Thiazides - Nonmercurial diuretics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Diuretics
Nonmercurial diuretics : Thiazides : i. Chlorthiazide ii. Benzthiazide (Exna, Aquataq)
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Thiazides
Mode of action of thiazides and hydrothiazides: The sites of action for these drugs are cortical diluting segment or DT. Here they inhibit Na+-Cl– symport at the luminal membrane.
i. Chlorthiazide
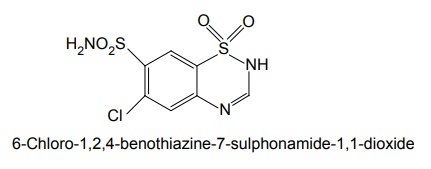
Synthesis
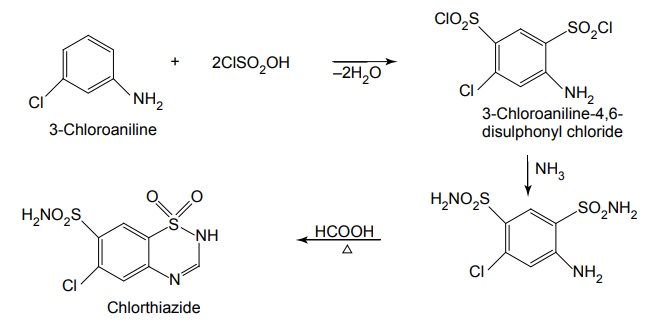
Properties and uses: Chlorthiazide is a white crystalline powder, soluble in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides, slightly soluble in water and in alcohol and sparingly soluble in acetone. It is a prototype benzothiadiazine derivative, used in the treatment of oedema associated with congestive heart failure, renal, and hepatic disorders.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in dimethylformamide and titrate against 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide in 2-propanol. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
ii. Benzthiazide (Exna, Aquataq)
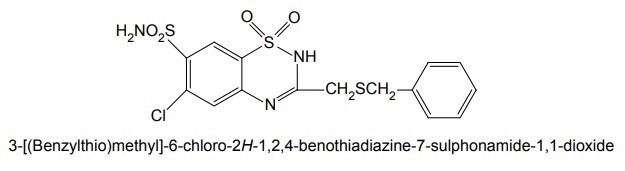
Synthesis
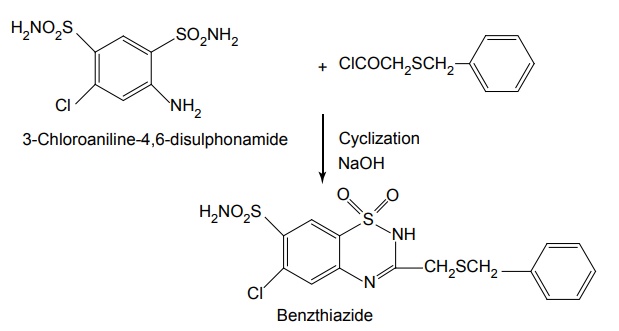
Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder with a characteristic odour and taste. Benzthiazide is soluble in water, alcohol, chloroform or ether, and in alkaline solutions. It is used in the treatment of oedema associated with congestive heart failure, renal, and hepatic disorders.
Dose: Usually as diuretic initial dose is 50 to 200 mg per day; maintenance, 50 to 150 mg per day; usual, antihypertensive, initial, 50 mg twice/day; maintenance, maximal dose of 50 mg thrice daily.
Related Topics
