Clove
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Volatile Oils
Clove consists of the dried flower buds of Eugenia caryophyllus Thumb., belonging to family Myrtaceae.
CLOVE
Synonyms
Clove buds, Clove flowers.
Biological Source
Clove consists of the dried flower buds of Eugenia caryophyllus Thumb., belonging
to family Myrtaceae.
Geographical Source
Clove tree is a native of Indonesia. It is cultivated mainly
in Islands of Zanzibar, Pemba, Brazil, Amboiana, and Sumatra. It is also found
in Madagascar, Penang, Mauritius, West Indies, India, and Ceylon.
Cultivation and Collection
Clove tree is evergreen and 10 to 20 m in height. The plant
requires moist, warm and equable climate with well-distributed rainfall. It is
propagated by means of seeds. The seeds are sown in well-drained suitable soil
at a distance of about 25 cm. The plants should be protected against pests and
plant diseases. Initially it has to be protected from sunlight by growing
inside a green house or by con-structing frames about 1 m high and covering
them with banana leaves. As the banana leaves decay gradually more and more
sunlight falls on the young seedlings and the seeds are able to bear full
sunlight when they are about 9 months old. The seedlings when become 1 m high, they
are transplanted into open spaces at a distance of 6 m just before the rainy
season. The young clove trees are protected from sun even for a longer period
by planting banana trees in between. The drug can be collected every year
starting from 6 years old till they are 70 years old.
Clove buds change the colour as they mature. At the start of
the rainy season long greenish buds appear which change to a lovely rosy peach
colour and as the corolla fades the calyx turns yellow and then red. The buds
are collected during dry weather in the month of August to December. The
collection is done either by climbing on the tree or by using some ladders or
with the help of mobile platforms. In some places the trees are even beaten
using bamboo sticks for the collection of the bud. The drugs which are
collected are then separated from the stalks and then placed on coconut mats
for drying under sun. The buds loose about 70% of its weight, whereas drying
and change their colour to dark reddish-brown. The dried clove is graded and
packed.
Characterisitics
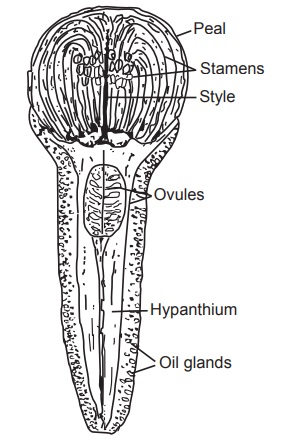
Clove is reddish-brown in colour, with an upper crown and a
hypanthium. The hypanthium is sub-cylindrical and tapering at the end. The
hypanthium is 10 to 13 mm long, 4 mm wide, and 2 mm thick and has schizolysigenous
oil glands and an ovary which is bilocular. The Crown region consists of the
calyx, corolla, style and stamens. Calyx has four thick sepals. Corolla is also
known as head, crown or cap; it is doineshaped and has four pale yellow
coloured petals which are imbricate, immature, and membranous. The ovary
consists of abundant ovules. Clove has strong spicy, aromatic odour, and
pungent and aromatic taste.
Microscopy
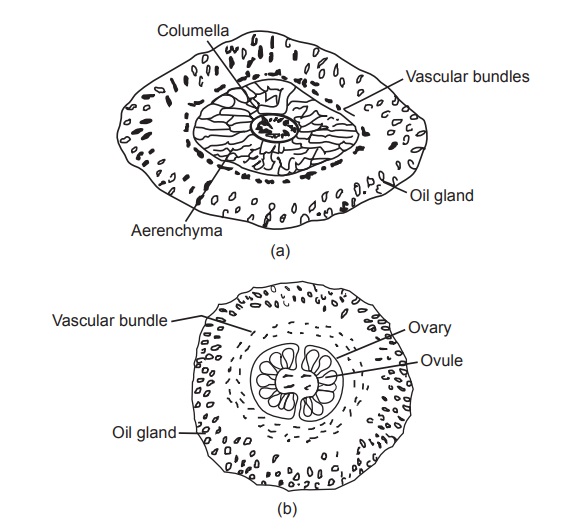
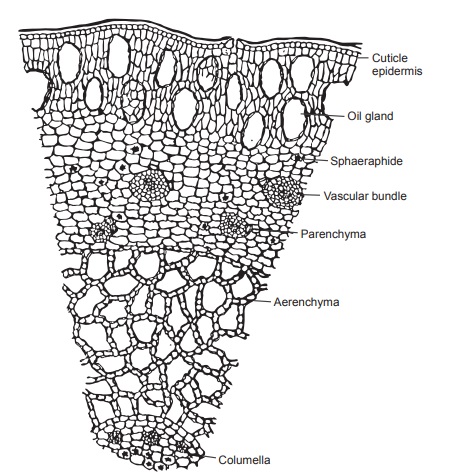
The transverse section should be taken through the short
upper portion which has the bilocular ovary and also through the hypanthium
region. The transverse section through the hypanthium shows the following
characters. It has a single layer of epidermis covered with thick cuticle. The
epidermis has ranunculaceous stomata. The cortex has three distinct region: the
peripheral region with two to three layers of schizolysigenous oil glands,
embedded in parenchymatous cells. The middle layer has few layers of
bicollateral vascular bundle. In the inner portion it has loosely arranged
aerenchyma cells. The central cylinder contains thick-walled parenchyma with a
ring of bicollateral vascular bundles and abundant sphaeraphides. The T.S.
through ovary region shows the presence of an ovary with numerous ovules in it.
Chemical Constituents
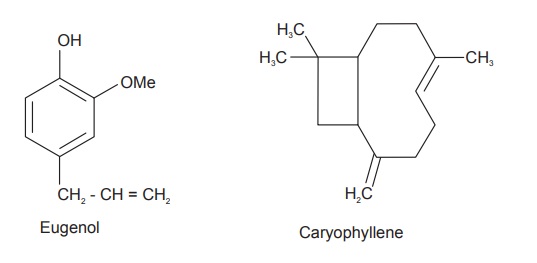
Clove contains 14–21% of volatile oil. The other
constituents present are the eugenol, acetyl eugenol, gallotannic acid, and
two crystalline principles; α- and β- caryophyllenes, methyl furfural, gum,
resin, and fibre. Caryophyllin is odourless component and appears to be a
phytosterol, whereas eugenol is a colourless liquid. Clove oil has 60–90%
eugenol, which is the cause of its anesthetic and antiseptic properties.
Chemical Tests
1. To a thick section through
hypanthium of clove add 50% potassium hydroxide solution; it produces
needle-shaped crystals of potassium eugenate.
2. A drop of clove oil is dissolved in
5 ml alcohol and a drop of ferric chloride solution is added; due to the
phenolic OH group of eugenol, a blue colour is seen.
3. To a drop of chloroform extract of
clove add a drop of 30% aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide saturated with
sodium bromide; Needle and pear shaped crystals of sodium eugenate arranged in
rosette are produced immediately.
Uses
Clove is used as an antiseptic, stimulant, carminative,
aromatic, and as a flavouring agent. It is also used as anodyne, antiemetic.
Dentists use clove oil as an oral anesthetic and to disinfect the root canals.
Clove kills intestinal parasites and exhibits broad antimicrobial properties
against fungi and bacteria and so it is used in the treatment of diarrhea,
intestinal worms, and other digestive ailments. Clove oil can stop toothache. A
few drops of the oil in water will stop vomiting, eating cloves is said to be
aphrodisiac. Eugenol is also used as local anaesthetic in small doses. The oil
stimulates peristalsis; it is a strong germicide, also a stimulating expectorant
in bronchial problems. The infusion and Clove water are good vehicles for
alkalies and aromatics.
Adulterants
The clove is generally adulterated by exhausted clove, clove
fruits, blown cloves and clove stalks. The exhausted cloves are those from
which volatile oil is either partially or completely removed by distillation.
Exhausted cloves are darker in colour and can be identified as they float on
freshly boiled and cooled water. Clove fruits are dark brown in colour and have
less volatile oil content. These can be identified by the presence of starch
present in the seed of the fruit. Blown Cloves are entirely developed clove
flowers from which corolla and stamens get separated. While sepa-ration,
sometimes the stalks are incompletely removed and the percentage of volatile
oil in clove stalk is only 5%. As clove stalks contain prism type of calcium
oxalate crystals and thick-walled stone cells which are absent in clove the
clove stalk can also be detected.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparation known as
Himsagar tail (Dabur).
