Cummin/Cumin
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Volatile Oils
It consists of dried ripe fruits of Cuminum cyminum Linn., belonging to family Umbelliferae.
CUMMIN/CUMIN
Synonyms
Jira, cumin fruit.
Biological Source
It consists of dried ripe fruits of Cuminum cyminum Linn., belonging to family Umbelliferae.
Geographical Source
It is indigenous to Nile territory. It is cultivated in
Morocco, Sicily, India, Syria, and China. In India, except Assam and West
Bengal, it is cultivated in all states. About 90% of the world production is
from India, and most of it comes from Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Characteristics
It is brown-coloured, ridges are light in colour,
characteristic and aromatic odour and having characteristic and aromatic
taste. It is 4–6 mm in length and about 2 mm thick, elongated, and tapering at
both ends. Each mericarp is having fine longitudinal ridges. Alternating with
these are secondary ridges which are flat and bear conspicuous emergences.
Microscopy
The transverse section of mericarp exhibits an oily
endosperm and six vittae, of which four are on dorsal surface and two on
ventral surface. The large pluriserial hairs, characteristic to it, are
present.
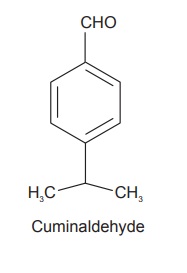
Chemical Constituents
Cumin fruits contain 2.5–4% volatile oil, 10% fixed oil, and
proteins. Volatile oil mainly consists of 30–50% cuminaldehyde, small
quantities of α-pinene, β-pinene, phellandrene, cuminic alcohol, hydrated
cuminaldehyde, and hydro-cuminine.
Uses
Cumin fruits are used as carminative, stimulant and in
diarrhoea. The oil of cumin is used to flavor curries and other culinary
preparations, confectionary, beverages, and cordials.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Lukol (Himalaya Drug Company), Hajmola (Dabur), K.G. Tone (Aimil
Pharmaceuticals), and M2-tone syrup (Charak Pharma Pvt. Ltd.).
