Brain
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : The Feed-Fast Cycle
Although contributing only 2% of the adult weight, the brain accounts for a consistent 20% of the basal O2 consumption of the body at rest. Because the brain is vital to the proper functioning of all organs of the body, special priority is given to its fuel needs.
BRAIN
Although contributing
only 2% of the adult weight, the brain accounts for a consistent 20% of the
basal O2 consumption of the body at rest. Because the brain is vital
to the proper functioning of all organs of the body, special priority is given
to its fuel needs. To provide energy, substrates must be able to cross the
endothelial cells that line the blood vessels in the brain (the blood–brain
barrier [BBB]). In the fed state, the brain exclusively uses glucose as a fuel
(GLUT-1 of the BBB is insulin independent), completely oxidizing approximately
140 g/day to CO2 and H2O. The brain contains no
significant stores of glycogen and is, therefore, completely dependent on the
availability of blood glucose (Figure 24.8, 1).
[Note: If blood glucose levels fall below 40 mg/100 ml (normal fasted blood
glucose is 70–99 mg/100 ml), cerebral function is impaired.] The brain also
lacks significant stores of TAG, and the FAs circulating in the blood make
little contribution to energy production because FAs bound to albumin do not
efficiently cross the BBB. The intertissue exchanges characteristic of the
absorptive period are summarized in Figure 24.9.
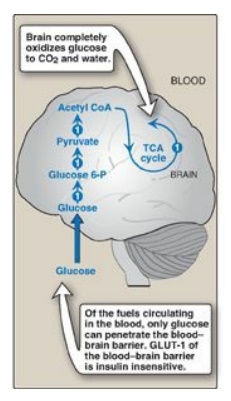
Figure 24.8 Major metabolic
pathways in brain in the absorptive state. [Note: The numbers in circles, which
appear both in the figure and in the text, indicate important pathways for
carbohydrate metabolism.] CoA = coenzyme A; TCA = tricarboxylic acid; P =
phosphate; GLUT = glucose transporter.
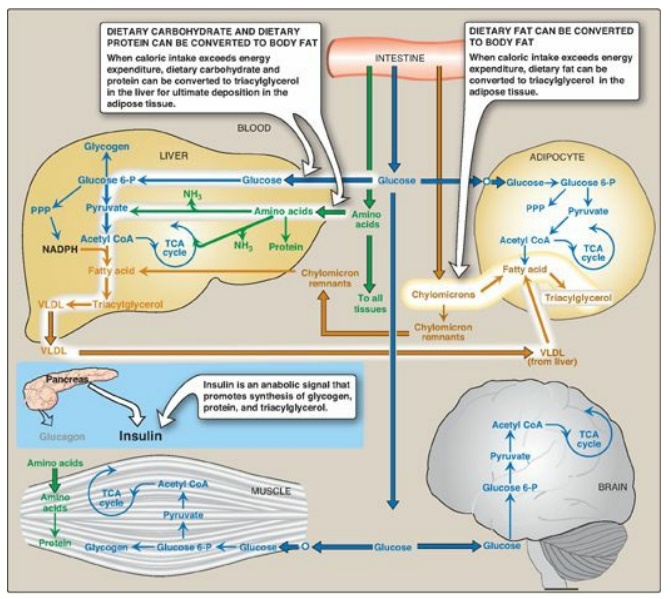
Figure 24.9 Intertissue
relationships in the absorptive state and the hormonal signals that promote
them. [Note: Small circles on the perimeter of muscle and the adipocyte
indicate insulin-dependent glucose transporters.] P = phosphate; PPP = pentose
phosphate pathway; CoA = coenzyme A; NADPH = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
phosphate; TCA = tricarboxylic acid; VLDL = very-low-density lipoprotein.
Related Topics
