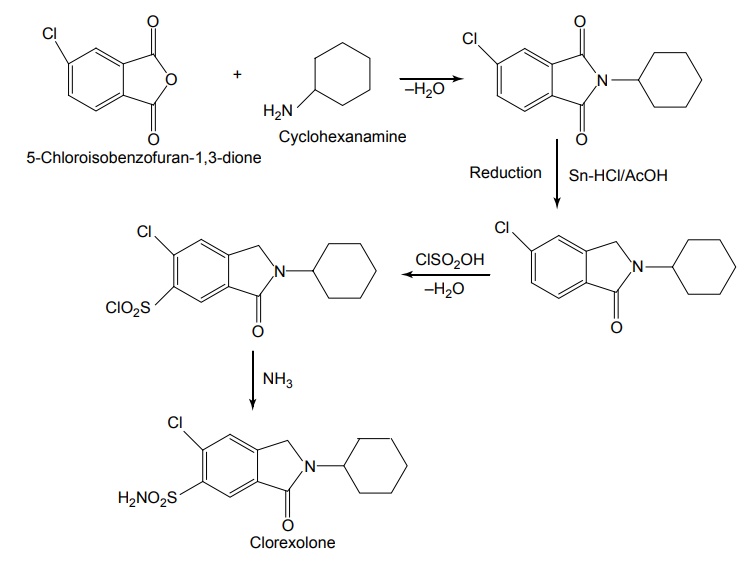
Related Topics
