Anilides
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Local Anaesthetics
a. Lidocaine HCl (Synonym: Lignocaine, Xylocaine) b. Bupivacaine (Marcaine) c. Mepivacaine (Carbocaine hydrochloride, Polocaine) d. Prilocaine (Citanest hydrochloride) e. Etidocaine (Duranset)
Anilides Agents of this class are more stable to hydrolysis. They are more potent, have lower frequency of side effects, and induce less irritation than benzoic acid derivatives. Synthesis Metabolism: Undergoes N-de-ethylation to yield mono-ethyl glycinexylide followed by amidase action to N-ethyl glycine and 2, 6-dimethylaniline. Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder, very soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol. It is a potent local anaesthetic. It is reported to be twice as active as procaine hydrochloride in the same concentrations. It has local vasodilating action, but usually used with vasoconstrictor adrenaline to prolong the local anaesthetic activity. It is also used as class I anti-arrhythmic agent. Assay: Dissolve the substance in alcohol and add 0.01 M hydrochloric acid. Perform potentiometric titration using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light. Dose: Infiltration or epidural up to 60 ml (or 100 ml with epinephrine) as 0.5% solution. Dosage forms: Lidocaine gel B.P., Lidocaine and Chlorhexidine gel B.P., Lidocaine injection B.P., Lidocaine and adrenaline injection/Lidocaine and Epinephrine injection B.P., Sterile Lidocaine solution B.P. Synthesis Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder or colourless crystals, soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol. It is a long-acting local anaesthetic of the amide type, similar to mepivacaine and lidocaine, but about four times more potent. The effect of bupivacaine last longer than lidocaine hydrochloride. It is longacting local anaesthetic mainly employed for regional nerve block. Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of water and alcohol, to this add 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and carry out a potentiometric titration using 0.1 M ethanolic sodium hydroxide. Storage: It should be stored in well-closed airtight containers and protected from light. Dose: Regional nerve block, 0.25% to 0.5% solutions; Lumbar epidural block, 15 to 20 ml of 0.25% to 0.5% solution; Caudal block, 15 to 40 ml of 0.2% solution. Dosage forms: Bupivacaine HCl injection I.P., Bupivacaine injection B.P., Bupivacaine and Adrenaline injection/Bupivacaine and Epinephrine injection B.P. N-(2,6-dimethyl)-1-methyl-2-piperidin carboxamide Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder, freely soluble in water and in alcohol, very slightly soluble in methylene chloride. The duration of action is significantly longer than that of lidocaine, even without adrenaline. It is of particular importance in subjects showing contraindication to adrenaline. It is a local anaesthetic used for infiltration, peridural, nerve block, and caudal anaesthesia. Synthesis Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and alcohol. Perform potentiometric titration using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Dose: In filtration and nerve block, 20 ml of 1% or 2% solution in sterile saline; caudal and peridural, 15 to 30 ml of 1%; 10 to 25 ml of 1.5% or 10 to 20 ml of a 2% solution in modified Ringer’s solution. Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder or colourless crystals, very slightly soluble in acetone, freely soluble in water and alcohol. It is a local anaesthetic of the amide type, which is employed for surface infiltration and nerve block anaesthesia. Its duration of action is in between the shorter-acting Synthesis lidocaine and longer-acting mepivacaine. The solution of prilocaine HCl is specifically used for such patients who cannot tolerate vasopressor agents, patients having cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, hypertension, and thyrotoxicosis. Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and alcohol and perform potentiometric titration, using 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Dose: Usually, therapeutic nerve block, 3 to 5 ml of a 1% or 2% solution; infiltration, 20 to 30 ml of a 1% or 2% solution; peridural, caudal, regional, 15 to 20 ml of a 3% solution; infiltration and nerve block, 0.5 to 5 ml of a 4% solution. Dosage forms: Prilocaine injection B.P. Synthesis Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder, soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol. It is used clinically in epidural, infiltrative, and regional anaesthesia. It has greater potency and longer duration of action than lidocaine. Dose: Solution for injection: 1% without epinephrine and 1.5% with epinephrine.a. Lidocaine HCl (Synonym: Lignocaine, Xylocaine)
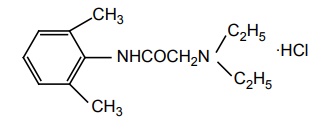

b. Bupivacaine (Marcaine)
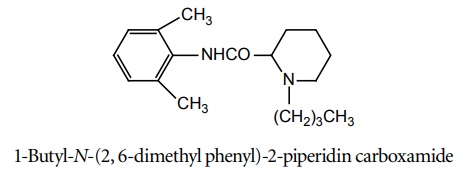
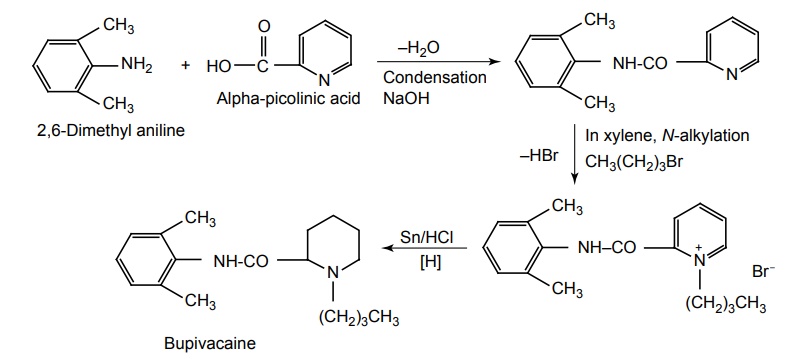
c. Mepivacaine (Carbocaine hydrochloride, Polocaine)
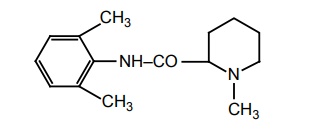
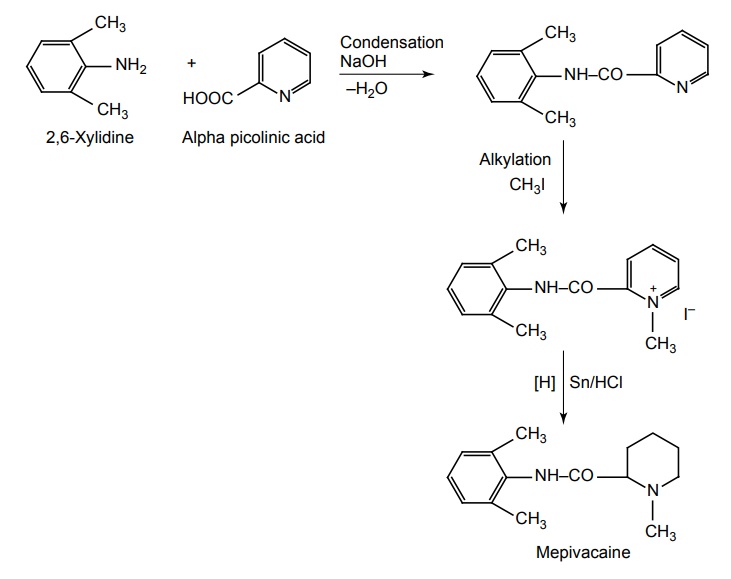
d. Prilocaine (Citanest hydrochloride)
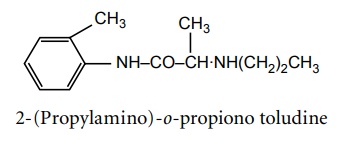
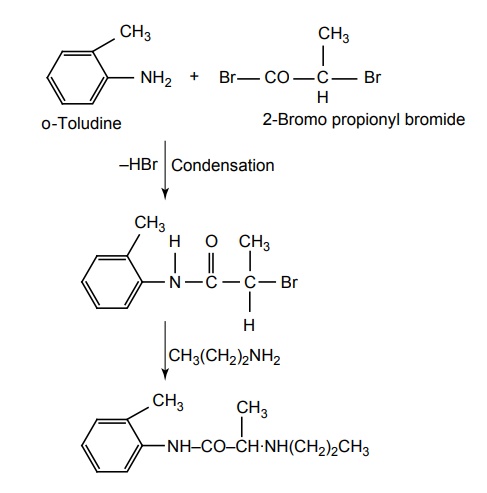
e. Etidocaine (Duranset)

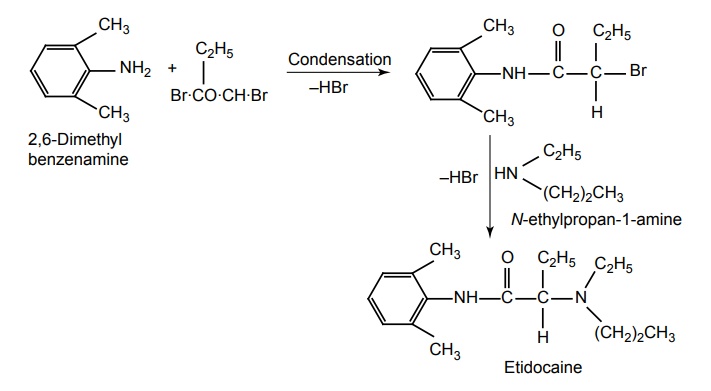
Related Topics
